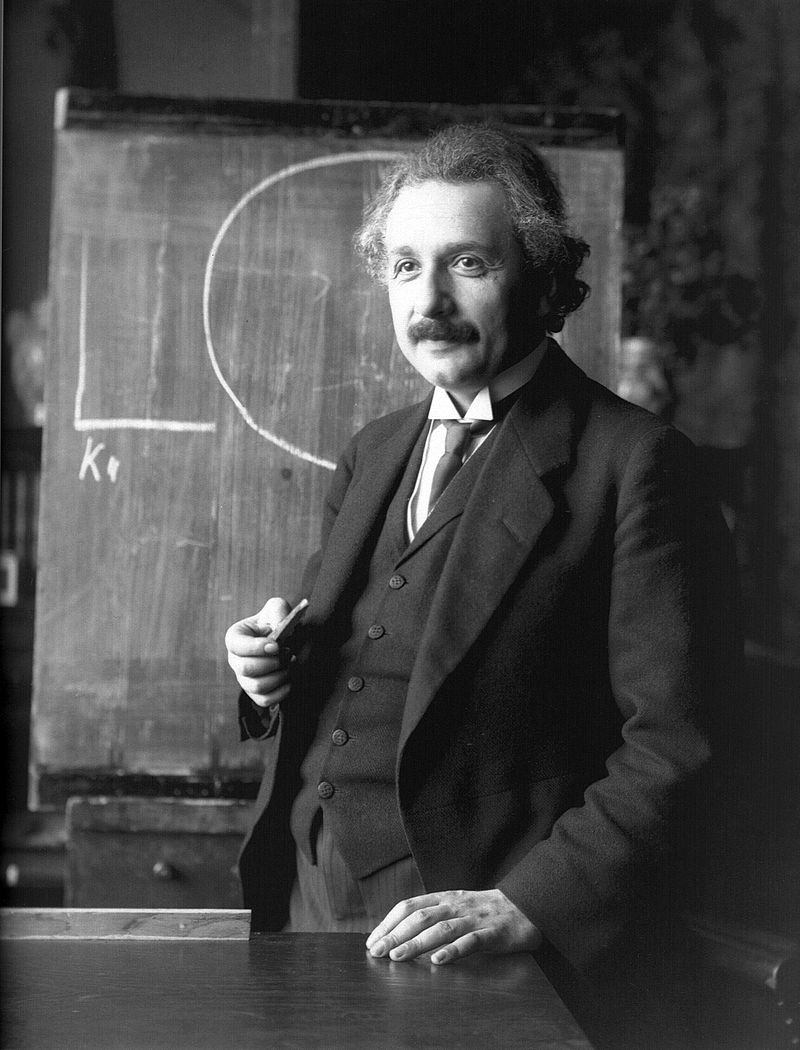ALBERT EINSTEIN
Geştiyarê Gerdûnê - Universe explorer
14 March 1879 Ulm Gemany, 18 April 1955 i Princeton New Jersey
"We are the universe and the universe is in us"
Home | Destpêk | Ana Sayfa

Zanistê pêşeng ê gerdûnî
Hebû (1) - tunebû (0).. her tişt li ser van her du peyvan ava bûye û ev her du peyv destpêka hemû çîroka me ye, hebû, nebû
Gerdûn bi zanetî yan jixweber hatibe avakirin em vê yekê hîna nizanin. Lê em pir baş pê dizanin ku Gerdûn ava ye û bi guhertineke berdwamî li dar e û li pêla demê diherike û diçe.

Will we ever understand the multifaceted paradoxes of science?
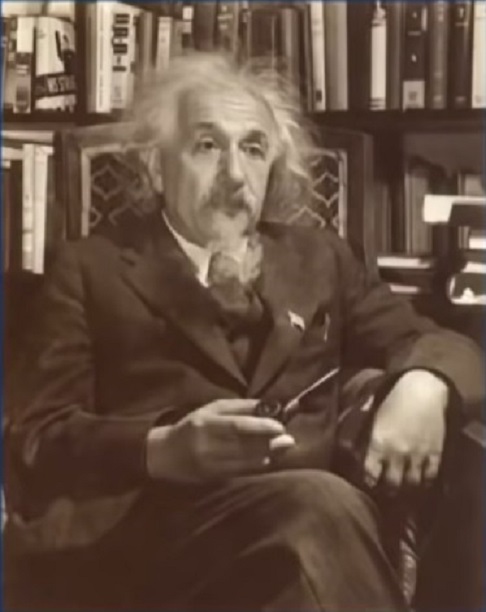

Människor enligt dårar; de är indelade i mer än åtta kategorier, ras, kön, nationalitet, ålder, status, hudfärg, religion och språk.
Men fenomenet är inte så komplicerat! Människor är bara uppdelade i två: bra människor och dåliga människor.
Albert Einstein
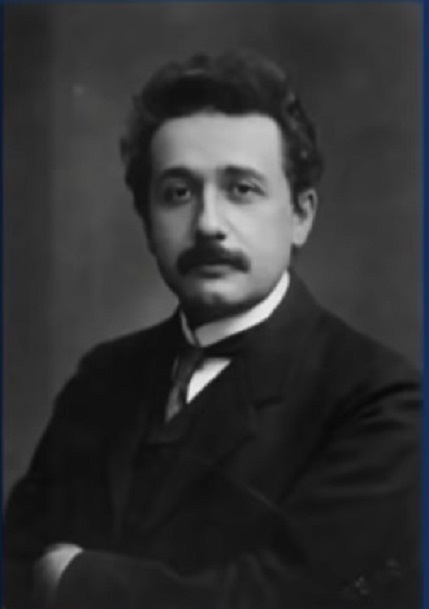

Büyük bilim insanı Albert Einstein'in yaşamından esinlenerek düşündiğim birkaç cümle:
Testere küçüktür ama koskoca bir ağacı DEVİRİR.
- İnsan kainatta gözle görülmeyecek kadar ufaktır ama uçsuz bucaksız KOCA kainattaki yıldızların haritasını çizebilen ve hatta o yıldızlara araç gönderen ve hatta yakın bir zamanda inşa ettiği araçlarla o yıldızlarım üstüne konabilen BÜYÜK AKIL sahibi olduğu kadar da büyük bir azim sahibidir.
Hayır insana hiçbir sınır konmasın. Çünkü insan bu büyük azim ve aklıyla neredeyse HERŞEYİN üstesinden gelebilecek kudrettedir.
ÇÜNKÜ İNSAN TANRININ SURETİNDE YARATILMIŞ ÇOK GÜÇLÜ BİR VARLIKTIR.
İstediğini yapar - Bırakın istediğini yapsın!
-- Engel OLMAYIN!
-- SINIRLAMAYIN!
GC |
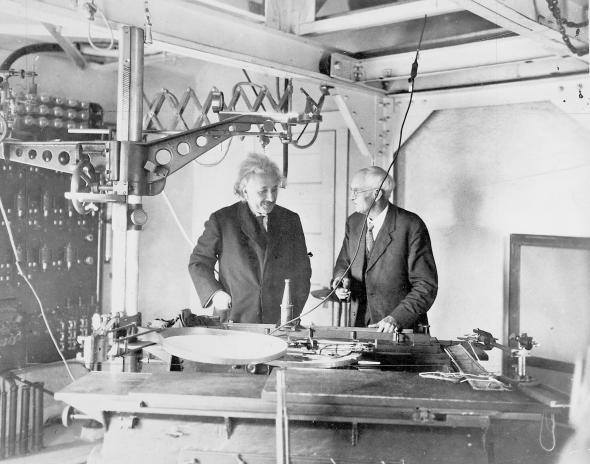
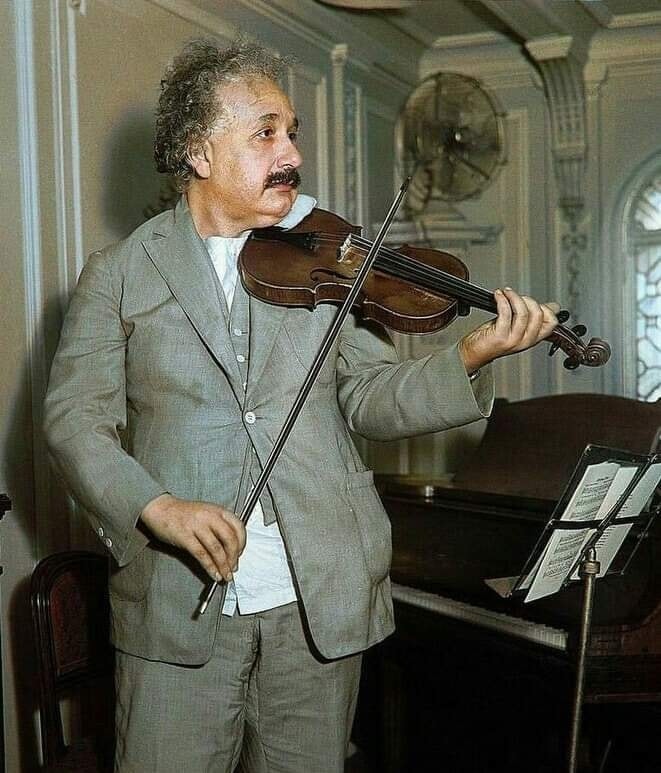
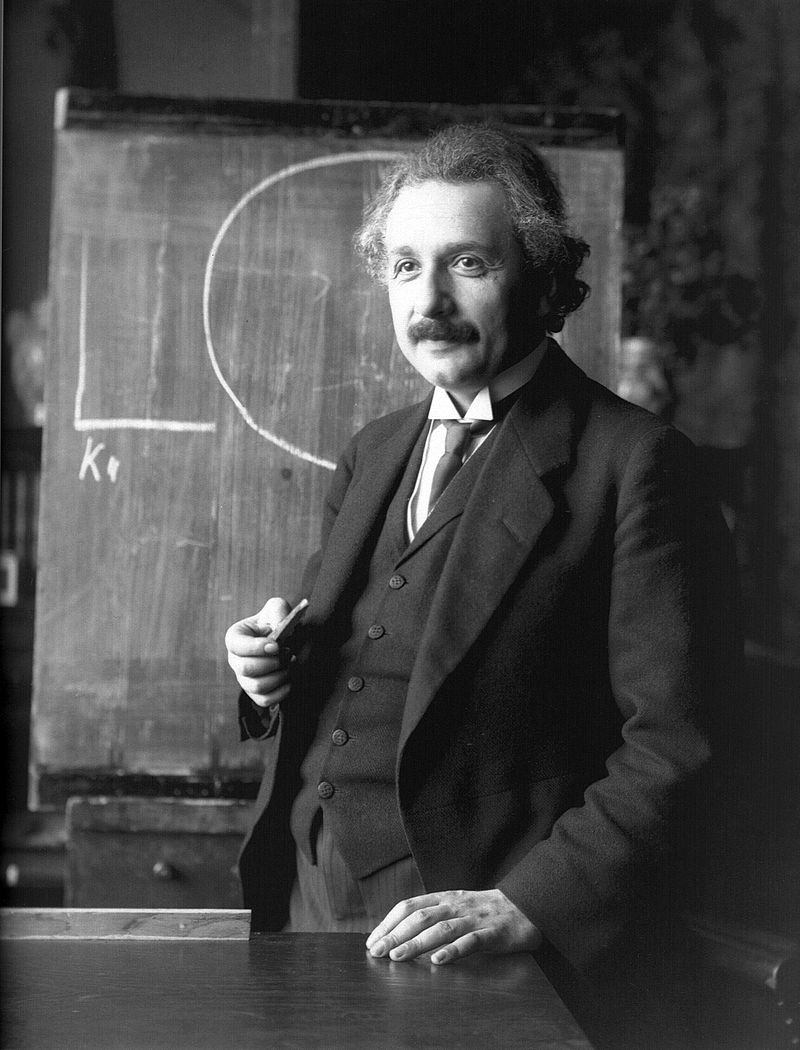



Albert Einstein violonist
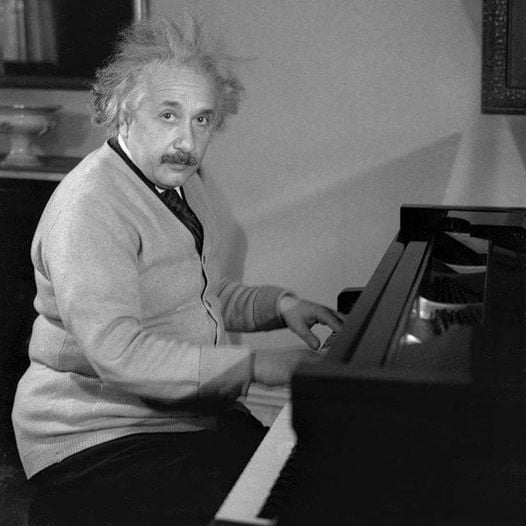


Albert Einstein the piano player
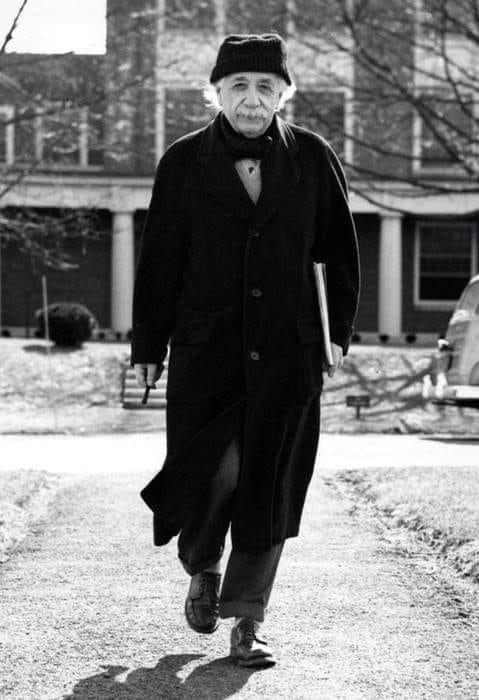
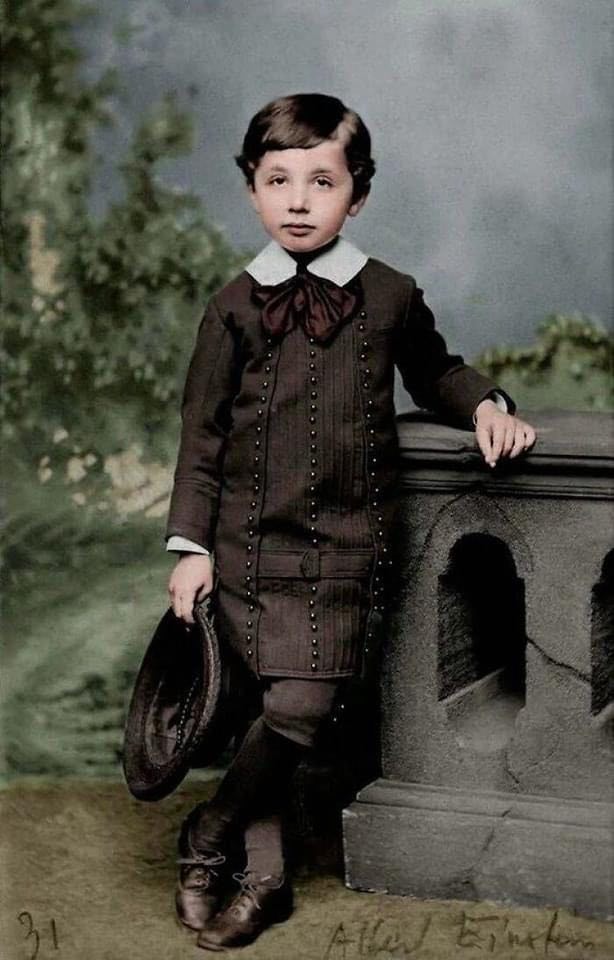


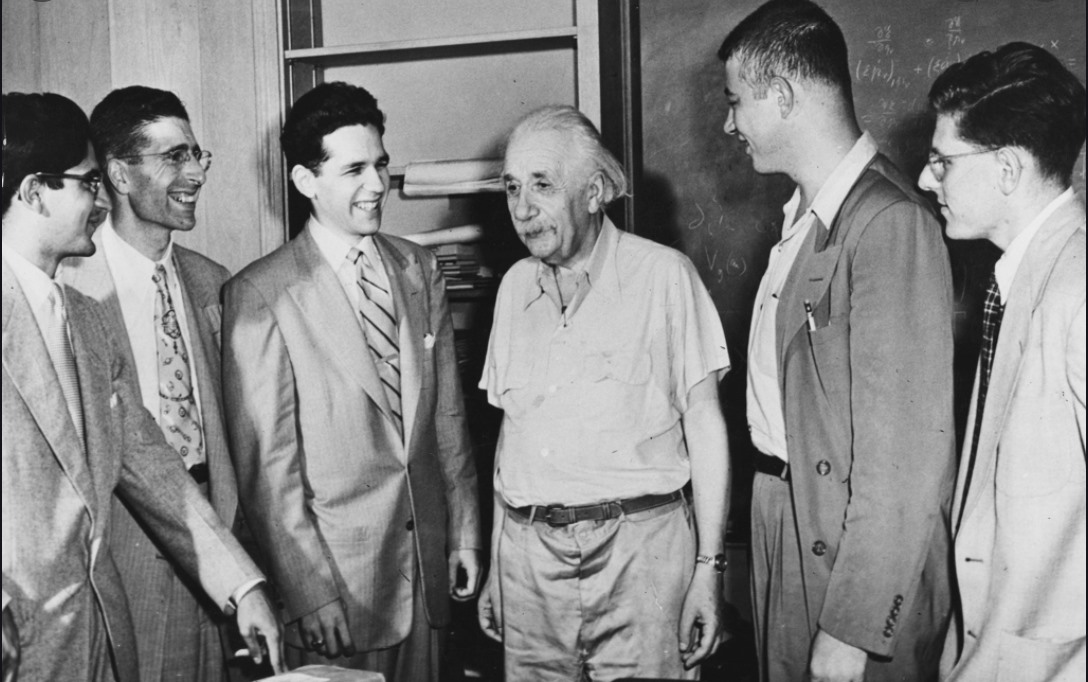
Albert Einstein At 5 Years Old. Munich, 1884. [colorized].

14 years

Einstein Amerikan üniversitelerinde ders verirken, öğrencilerin ona en çok sorduğu soru şuydu:
- Tanrı'ya inanır mısın?
Ve her zaman cevapladı:
- Spinoza'nın tanrısına inanıyorum.
Baruch de Spinoza, Descartes ile birlikte 17. yüzyıl felsefesinin en büyük rasyonalistlerinden biri olan Hollandalı bir filozoftur.
(Spinoza): Tanrı şöyle der:
Dua etmeyi bırak
Dünyaya gitmeni ve hayatının tadını çıkarmanı istiyorum. Şarkı söylemeni, eğlenmeni ve senin için yaptığım her şeyin tadını çıkarmanı istiyorum.
Kendi inşa ettiğin o karanlık, soğuk tapınaklara gitmeyi bırak ve `` Evim dağlarda, ormanda, nehirlerde, göllerde, kumsallarda. Orası yaşadığım yer ve sana olan sevgimi ifade ettiğim yer orası.
Sefil hayatın için beni suçlamayı bırak. Sana hiçbir zaman sende yanlış bir şey olduğunu ya da günahkar olduğunu ya da cinselliğinin kötü bir şey olduğunu söylemedim. Seks, size verdiğim ve sevginizi, coşkunuzu, neşenizi ifade edebileceğiniz bir hediyedir. Bu yüzden seni inandırdıkları hiçbir şey için beni suçlama.
Benimle hiçbir ilgisi olmadığını düşündüğün ayetleri okumayı bırak. Beni gün doğumunda, manzarada, arkadaşlarının gözünde, oğlunun gözlerinde okuyamazsan ... beni hiçbir kitapta bulamazsın!
Bana sormayı bırak '' bana işimi nasıl yapacağımı söyler misin? '' Benden bu kadar korkmayı bırak. Seni yargılamıyorum, seni eleştirme, sinirlenme ya da kızma. Ben saf aşkım .
Af dilemeyi bırak, affedilecek bir şey yok. Seni yaptığım zaman, seni tutkularla, sınırlamalarla, sevinçlerle, duygularla, ihtiyaçlarla, tutarsızlıkla doldurdum ... özgür irade. Sana verdiğim bir şeye cevap verdiğin için seni nasıl suçlayabilirim? Seni yaratan ben olduğum zaman, olduğun için seni nasıl cezalandırabilirim? Sonsuza dek yaramazlık yapan tüm çocuklarımı yakmak için bir yer yapabilir miyim sence? Bu ne tür bir tanrı yapar?
Akranlarınıza saygı gösterin ve kendiniz için istemediğiniz şeyi yapma. Tek istediğim, hayatında dikkatli olmanın rehberin olduğuna dikkat etmen.
Sevgililer, bu hayat bir sınav değil, yolda bir adım, prova, cennetin başlangıcı değil. Bu hayat burada ve şimdi tek ve ihtiyacınız olan tek şey.
Seni tamamen özgür kıldım, ödül ya da ceza yok, günah ya da erdem yok, kimse keçeli kalem takmıyor, kimsenin sabıkası yok.
Hayatınızda kesinlikle özgürce yaratabilirsiniz. Cennet ya da cehennem.
Bu hayattan sonra bir şey olur mu söyleyemem ama sana bir ipucu verebilirim. Böyle yaşamak yok. Sanki eğlenmek, sevmek, var olmak için tek şansınız bu.
Yani bundan sonra hiçbir şey yoksa, o zaman size verdiğim fırsattan zevk almış olacaksınız. Ve yaparsanız, emin olun ki doğru mu yoksa yanlış mı davrandığınızı sormayacağım, soracağım. Hoşuna gitti mi? Eğlendin mi? En çok neyi sevdin? Ne öğrendin?...
Bana inanmayı bırak; inanmak kabul etmek, tahmin etmek, kendinizi tanıtmak demektir. Bana inanmanı istemiyorum, kendine inanmanı istiyorum. Sevgilinizi öptüğünüzde, küçük kızınızı cebinize koyduğunuzda, köpeğinizi okşadığınızda, denizde yıkandığınızda beni içinizde hissetmenizi istiyorum.
Beni ne kadar egomanyak bir tanrı olduğumu sanıyorsun?
Övülmekten sıkıldım. Teşekkür edilmekten bıktım. Minnettar hissediyor musun Kendinize, sağlığınıza, ilişkilerinize, dünyaya özen göstererek bunu kanıtlayın. Sevincinizi ifade edin! Beni övmenin yolu bu.
İşleri karıştırmayı ve benim hakkımda bana öğretilenleri muhabbet kuşu olarak tekrarlamayı bırak.
Neden daha fazla mucizeye ihtiyacın var? Çok fazla açıklama var mı?
Kesin olan tek şey, burada olduğun, yaşadığın, bu dünyanın harikalarla dolu olduğudur.
- Spinoza

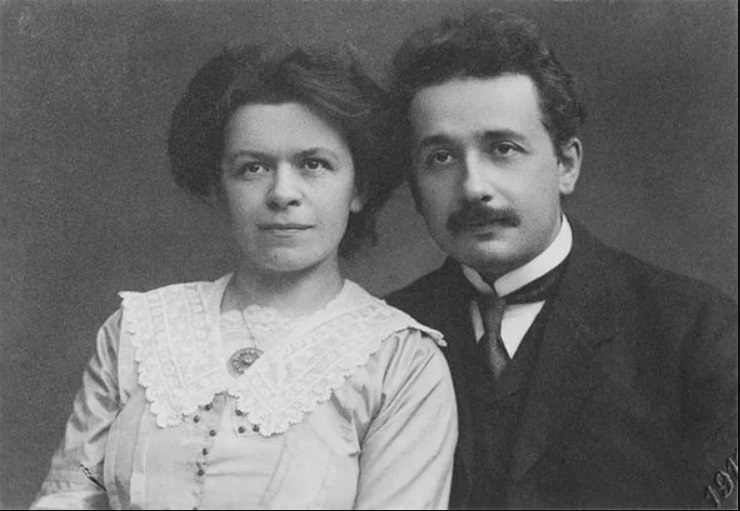
Mileva Maric was a remarkable woman, both as Albert Einstein's first wife and as a gifted mathematician and physicist in her own right.
There are indications that she may have had a significant influence on Einstein's early work, particularly the groundbreaking theories that forever changed physics.
Despite this, her contributions have often been overlooked or ignored in history. She was the only woman in her class at the prestigious Polytechnic Institute in Zurich, where she and Einstein first met. Her exceptional mathematical and scientific skills made her one of the few women of her time to venture into the world of science.
Her life story is both inspiring and tragic, as she faced personal challenges, struggles in her marriage, and the loss of her own career to support Einsteins work.
Discussions about her role in Einsteins successes remain a subject of debate among historians and scholars.

1939
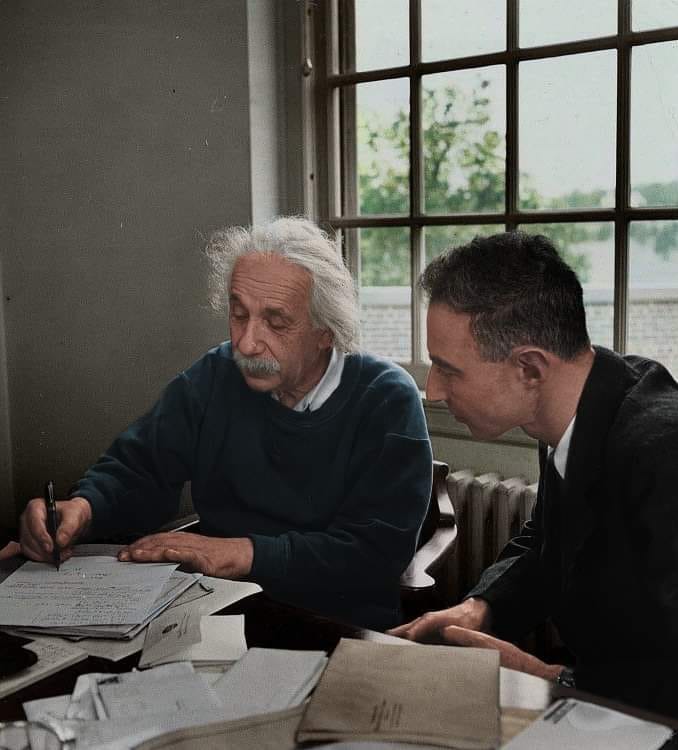
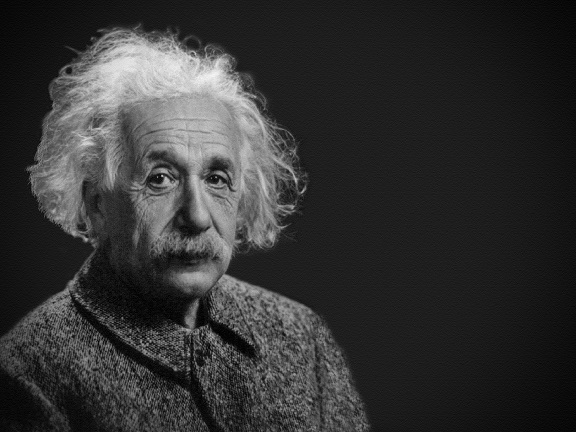
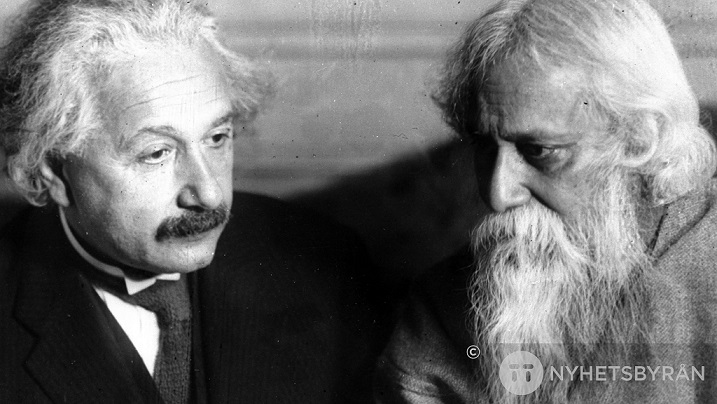
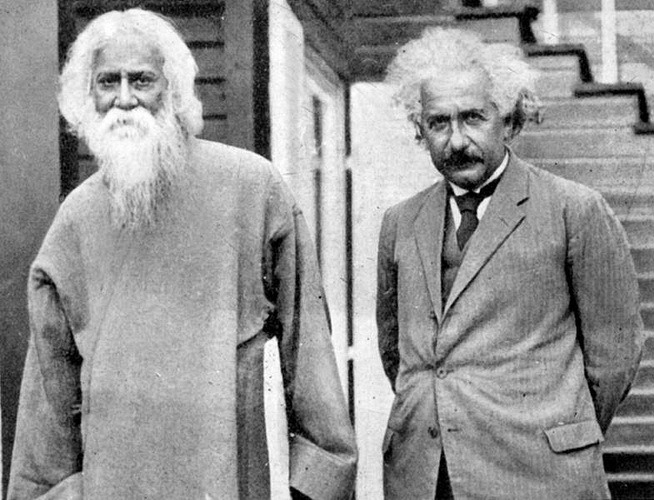









Albert Einstein met fellow Nobel Prize laureate Rabindranath Tagore at his home in the outskirts of Berlin in 1930.
The two distinguished minds explored the concepts of science, consciousness and philosophy.
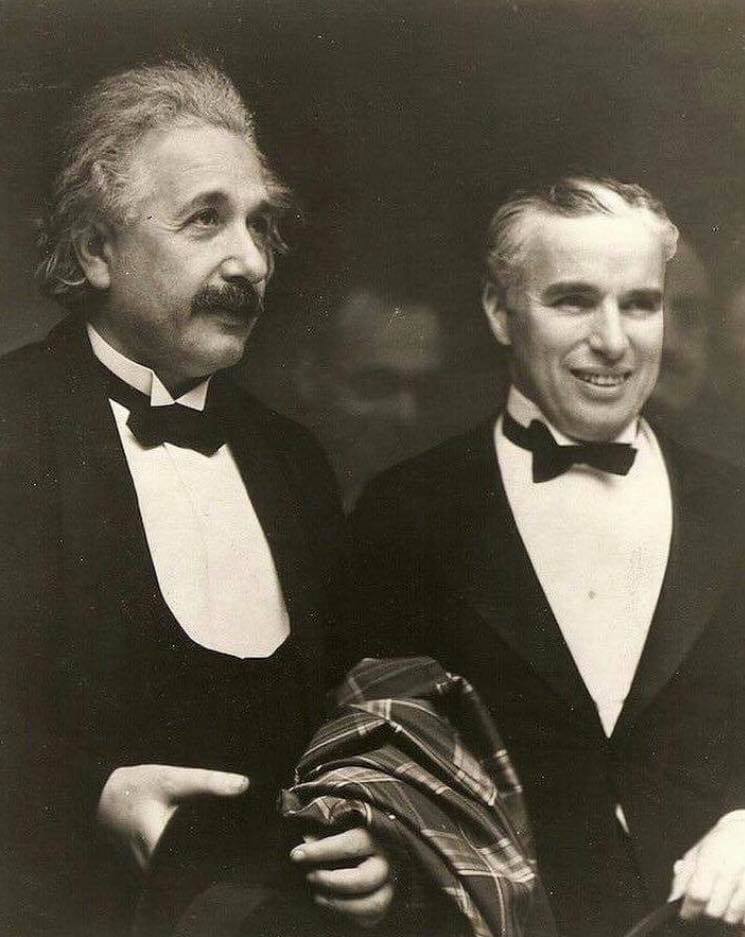

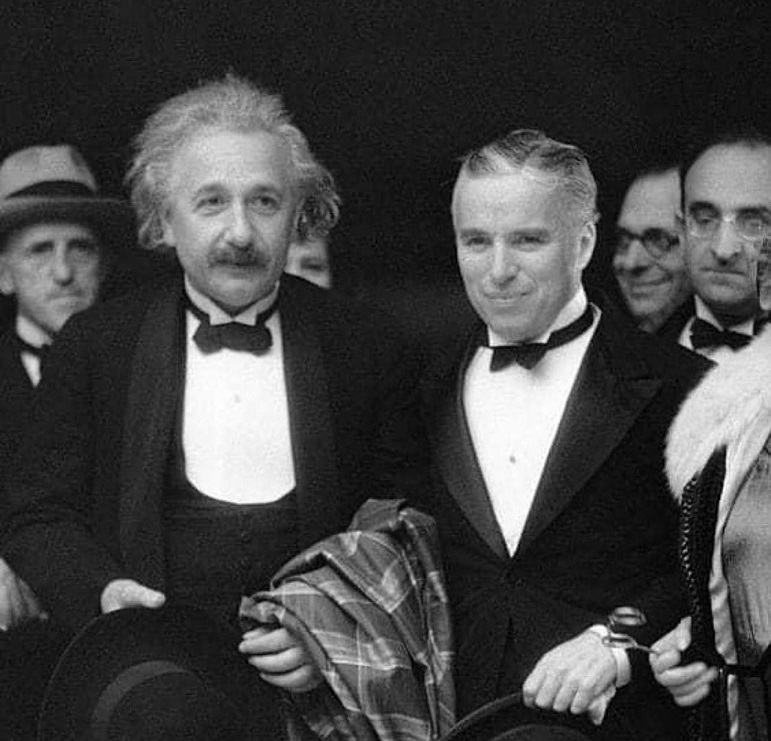
Albert Einstein & Charlie Chaplin
Albert Einstein till Charlie Chaplin: Jag beundrar din universala konst. Du säger inte ett enda ord men hela världen förstår vad du menar.
Charlie Chaplin svarar: Ja, men din berömdhet överträffar allt och alla. Ingen förstår vad du säger men hela världen beundrar dig ändå.
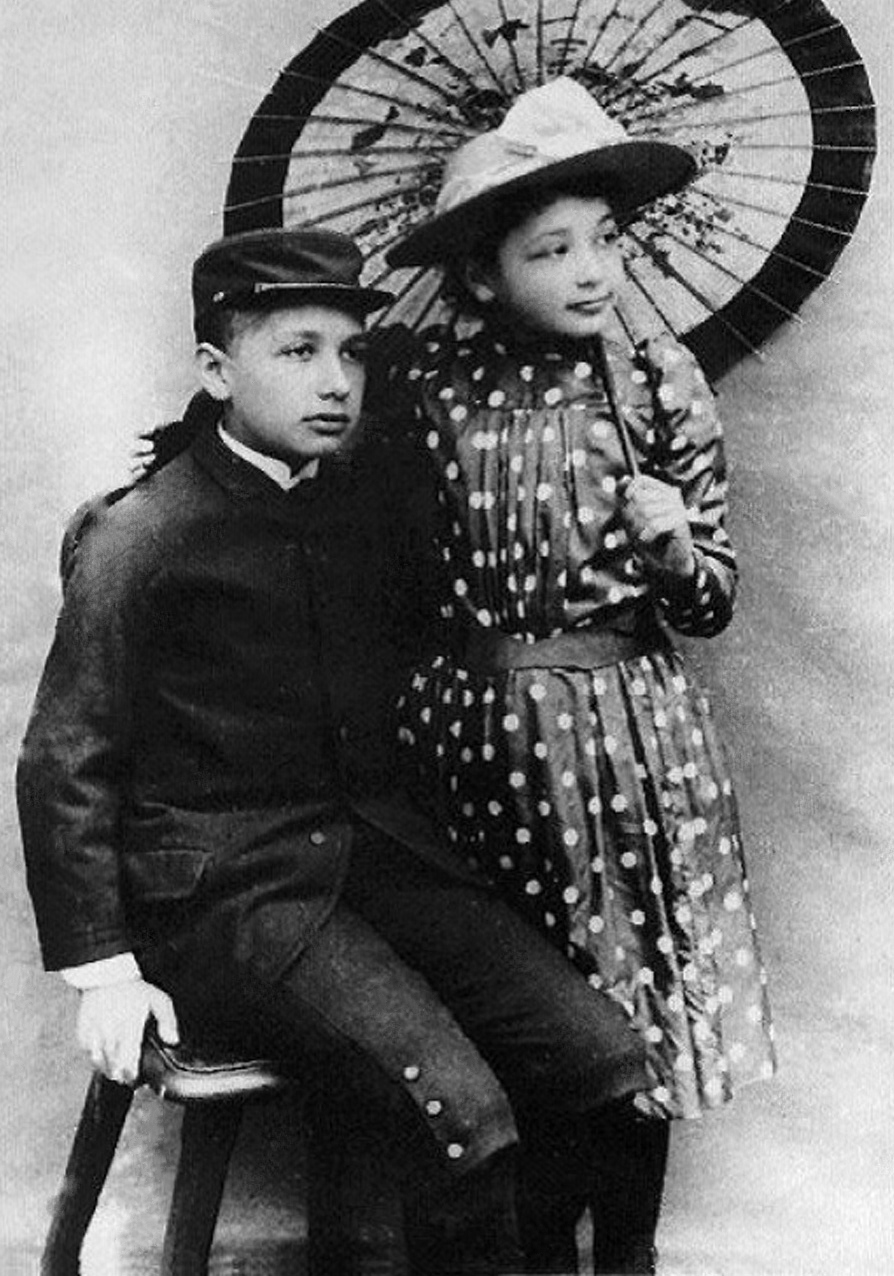






Albert Einstein and his sister, Maria, circa 1893.
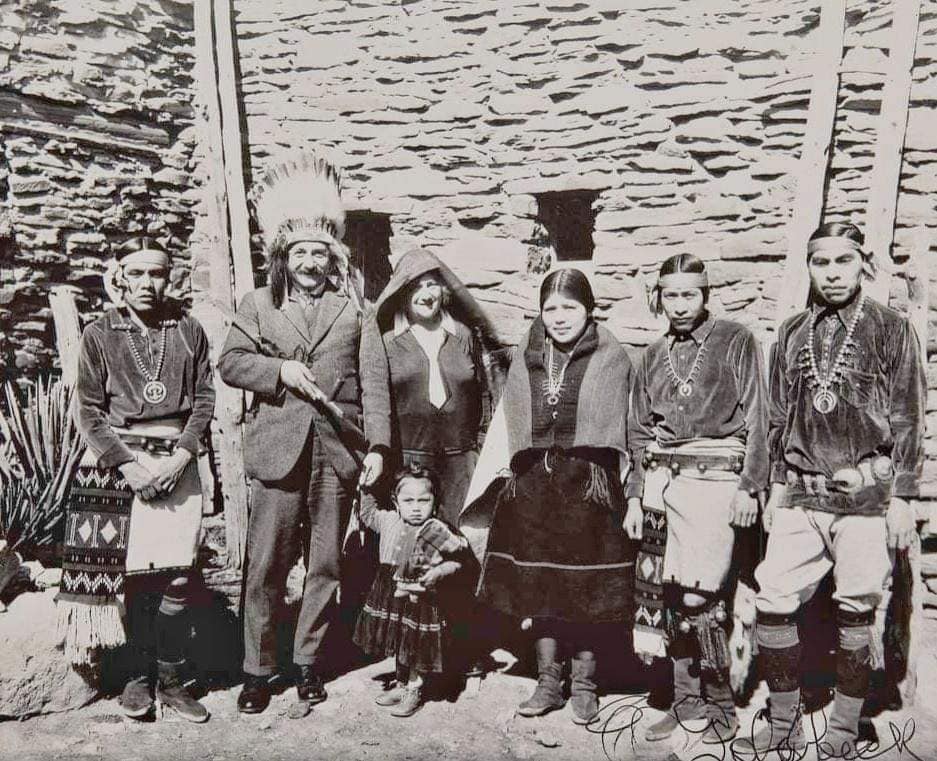

Albert Einstein sporting a Native American head- drees and peace pipe at grand canyon in 1931


UÇSUZ BUCAKSIZ UZAY DERİNLİKLERİNİ ESKİ DÜŞÜNCE METOD VE PARADİGMASI DIŞINDA OLAN YENİLENMİŞ BİR DÜŞÜNCE METODUYLA ANCAK DAHA FAZLA KAVRAYABİLİRİZ
Bildiğimiz eski metodla düşüğümüz için, şimdiye kadar ulaşamadığımız kainat ve politika sırlarına, alışılmış düşünce yolumuzu yöntemimizi ve bilinç edinme güzergahımızı değiştirerek ancak ulaşabiliriz.
Yani şimdiye kadar ulaşamadığımız o sırlara, düşünce yöntemi boyutumuzu değiştirmekle ulaşmamız mümkündür.
Şimdiki düşünce boyutumuzda engeller ve sınırlar vardır. Ne zaman ki bu engelleri ve sınırları aşarsak, o zaman bu sırların üstündeki perde bizim için aralanır.
Mezopotamya ilk medeniyetinin ve antik çağın astronomi alimlerinden tutun, ta modern çağın Einstein gibi bilim adamlarına kadar hepsi, uzay derinliklerini sadece düşünce vasıtasını kullanarak uçsuz bucaksız uzay derinliklerini faraziye teorileriyle araştırdıklarında, önce alışılagelmiş, geleneksel düşünme metoduyla bir yere varamadılar. Gerçeğe yakın faraziyeler üretebilmek için yukarıda bahsi edilen yeni düşünce tarzını buldular sonra.
Bu yeni düşünme metoduyla, asla ayak basmadıkları uçsuz bucaksız uzay deriliklerine gidip, kainat hakkında artık daha sağlıklı ve gerçekçi faraziyeler yürütebildiler ve hatta sabit hakikatlere bile ulaştılar.
Bunun içindir ki insanoğlu hala dünya atmosferinden çıkmadan çok önce, düşünce yoluyla dünyadan çıkıp, ta kainatın uç derinliklerine kadar varabilmişti. Uzayı tahlil eden, tanıyan insan, bugün dünyanın doğa yapısını da çok yakından tanıyor. Dünya kendi başına bir sistem ve mekanizması olan 'yaşayan' bir gezegendir. Dünya üzerinde sonradan peydahlanan insanlar ise, dünya doğasının en temel öğesi olmasalar da bugün dünya gezegeninin doğasını olumsuz yönde etkileyen ve giderek çoğalan bakteriyeler ve hatta mikroplardır. İnsan hücreleri tek hücreli amiplerden ta günümüze kadar kendini mütemadiyen egoistçe üretip yeniliyor. Politika da bu mikropların nasıl birbirine zarar vermeden yaşama klavuzudur.
Özellikle Amerika uzay araştırmaları bakımından dünyanın en gelişmiş ülkesidir. Amerika bugün uzay ve dünya gezegeni hakkında oldukça önemli sırlara vakıftır. Bu bakımdan Amerika, siyaseti de, insan mizaç ve tabii yapısına uyarlanmış bir şekilde yapıyor, yani insan doğası gibi EGOİSTÇE yapıyor.
Kısacası, ne insan düzeldi ve nede buna bağlı olarak insanın yaşama klavuzu olan politika rasyonel bir hal aldı ve alacak.
Sonumuz hiç hayırlı görünmüyor. En nihayet global bir anarşi ve kaos ortamına sürüklenmezsek ne iyi olurdu.
Goran Candan |


When Albert Einstein stayed at a Japanese hotel in 1922, he found himself without any cash for tips. So he scribbled two notes and handed them to
the bellhop,
reportedly telling him, One day these will be worth something. They sold in 2017 for $1.56 million.
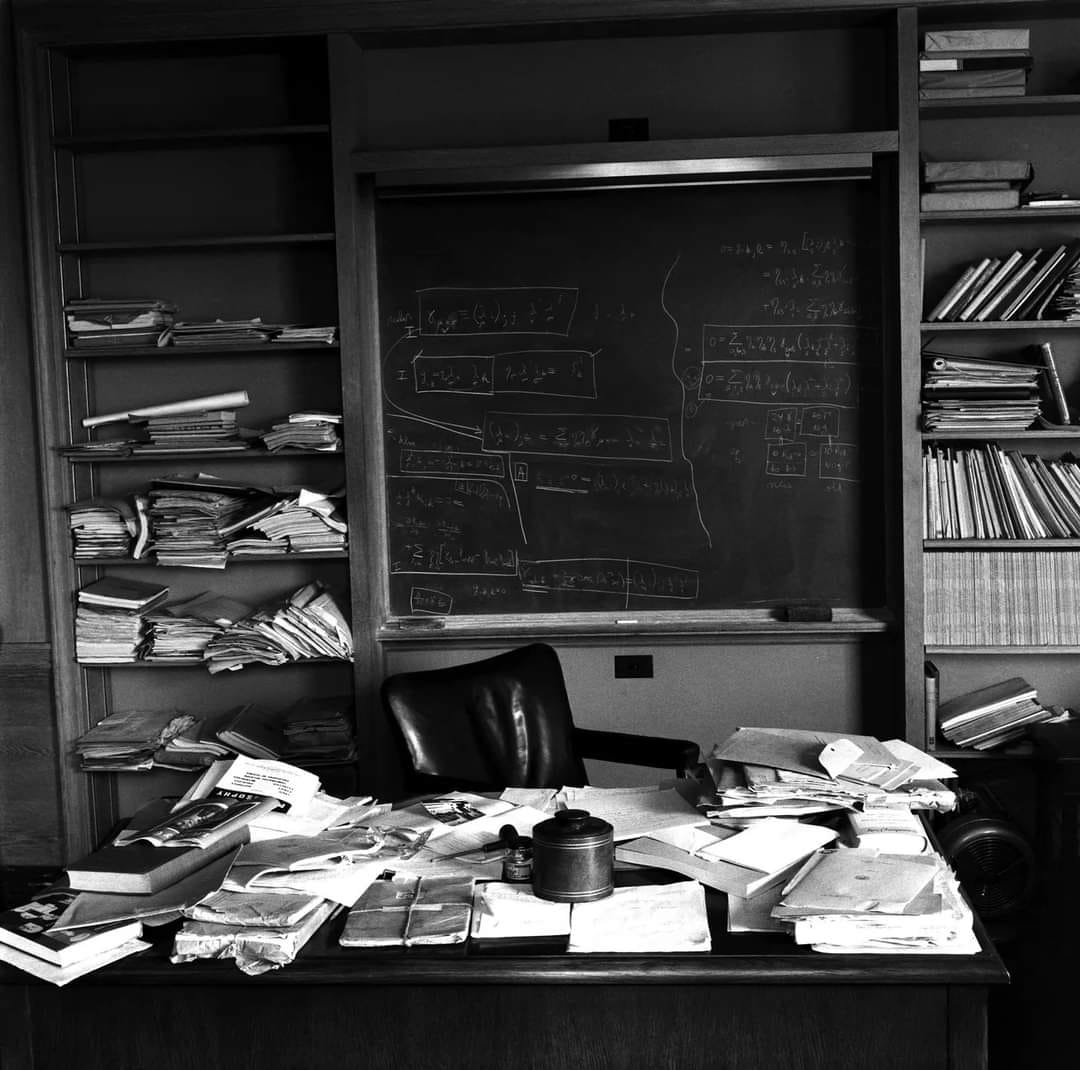

A picture taken for the world's most famous scienst Einstein's office a few hours after his death on April 18, 1955.

Albert Einstein, Nicola Tesla and other at the Acropoli in Athens
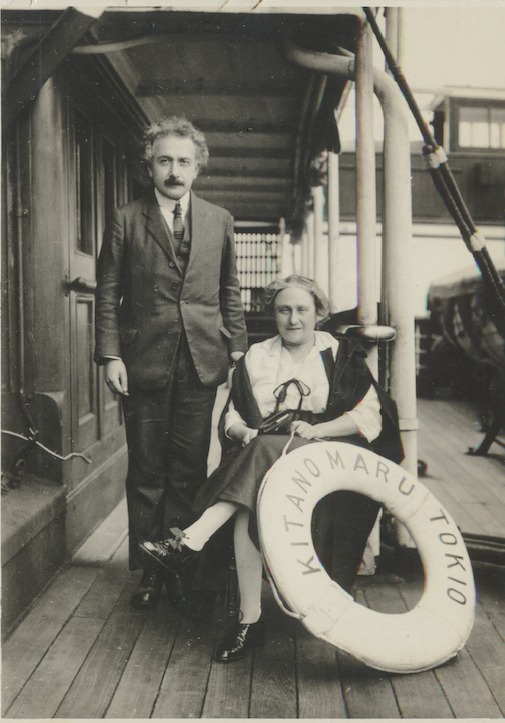

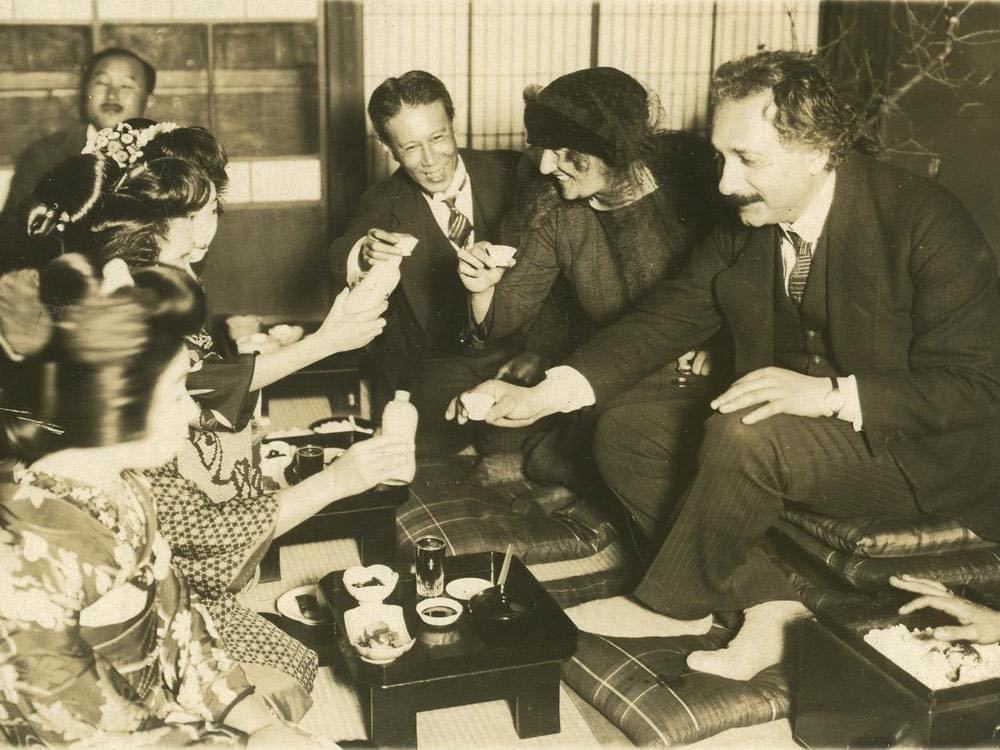
Einstein and his wife, Elsa, leave on six-month boat journey to the Far East on October, 1922.
When they checked into their hotel in Japan, thousands of people stood outside waiting for the Einsteins to wave from the balcony.

Albert Einstein 1933 yılında 54 yaşındayken bisiklete bindi
Albert Einstein'ın 5 Şubat 1930'da oğluna gönderdiği mektupta şöyle yazıyordu:
**"Hayat bisiklete binmek gibidir. Dengenizi korumak için hareket etmeye devam etmelisiniz."
Sadece başarılı bir insan olmaya çalışmayın, aynı zamanda değerli bir insan olmaya çalışın. Başarı elde ettiklerinizle ölçülür, değer ise verdiklerinizle.
Aptal, aynı şeyi tekrar tekrar yapıp farklı sonuçlar bekleyen kişidir.
Dünya, kötülük yapanlar yüzünden değil, kötülük yapmayanlar yüzünden tehlikeli bir yerdir.
Eğitim, gerçekleri öğrenmek değil, zihnin düşünmeye eğitilmesidir.
Başkalarının gürültüsünün iç sesinizi bastırmasına izin vermeyin ve kimsenin size sınır koymasına izin vermeyin, çünkü tek sınır, kendinize koyduğunuz sınırlardır. "**













Fazla tevazunun sonu vasat insandan nasihat dinlemektir.
(Ama olsun, bir zararu yoktur. İbn Haldun bu sözü Ortadoğu'da koyu cahilliğin çok yoğun ve yaygın olduğu bir dönemde söylemişti.)




With Marlyn Monroe

Tarımı ihmal eden ülke intihar ediyor demektir. Gelişmiş ülkelerin semalarında ne kadar uçağın uçtuğu önemli değil,
ne kadar arının uçtuğu önemlidir. Eğer arılar ölürse, sonraki yıllarda insanlar da ölür.
Doğal Kaynakların Sınırsız Olduğu Yanılgısı
Kürd atasözü Ava bira bi tevdira der ki: Kuyu suyu bile olsa idareli kullan, çünkü onun da bir sonu vardır. Bu söz, yalnızca bireysel tüketimi değil, aynı zamanda küresel düzeyde doğal kaynakların kullanımını da özetleyen derin bir bilgelik içerir. Dünya, üzerinde yaşayan tüm insanları besleyebilecek kadar büyük ve zengin kaynaklara sahip gibi görünse de, bu kaynaklar sınırsız değildir. Ne yazık ki, insanlık bu gerçeği göz ardı ederek üretim ve tüketimde aşırı israfa yönelmektedir.
Özellikle su, enerji ve tarım alanındaki sorumsuz tüketim, gezegenimizin doğal dengesini bozuyor. Örneğin, dünya genelinde tarımsal sulamanın yaklaşık %60ı israf ediliyor. Sanayileşmiş ülkelerde kişi başına düşen su tüketimi, gelişmekte olan ülkelere kıyasla üç kat daha fazla olmasına rağmen, suyun geri dönüşümü ve sürdürülebilir kullanımı konusunda yeterli önlemler alınmıyor. Tarımsal üretimde bilinçsiz kimyasal madde (pestisit )ve gübre kullanımı da hem su kaynaklarını kirletiyor hem de toprağın verimini uzun vadede düşürüyor.
Benzer şekilde, enerji tüketimi de büyük bir israfla devam ediyor. Fosil yakıtların hızla tükenmesine rağmen, yenilenebilir enerji kaynaklarına yapılan yatırımlar yeterli seviyeye ulaşmış değil. Dünya çapında elektrik üretiminin yaklaşık %60ı hala kömür ve doğalgaz gibi fosil yakıtlardan sağlanıyor. Bu durum hem çevresel kirliliği artırıyor hem de gelecek nesiller için enerji krizine zemin hazırlıyor. Oysa rüzgar, güneş ve hidroelektrik gibi yenilenebilir kaynaklara yönelmek, uzun vadede hem çevreyi koruyacak hem de enerji arz güvenliğini sağlayacaktır.
İnsanlığın enerji sorununu kökten çözecek olan sonsuz bir potansiyele sahip füzyon enerjisi konusunda neredeyse hiçbir ciddi yatırım yapılmıyor. Oysa bu teknoloji, fosil yakıtlara olan bağımlılığı sona erdirerek temiz, sürdürülebilir ve sınırsız bir enerji kaynağı sunabilir. Buna rağmen, mevcut enerji politikaları hala kömür, petrol ve doğalgaz gibi tükenmekte olan kaynaklara dayanıyor. Füzyon enerjisine yapılan araştırmalar yavaş ilerlerken, iklim krizi ve enerji güvenliği sorunları giderek derinleşiyor.
Tüketim alışkanlıklarımız da bu israfın önemli bir parçası. Dünya genelinde her yıl 1,3 milyar ton gıda israf ediliyor. Yani üretilen gıdaların üçte biri çöpe gidiyor. Oysa bu miktar, açlık çeken milyonlarca insanın beslenmesine yetecek düzeyde. Ayrıca gereksiz tüketim alışkanlıkları, plastik atık krizine yol açarak doğayı ciddi şekilde tehdit ediyor. Bilinçsiz tüketim ve israf devam ettiği sürece, dünyanın sunduğu kaynaklar hızla tükenmeye devam edecek.
Doğal kaynaklarımızı sınırsız sanmak büyük bir yanılgıdır. İnsanlık, üretimde ve tüketimde daha bilinçli hareket etmezse, bu kaynakların sonunu hızlandıracaktır. Çözüm ise israfı en aza indirerek sürdürülebilir bir yaşam tarzını benimsemektir. Tıpkı atasözünde dendiği gibi, Kuyu suyu bile olsa idareli kullan çünkü kaynaklarımız sınırsız değil.
Goran Candan
____
NOT: 2008-2009 yılında Stockholm Üniversitesinde İktisat Tarihini okurken Kürdistanda kirli enerji konulu bir çalışmam:
Någonting är nytt under solen
https://www.saradistribution.com/kurdistanda-kirli-enerji.htm |


Güç daima ahlaken düşük olan insanları kendine çeker. Einstein

Dinya cihekî xeternak e, ne ji ber yên ku xerabiyê dikin, lê ji ber yên ku li hevber vê xirabiyê tiştekî nakin.
(Dünya kötülük yapanlar yüzünden değil, seyirci kalıp hiçbir şey yapmayanların yüzünden tehlikeli bir yerdir)
Albert Einstein

EINSTEIN QUANTUM THEORY OF LIGHT

Earths magnetic song recorded for the first time during a solar storm
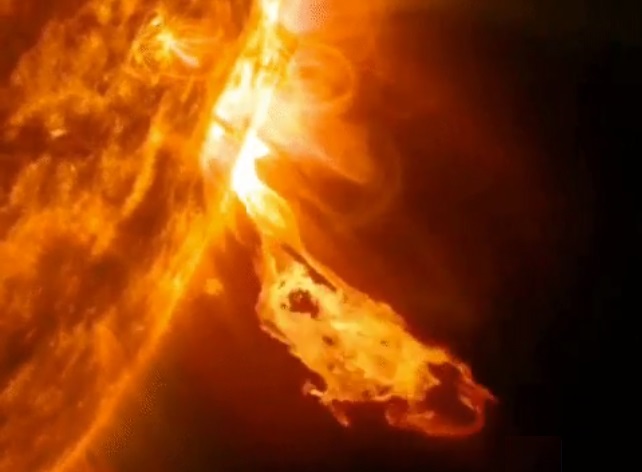
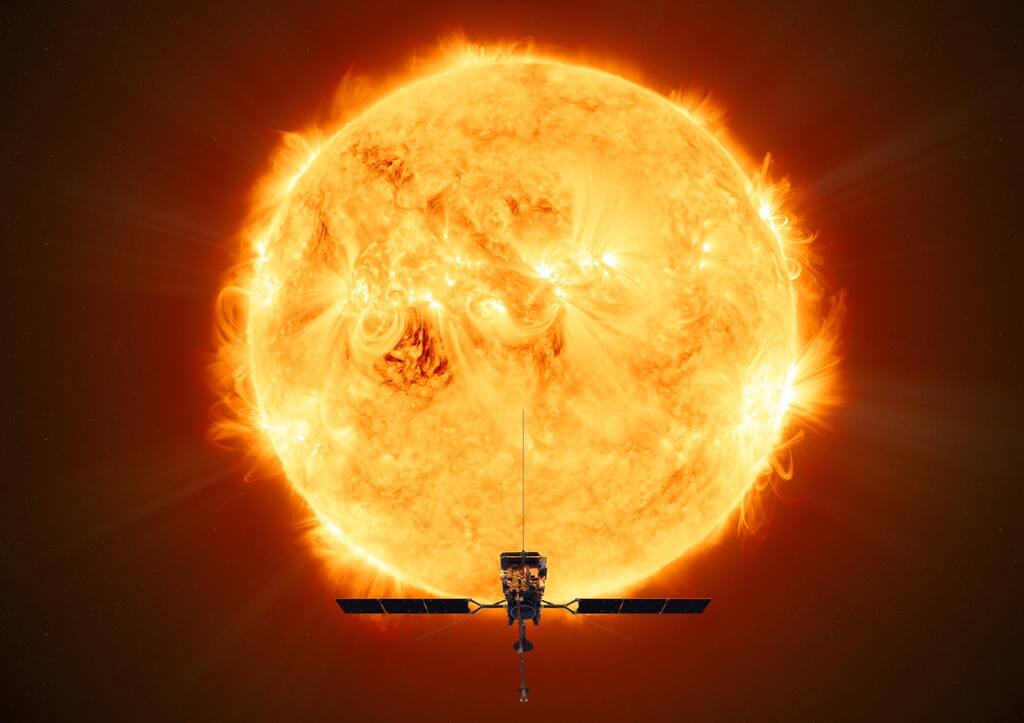



NASA telescope 42 million km closer to The Sun

Earth vs The Sun
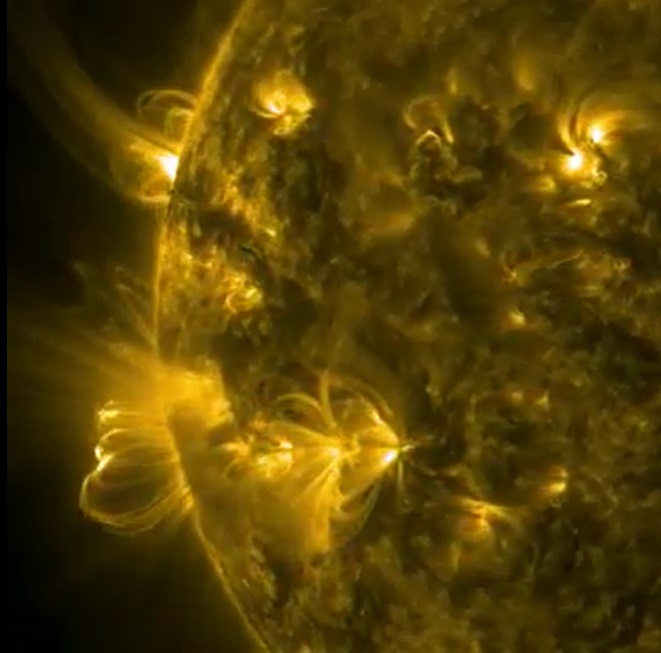

Xwedê
Aha ev e ya ku jiyanê dide me û
Ew jî;
Roj bi roj, kêlî bi kêlî û çirk bi çirk:
DIVEMIRE!

Wêneyên hetavê di heman demê de, li heman cihî, her meh hatiye kişandin
Photographs of the Sun taken at the same time, at the same spot, every month
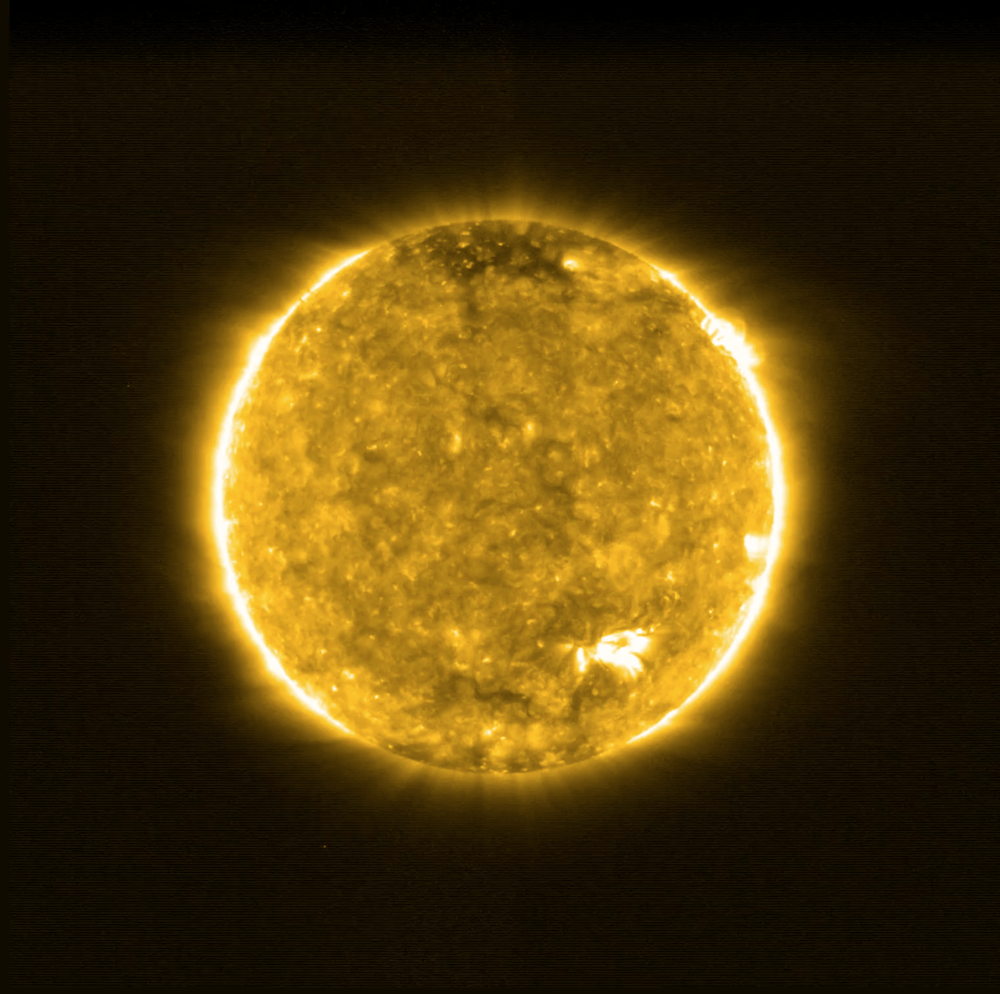
Our Sun. The Sun, as seen from the Solar Orbiter. (Credit: NASA/ESA)
So, you like astrophotography. You spend money and time to photograph the many wonders of the universe to try to get the best images you can.
But do you really know what it is that you are photographing?
We are so often caught up in technical details, all worried about using the right equipment and technique, that we may forget the very nature of what we are trying to capture.
Today we introduce a new type of article, to uncover together the nature of the things that keep us up all night.
But lets begin with a target that is very special to us, the only target that keeps astrophotographers busy photographing in the daytime.

So What Is The Milky Way Exactly?
The galaxy that we live in is known as the Milky Way galaxy. It consists of a collection of stars and planets that are gravitationally bound together in a swirling spiral. One of those planets is earth.
According to a NASA report, our galaxy is only one in about 2 trillion galaxies. Groups of these galaxies are combined into clusters; the group we belong to is creatively known as the Local Group.
Why Do We Call The Milky Way, The Milky Way?
As you can see in the many images of the Milky Way, you will see a dim, milky looking glow circling the outer edge. This is caused by the countless bright burning stars that surround it.
In ancient times, the Romans would call it via lactea, which, when translated, roughly means milky way/road.
Click here to read more!

How light phenomenon created
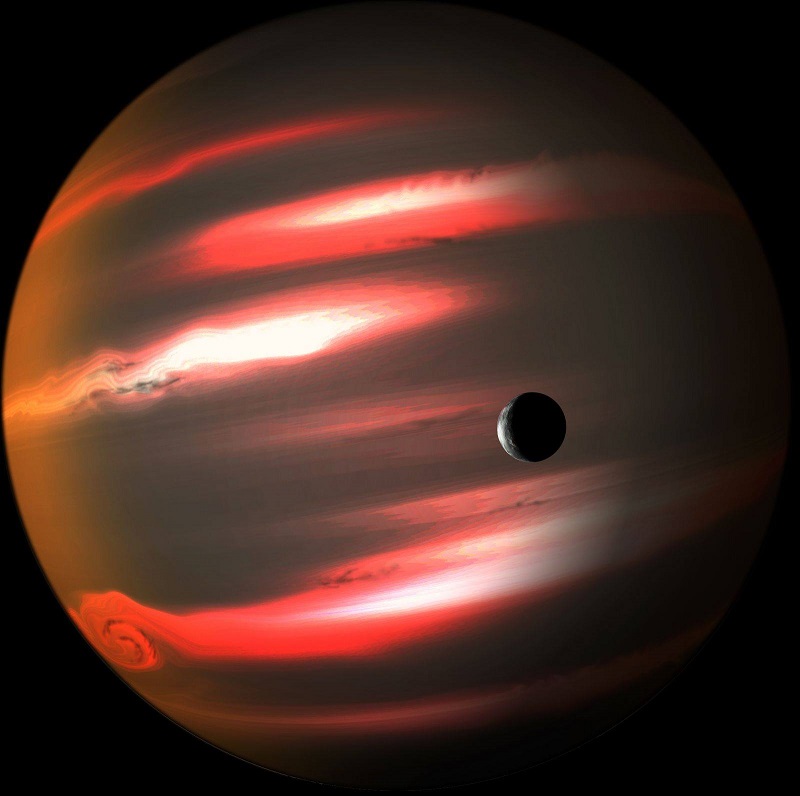

TrES-2 b: Den mörkaste planeten
750 ljusår från vår sol, i Dracos konstellation, är stjärnan GSC 03549-02811 A, en gul stjärna, liknande vår sol.
0,04 AU från sin stjärna, roterar på en cirkulär bana runt sin sol, är planeten TrES-2 b. Hans år varar bara i 2,4 dagar. Planeten har tidvattenkoppling med sin stjärna, visar alltid samma ansikte mot sin sol.
Det är en gasformig planet, typen "Hot Jupiter" , som Jupiter, men väldigt, väldigt mörk: den speglar bara 1 % av ljuset den får från sin stjärna.
Dessutom ger innervärme, ett rödaktigt glitter.
Det upptäcktes sommaren 2011.
What Will Happen to the Sun?
The Sun will consume Mercury and Venus and maybe Earth, too.
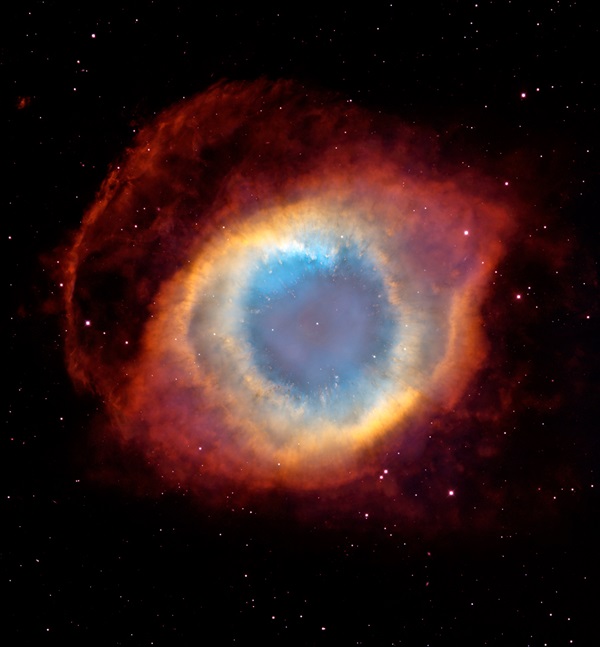
STELLAR CORPSE. After the Suns death, much of its matter will dissipate as a planetary nebula, a slowly expanding bubble of gas.
The Helix Nebula in Aquarius represents one of the skys most beautiful such objects.
The Sun is an ordinary star. It bathes the solar system with light and heat, making life possible on Earth. Its as regular as clockwork, and it sets our daily life cycles in conjunction with Earths spin. Little wonder ancient peoples revered the Sun as a god. Yet the Sun will not always be steady and reliable. Billions of years from now, the Sun's finale will turn Earth and the entire inner solar system into a very nasty place.
At 4.6 billion years old, the Sun is about halfway through its life. Its adulthood, called the main sequence phase, lasts 10 billion years. When the Sun runs out of hydrogen fuel, it must generate energy by fusing heavier elements.
At that point, its main sequence phase is over. In one of the most peculiar transformations we know of, the Suns helium core, about the size of a giant planet, will contract and heat up. And, in response, the Sun will expand by 100 times.
The swollen Sun will consume the planets Mercury and Venus and possibly Earth as well. Astronomers watching from another solar system would classify this bloated version of our Sun as a red giant.
With the Suns transformation into a red giant come new types of fusion reactions. An outer shell will fuse hydrogen as the byproducts fall inward, further compressing and heating the core. When the core reaches 180 million degrees F (100 million degrees C), its helium will ignite and begin to fuse into carbon and oxygen.
The Sun will shrink somewhat, but, after a time, and for 100 million years, it will again expand. It will then brighten significantly as it plunges toward the end of its helium-burning phase, when vigorous outflows called stellar winds strip the Suns outer layers. This will lead to the Suns final life phase a cyclical, gentle shedding of gas into what astronomers call a planetary nebula.
As the swollen Sun incinerates the solar systems inner planets, its outer icy worlds will melt and transform into oases of water for tens or hundreds of millions of years. Our solar system will then harbor not one world with surface oceans, says astronomer S. Alan Stern of NASA's Science MIssion Directorate, but hundreds all the icy moons of the gas giants, as well as the icy dwarf planets of the Kuiper Belt. Plutos temperature, says Stern, will resemble that of Miami Beach.
A question Stern and other planetary scientists are asking: Will the outer worlds with newfound water evolve life in the relatively brief intervals they have to do so? The liquid water on these worlds might exist for only a few hundred million years. After that, the Suns luminosity will dim to the point where these new water worlds will permanently refreeze. Hydrocarbons that could contribute to lifes emergence are already there, though. So, its possible that, in its death throes, our Sun may seed new life.
Some 10 billion red giants blaze today in the Milky Way Galaxy. Among all of these aged stars, might some have spawned new life on worlds that remained frozen during the stars main sequence phases? Its possible, say astronomers, but only time and a whole lot more research will tell.
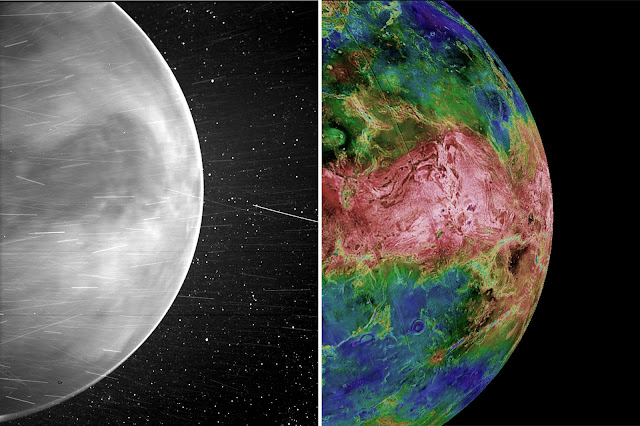
First Ever Images Of Venus Surface 2022
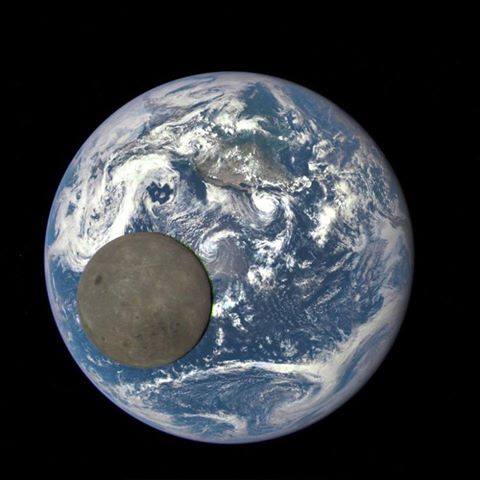
The moon passed between Nasa's Deep Space Climate Observatory and the Earth, allowing the satellite to capture this rare image of the moon's far side in full sunlight.
We normally don't see this side of the moon. As the moon is tidally locked to the earth and doesn't rotate, we only ever see the one face from the earth. Awesome shot! (2015)


'Mare Tranquillitatis' at the Moon surface

GERDÛN
(UNIVERS)
THE UNIVERSE IS WONDERFUL BUT COLD
Komplike bir fenomen gibi bize gözükse de, Evrenin işleyen bir mekanizma ve dinamiği vardır.
Bu mekanik ve dinamik bileşkeninde sürekli hareket ve sürekli değişim yaşayan Evrende yeni yıldız ve gezegenler doğup geliştiği gibi de, bunlar aynı etkenlerden dolayı da ölüyorlar..
Acaba insan ırkı kendini Evrende ebedişetirebilecek bir atılım gerçekleştirebilecek midir, yoksa içinde hayvan gibi debelendiği sosyal ve siyasal sorunların menfi etkisinin kurbanı olarak kendi kendini yok edecek bir eşekliğe imza mı atacaktır?
En büyük soru hala budur: olmak veya olmamak:
To be or not to be..

Biolojikmen insandan daha mükemmel dünya dışı bir canlı varlığın kainattaki mevcudiyeti büyük bir ihtimal dahilindedir.
Ayrıca bu bizden katbekat daha gelişkin dünyadışı canlı varlıkların yaratıcılarımız veya yeniden yapılandırıcılarımız oldukları yönündeki ihtimal de güçlüdür..
Önümüzdeki 20 yılda bu soruya büyük bir oranda cevap almış veya bulmuş olacağız.

We will definitely NOT be one of them.
The human race must find many new planets in the Universe and expand on several billion planets.
Evil in man can be curbed. Man will eventually become a perfect creator/god of good things just as the Prophet Zarathusra called in the 600s BC: pendari nig, guftari nig, kirdari nig, that is, good thoughts, good words, good deeds.
|
The Milky Way is probably full of dead civilizations

(Image: © European Souther Observatory)
Most of the alien civilizations that ever dotted our galaxy have probably killed themselves off already.
That's the takeaway of a new study, published Dec. 14 to the arXiv database, which used modern astronomy and statistical modeling to map the emergence and death of intelligent life in time and space across the Milky Way. Their results amount to a more precise 2020 update of a famous equation that Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence founder Frank Drake wrote in 1961. The Drake equation, popularized by physicist Carl Sagan in his "Cosmos" miniseries, relied on a number of mystery variables like the prevalence of planets in the universe, then an open question.
This new paper, authored by three Caltech physicists and one high school student, is much more practical. It says where and when life is most likely to occur in the Milky Way, and identifies the most important factor affecting its prevalence: intelligent creatures' tendency toward self-annihilation.
"Since Carl Sagan's time, there's been lots of research," said study co-author Jonathan H. Jiang, an astrophysicist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory at Caltech. "Especially since the Hubble Space Telescope and Kepler Space Telescope, we have lots of knowledge about the densities [of gas and stars] in the Milky Way galaxy and star formation rates and exoplanet formation ... and the occurrence rate of supernova explosions. We actually know some of the numbers [that were mysteries at the time of the famous 'Cosmos' episode]."
The authors looked at a range of factors presumed to influence the development of intelligent life, such as the prevalence of sunlike stars harboring Earth-like planets; the frequency of deadly, radiation-blasting supernovas; the probability of and time necessary for intelligent life to evolve if conditions are right; and the possible tendency of advanced civilizations to destroy themselves.
Modeling the evolution of the Milky Way over time with those factors in mind, they found that the probability of life emerging based on known factors peaked about 13,000 light-years from the galactic center and 8 billion years after the galaxy formed. Earth, by comparison, is about 25,000 light-years from the galactic center, and human civilization arose on the planet's surface about 13.5 billion years after the Milky Way formed (though simple life emerged soon after the planet formed.)
In other words, we're likely a frontier civilization in terms of galactic geography and relative latecomers to the self-aware Milky Way inhabitant scene. But, assuming life does arise reasonably often and eventually becomes intelligent, there are probably other civilizations out there mostly clustered around that 13,000-light-year band, mostly due to the prevalence of sunlike stars there.
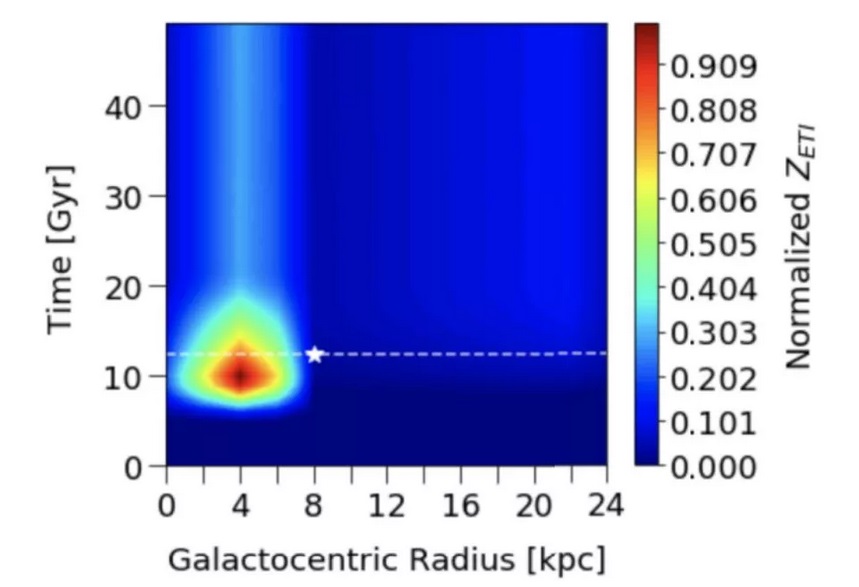
A figure from the paper plots the age of the Milky Way in billions of years (y axis) against distance from the galactic center (x axis), finding a hotspot for civilization 8 billion years after the galaxy formed and 13,000 light years from the galactic center. (Image credit: Cai et al.)
Most of these other civilizations that still exist in the galaxy today are likely young, due to the probability that intelligent life is fairly likely to eradicate itself over long timescales. Even if the galaxy reached its civilizational peak more than 5 billion years ago, most of the civilizations that were around then have likely self-annihilated, the researchers found .
This last bit is the most uncertain variable in the paper; how often do civilizations kill themselves? But it's also the most important in determining how widespread civilization is, the researchers found. Even an extraordinarily low chance of a given civilization wiping itself out in any given century say, via nuclear holocaust or runaway climate change would mean that the overwhelming majority of peak Milky Way civilizations are already gone.
The paper has been submitted to a journal for publication and is awaiting peer review.
Originally published on Live Science.

A world-like new world .. Kepler-186 f

Erd, Cîhan, Dunya
Zeman li gerîneka (planet) dunyayê, bi ger û liva dunyayê tê têgehînê/pîvanê.
Zeman li gerdûnê (kaînatê) jî, bi liva berdewamî ya firehbûna gerdûnê tê têgehînê/pîvanê.
Encam: Heger gerdûn nebe, zeman jî nîn e.
MA DEM Û WAR GUHERBER E GELO?
(COSMIC MOVEMENT & ACCELARATION?)

Dem dilive û GUHERBER e. Her wek demê gelo war jî guherber e, gelo war jî dilive? Bi gotineke din ERDÊ BIN LINGÊ ME DIŞEMITE YAN NA?
Bersivê ta nuha kes nizane. Zaniyarên gerdûnî (kosmolog) dibêjin ku Gerdûn (Universe) her ku dihere BERFIREH (ekspans/expand) dibe. Çawa
ku dem diherike her wisa jî hemû STÊR û GERÎNEKÊN li Gerdûnê jî bi hêzeke mezin ji hev dûr dikevin. Aha em li vir in: zaneyên me hîna nizanin ku
em li ciyê xwe ne yan dişemitin.. XweDA /XweZa dawiya me ya bi xêr ke.
Ewca Nehtaq
(Ezmanê Nehqat)
(Heşt gerînek, kewkeb/planet û stêrê muqîm Xor dibe Ewca Nehtaq)
1- Tîr (Merkur)
2- Gelawêj (Venus)
3- Cîhan/Dunya (Earth)
4- Merd/Behram/Merîx (Mars)
5- Muşterî (Jupîter)
6- Keywan/Zuxal (Saturn)
7- (Uranus)
8- Sil (Neptun)
9- Xor (Stêrê muqîm)
______
Xor (stêrê muqîm Xor)
Cîhan/Dunya, Venus, Mars, Merkurus, Jupîter, Saturnus, Uranus, Neptunus
|


Malstêra ( Galaksiya) Me û Stêrên li derdora wê

Stephan's Quintet
Our Galaxy's Black Hole Suddenly Lit Up and Nobody Knows Why
In May, the supermassive black hole at the core of the Milky Way became 75 times brighter in just two hours.
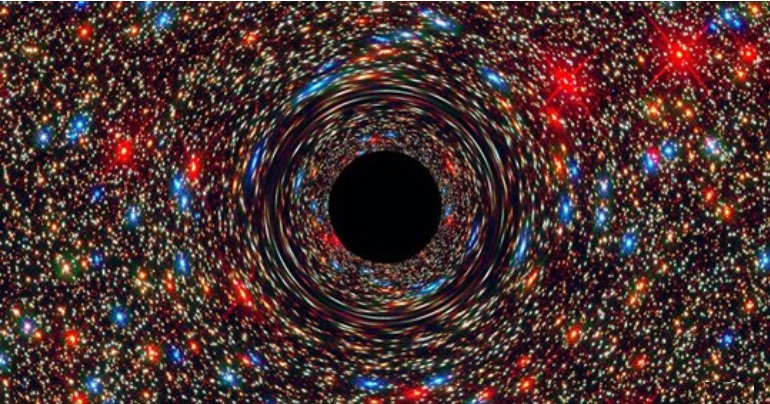

SIMULATION OF A SUPERMASSIVE BLACK HOLE. IMAGE: NASA, ESA, AND D. COE, J. ANDERSON, AND R. VAN DER MAREL (STSCI)
The supermassive black hole that lives at the center of our galaxy has been mysteriously sparkling as of late, and nobody knows the reason.
This dark behemoth, known as as Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*), is four million times as massive as the Sun. Though no light escapes its boundaries, astronomers can observe the holes interactions with bright stars or dust clouds that surround it.
On the night of May 13, 2019, UCLA astronomer Tuan Do and his colleagues were watching Sgr A* using the Keck Telescope on the summit of Mauna Kea in Hawaii. In a period of just two hours, they witnessed the black hole become 75 times brighter in the near-infrared band of the light spectrum.
That spring evening, the Milky Ways supermassive black hole reached much brighter flux levels in 2019 than ever measured at near-infrared wavelengths, according to a forthcoming study, led by Do and published on the arXiv preprint server.
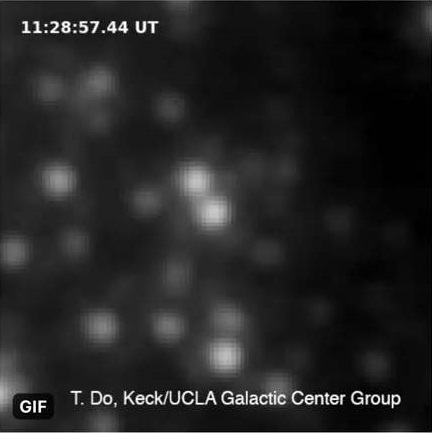
Here's a timelapse of images over 2.5 hr from May from @keckobservatory of the supermassive black hole Sgr A*
The black hole is always variable, but this was the brightest we've seen in the infrared so far. It was probably even brighter before we started observing that night!
Click to read more here |
Hawkings 50-Year Mystery About Falling into Black Holes Has Finally Been Solved

NASA
If you lurch into the event horizon of a black hole, will you ever come out? According to a series of new calculations which just solved a 50-year old problem even Stephen Hawking couldnt figure out, the answer is yes.
Its being described as a landmark calculationthe biggest thing to happen in the field since the work of the famous British physicist established the problem in the first place.
Since the 1970s, physicists have been grappling with a logical contradiction in calculations surrounding a black hole called the black hole information paradox.
Hawking would use his semiclassical quantum/general-relativity hybrid-explanation of the physics of a black hole to describe what happens to matter in and around it.
He discovered that quantum uncertainty causes small amounts of radiation to emanate from a black hole called Hawking radiation. This eventually causes it to lose mass and evaporate into nothingness. If the black hole loses mass and eventually disappears, then what falls in must appear again somewhere. The question is: where/how/why does the information escape?
The authors of the new calculations, including scientists from UC Santa Barbara, have uncovered additional effects permitted by general relativity but that Hawking didnt include, which describe a strange situation in which information that falls into a black hole will eventually come out, and that this phenomenon happens at the same time, and is partially to blame for the evaporation of a black hole.
Quantum entanglement
The way in which it works is through quantum entanglement, a phenomenon which simply means that particles of matter can be linked on the quantum level, and display patterns and reactivity to each other even though they could be separated by thousands of miles.
Don Page, a physicist at the University of Alberta, was a graduate student whose studies of black holes were key in helping his advisor, Stephen Hawking, make his realization that black holes emit radiation. In 1980, Page broke with Hawking and argued that information must be released or preserved in black holes, causing a schism among physicists at the time.
RELATED: Biggest Bang Since The Big Bang Creates a Black Hole Science Says Should Not Exist
Page would go on to establish a timeline of a black holes lifespanshaped like an upside-down V known as Page time or the Page curveit described how information which fell into the black hole would escape through emitted Hawking radiation until the black hole was no more. This was called entanglement entropy, and set up physicists for a 30-year lay up to make a slam dunk calculation.
The V-shaped decline
Over the past two years, physicists have shown that the entanglement entropy of black holes really does follow the Page curve, indicating that information gets out, explains George Musser writing for Quanta Magazine.
The slam dunk was started in October 2018 by Ahmed Almheiri at the Institute for Advanced Study when he used quantum computing to create a universe in which a simple black hole system located at the center of space began emitting radiation as per Hawkings theory.
MORE: Unprecedented New Photos of the Suns Surface Are Being Hailed as Landmark Achievement for Science
The system begins to radiate as one entangled particle enters and another one leaves. This process continues, and the number of entangled particles increases, increasing the level of entanglement entropy.
If one imagines the black hole as the contents of a snow globe, and the glass of the globe as the event horizon (the edge of the black hole where the laws of physics begin to break down), Almheiri found that as the entangled entropy grew within the system, a quantum extremal surface, formed on the glass of the snow globe, just inside the event horizon.
Everything inside the quantum extremal surface is not part of the black hole, but rather like a collection of entangled particles which no longer contribute to the entropy in the system. Furthermore, the innermost particles in the simulated black hole became likewise detached from the black hole, forming something which Almheiri called the island.
CHECK OUT: Teen Discovered New Planet 6.9 Times Bigger Than Earth Just Days into NASA Internship
At this point, non-entangled radiation begins to be emitted, and the black hole breathes itself out of existence.
On to the next one
In demonstrating that entanglement entropy of black holes followed the Page curve, Almheiri and his friends confirmed that black holes do in fact release information, though it comes out in such disorder as to appear like an encrypted password.
By now if ones brain is still working after all this, Almheiris research amazingly includes theoretical tools that would allow researchers to decrypt the scrambled entangled particles in the quantum extremal surface, and figure out what they are and where they came from.
Last year, having just solved a 50-year puzzle and proved Pages lifes work, the team decided to focus on the mysterious island of particles that were inbut not of the black hole. The island is part of the radiation, but havent flown out or been transferred to the extremal surface.
READ: Star-Gazer Reveals Stunning Pictures of Space He Takes From His Back Garden
This disconnect is theorized as being part of the reason why black holes go down the other side of the Page curve, and if solving the black hole information paradox seemed hard, Musser described the issue of the mysterious island as causing the team to look off into the distance, momentarily lost for words.
SHARE This Quantum Breakthrough With Pals on Social Media
|

"Dikkat ettim de, her şeyin kaderde yazılmış olduğunu ve kaderi değiştirmek için hiçbir şey yapılamayacağını iddia edenler
bile,
yolda karşıdan karşıya geçmeden önce sağa sola bakıyorlar" .
Stephen Hawking
For The First Time, NASA Witnesses Black Hole Giving Birth To Stars
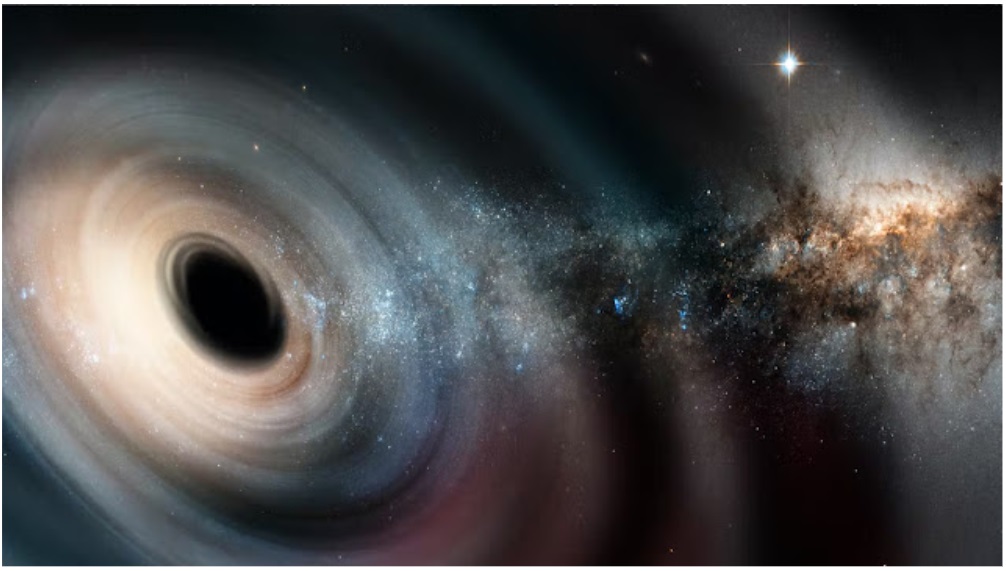


However, according to recent research, they are just as capable of producing stars as they are of consuming them
Astronomers have reached this conclusion after observing a black hole 30 million light-years distant produce stars in the dwarf starburst galaxy known as Henize 2-10.
The finding, which was made possible by NASAs Hubble Space Telescope, is the first time that black holes have given strong indications that they stimulate star formation in very tiny galaxies, according to experts, raising the issue of what function black holes play.
Amy Reines, the primary author of new research published Wednesday in the journal Nature, described the peculiar characteristics of Henizes black hole.
Scientists discover space superhighway between asteroid belt & Neptune
New gravitational 'superhighway' is discovered in the Solar System that could make interplanetary spaceflight much faster than was previously thought possible

The highways allow space rocks to travel through space far faster than previously thought - for example, travelling between
Jupiter and Neptune in under a decade
- Researchers gathered data on millions of gravitational interactions and orbits
- This allowed them to understand the superhighway between the gas giants
- The superhighway allows asteroids to travel at far faster speeds than otherwise
By Ryan Morrison For Mailonline
Published: 10 December 2020
A new 'superhighway' network running through the Solar System has been discovered by astronomers, and it could speed up space travel in the future.
Researchers from the University of San Diego looked at the orbits of millions of bodies in our Solar System and computed how they fit together and interact.
The highways allow objects to move through space much faster than previously thought possible for example, travelling between Jupiter and Neptune in under a decade.
One day, NASA or other space agencies could make use of these superhighways to speed up travel time from the Earth to distant parts of the Solar System, but the team can't yet say how it would work or how much faster journeys would become.
To discover these 'celestial autobahns', the team looked at space manifolds invisible structures consisting of a series of connected arches, which are generated by gravitational interactions in the Solar System.
In order to understand how these arches interconnect, the team had to examine the orbits of millions of objects including comets, moons and planets.
In a paper published in Science Advances, the researchers observed the structures between objects extending from the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter to Uranus and beyond.
Space manifolds act as the boundaries of dynamical channels that is connections between gravitational interactions enabling fast transportation into the inner and outermost reaches of the Solar System.
'We reveal a notable and hitherto undetected ornamental structure of manifolds, connected in a series of arches that spread from the asteroid belt to Uranus and beyond,' the team wrote in their paper.
This newly discovered celestial highway acts to shift objects over several decades, as opposed to the hundreds of thousands or millions of years in open space.
The most conspicuous arch structures are linked to Jupiter and the strong gravitational forces it exerts on the objects caught within its influence.
'Jupiter, being the most massive body in our planetary system, is responsible for most of the structures we've discovered,' study co-author Aaron J Rosengren, from the University of California San Diego, told MailOnline.
'But each planet generates similar "arches" and all of these structures can interact to produce quite complicated routes for transport.'
He added that small bodies located inside the 'manifold tubes' will follow prescribed trajectories.
'Orbits on these manifolds encounter Jupiter on rapid time scales, where they can be transformed into collisional or escaping trajectories, reaching Neptunes distance in a mere decade,' the researchers wrote.
'All planets generate similar manifolds that permeate the Solar System, allowing fast transport throughout, a true celestial autobahn.
'It should come at no surprise that Jupiter can induce large-scale transport on decadal time scales,' the authors wrote in their paper.
This has been seen in previous space missions, specifically designed for Jupiter-assisted transport. Flybys of the two Voyager missions are prime examples.
'That gravity assists can be enabled by manifolds is also well known to astrodynamicists,' according to the US team.
'Yet, their widespread influence on natural celestial bodies has been largely undervalued and unexplored.'
Populations of Jupiter-family comets, as well as small Solar System bodies known as Centaurs, are controlled by such manifolds on unprecedented time scales.
Some of these bodies will end up colliding with Jupiter or being ejected from the Solar System and one day arrive in a distance star system.
The structures were resolved by gathering data about millions of orbits in our Solar System and computing how these orbits fit within already-known space manifolds.
The results need to be studied further, according to the researchers, to understand how spaceships can make better use of the new superhighways.
The team also want to determine how such manifolds behave in the vicinity of Earth, as they have so far focused on those beyond the asteroid belt after Mars.
By understanding their role in the inner Solar System, they hope to understand how they control asteroid and meteorite encounters.
This could in future help astronomers and engineers understand the potential future impact on stellar dynamics of the growing population of artificial man-made objects in the Earth-Moon system.
The space highways could also one day be used by space agencies such as NASA and ESA to get their spacecraft to the outer planets faster.
NASA's 2001 Genesis mission, which collected a sample of solar wind particles and returned them to Earth for analysis, and its forthcoming and Artemis missions to the moon were all designed using manifold dynamics.
Meanwhile, the so-called Lagrange points regions of relative gravitational stability have become the outpost of over a dozen spacecraft missions.
'But, unlike the slow, though fuel efficient, backlanes used previously, the routes depicted in our study are very fast,' Professor Rosengren told MailOnline.
'Certainly, there are new opportunities, not just for interplanetary travel but also for the Earth-Moon system, which need further treatment.'
The findings were published in the journal Science Advances.
Super-Earths are real and they could be an even better place to live than Earth

- A super-Earth is a planet that's similar to Earth, but larger. Astronomers are discovering they may be one of the most common planets in our galaxy.
- These planets can be almost double Earth's radius and up to 10 times more massive.
- All that extra mass is what researchers think could really make super-Earths the perfect home.
Following is a transcript of the video.
Astronomers have found dozens of potentially habitable planets outside of our solar system. That's dozens of chances to discover the first alien life! Or plenty of places we could park our first interstellar colonies!
But with so many options, how do we know which is best? You might think the most Earth-like planets should be top of our list. After all, we've got water, land, an atmosphere, and trillions of life forms lapping it all up.
But according to a small group of researchers, there are bigger and better planets out there. They're called super-Earths.
Super-Earths may be some of the most common planets in our galaxy. Since 2009, the Kepler Space Telescope has discovered about 4,000 exoplanets. 30% of them are super-earths. And a few percent of those super-earths orbit within their host star's habitable zone:
That's a Goldilocks zone where the planet's surface is just the right temperature for liquid water. Not too cold or too hot. Now, there's a chance that some of these super-Earth's aren't rocky worlds like Earth. The larger ones could be made of mostly hydrogen and helium gas like Jupiter and Saturn which would not be hospitable for life.
But the reality is, astronomers are still gathering details as more data comes in. So, in the meantime, we'll explore what life on a rocky, habitable super-Earth might be like.
Liquid water is just the start. These planets can be almost double Earth's radius and up to 10 times more massive. And all that extra mass is what researchers think could really make super-Earths the perfect home. Because more massive planets have a stronger gravitational pull.
Super-Earth Kepler 20b, for example, is nearly double the size of Earth and is 10 times more massive. Making its surface gravity almost 3 times stronger. That stronger gravity means the planet can hold on to more air molecules forming a thicker atmosphere.
Which is great for protection against harmful space radiation. It also means mountains and hills would erode faster leaving a relatively flatter surface compared to Earth. Which might sound boring but scientists think this could actually spawn dozens of shallow islands across the planet.
Which, in turn, could be the perfect place for life to form and evolve. "Just as biodiversity in Earth's oceans is richest in shallow waters near coastlines, such an 'archipelago world' might be enormously advantageous to life."
There's just one problem leaving this tropical paradise would be extremely difficult. The escape velocity on Kepler 20b is more than double compared to Earth's. Which means either rockets would need more fuel to reach their destinations. For example, a mission similar to the Apollo moon landings would require twice the amount of fuel or, rockets could only carry a fraction of the payload.
For instance, SpaceX's Falcon Heavy can launch 50,000 kilograms of payload into Earth's orbit whereas it could only launch 40 kilograms into orbit around a super-Earth like Kepler 20b. That's about the weight of a German Shepherd.
Suffice it to say, leaving a super-Earth would be a far greater challenge. But if it looked like this, would you really want to say goodbye? We'll never know for sure until we visit one.
EDITOR'S NOTE: This video was originally published on July 6, 2018.


Dûrbînê (teleskop) Gerdûnî Spîtzer

Lost Galaxy
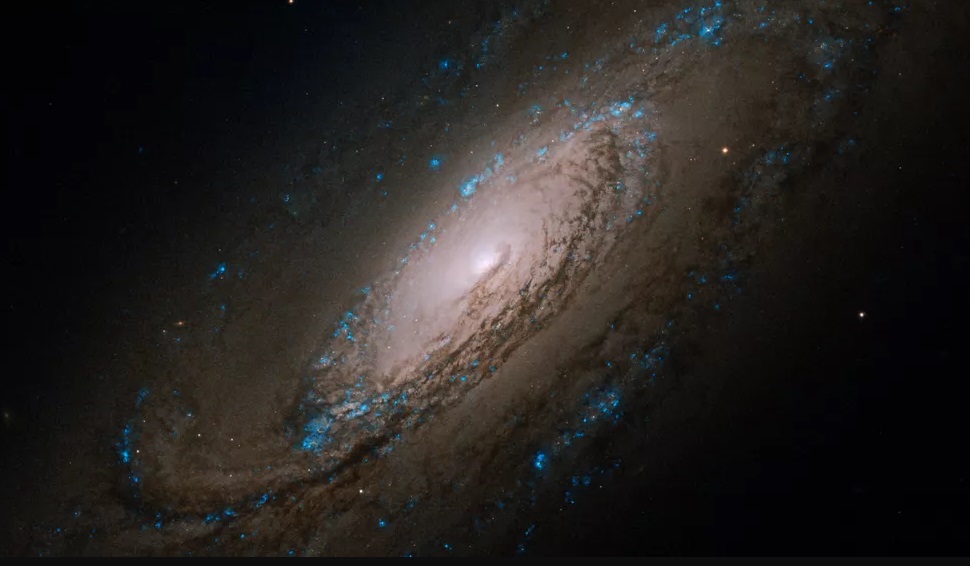


Scenic spiral galaxy NGC 5005.Hubble Pic. Nasa
Van stêrên nenas ên li ser ezmanên şeva tarî yên gerdûna bêserûber wê rojekê werine naskirin. Rojekê mirov wê xwe bigehînine ser wan stêran û her wek li ser vê stêra me, ya ku em jê re dibêjin dunya, li ser wan jî, wê mal, gund û bajar werine avakirin. Ciyê ku mirov ni karibe xwe bigehîne nîn e. Tiştê ku mirov ni karibe çêke nîn e, heger ku mirov xwe ji ser riya rast ne veqetîne.
Goran Candan
(Novela Erd/Înglîz, 2011. Diyarbekir)
_____________
BINGEHA van peyvên min li sala 1977an li Radyoya Moskvayê Bernameya Zimanê tirkî hat weşandin. Ji şeş heyvan bêhtir her roj saet 17:00 van peyvên min li vê bernameyê ji bo guhdaran dihat xwandin.
Li vê bernamê beşdarê pêşbirkeke nivîskî bûm û ev nivîsa min a li ser kûrahiya gerdûnî, li dunyayê duwemîn hat hilbijartin.
Pirsa ku min wisa xweş û durust bersivandibû wek hêjayî wergirtina xelata duwemîn a cîhanî hatibû dîtin ev bû: Gelo bi dîtina We lêkolînên li nav kûrahiya gerdûnî wê çi sûd û kelk bide bo mirovayetiyê? (Sizce uzay derinliklerinin incelenmesi insanlığa ne gibi yararlar sağlar?) Xelata yekemîn xortekî ji Kubayê wergirtibû. A sêyemîn jî xortekî ji Senegal li Afrîkayê.
Wek xelata duwemîn ji min re jî alayeke Bernameya Gerdûnî ya Rûsî, ya ku li stasyona MÎRî bi şanenavên (îmzeyên) du kozmonotan; Yûrî Romanenko û Georgî Grecko hat şandin. Wan, vê alayê li ser Stasyona Fezayî ya MÎRî bi şanenav (îmze) kiribûn. Wek têt zanîn, yekem rekora mayina dirêj a li fezayê, ya van her du kozmonotên sovyetî bû, ku ji ser 400 rojan li fezayê mabûn..
Hevalê min ê xweşdivî Ferit Metin ê Golgulî jî beşdarê vê pêşbirka nivîskî bû û wî jî xelatek ji Moskvayê wergirt. Li vê bernameya radyoyî ya cîhanî, nivîsên Ferit Metin û min, wisa bi mehan dihat duabarekirin. Wek li bîra min maye, Ferit Metin bi hûrgulî (tefsîlat) hemû bernameya fezayî ya Sovyet û Amerîkayê JIBER zanibû!
Piştî derba leşkerî ya 12yê îlonê 1980, diya min a reben ji ber tirsa dewleta tirk vê alayê avêt nav daşrê û av rêt ser. |
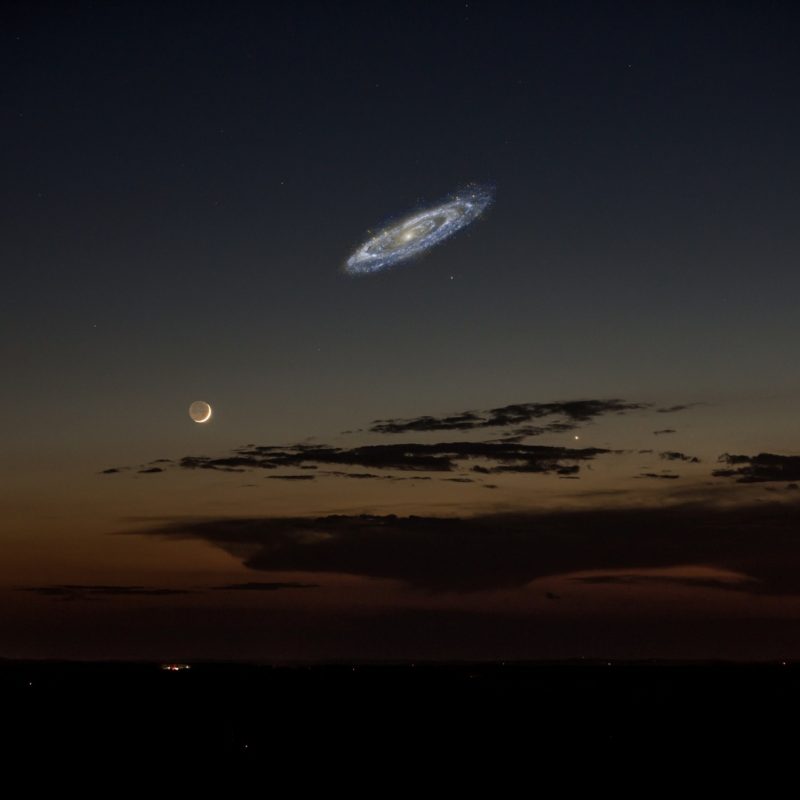

Andromeda and Milky Way galaxies are merging
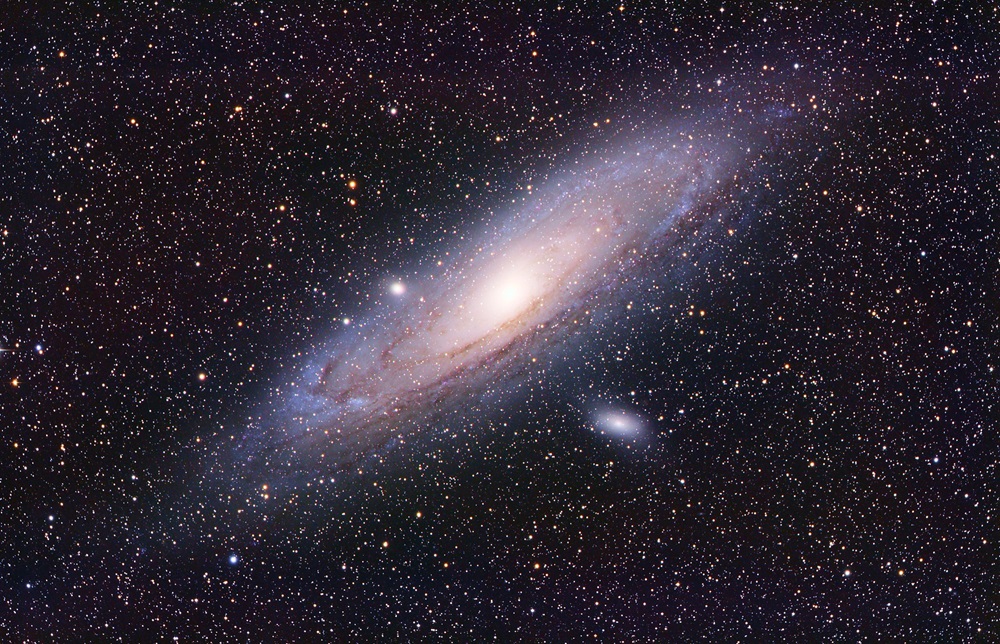

The Andromeda Galaxy (shown here with some of its satellites, 4,2 LY away from the earth), though larger and older, is sometimes considered a galaxy similar to our Milky Way.
New survey results suggest that the Milky Way may not be as normal as we think.
Kees Scherer
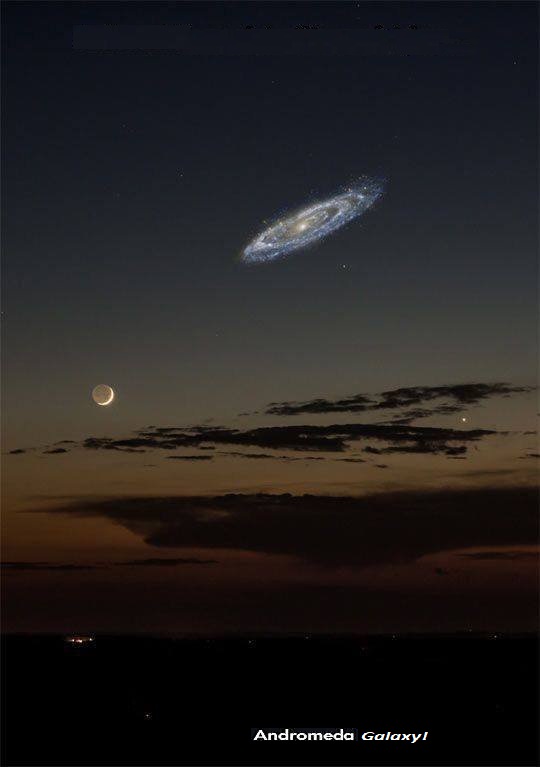

Andromeda
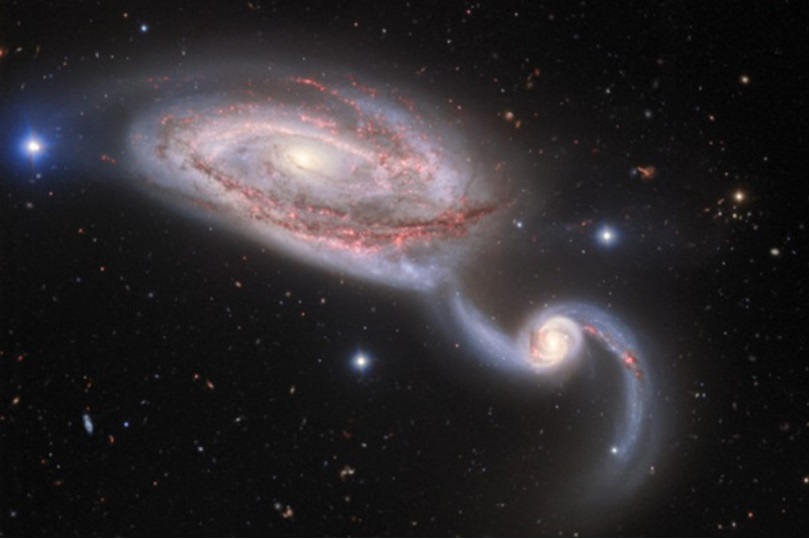



The galaxies NGC 5394 (the smaller one, on the right) and NGC 5395 (the larger one, on the left) are in the middle of colliding over the span of millions of years.
NSFs National Optical-Infrared Astronomy Research Laboratory/Gemini Observatory/AURA
Collisions between galaxies can take millions of years. The galaxies NGC 5394 and NGC 5395 are in the middle of one such ambling encounter.
The pair, located about 160 million light-years away from Earth, have already collided at least once, astronomers say. The stars in each of the galaxies are so far apart that any collisions between stars are very unlikely. However, the collision may have caused turbulent motions in the galaxies gases and triggered new bursts of star formation.

Galaxy M51

Evren'in %4'ünün görüntüsü
Dünya, sadece %4'ünü görebildiğimiz evrende minik bir galaksi içinde. Biz de o minik nokta içinde bir yerlerde.

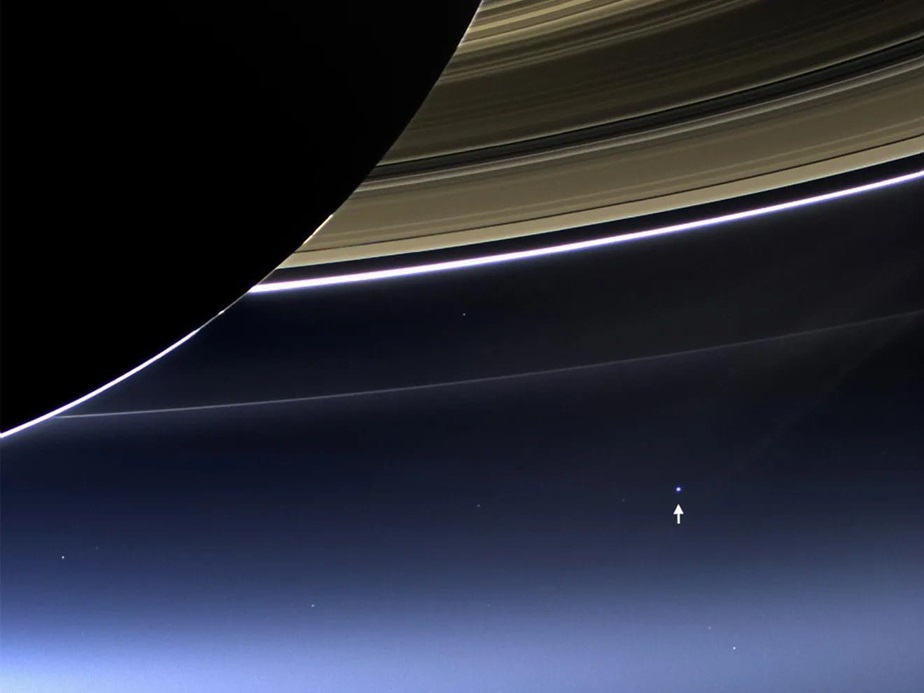
Em li vir in . We are here (Voyager's image)

We are here
This little dot is Earth about 6 Billion kilometers away (3.7 billion miles) taken by Voyager 1, as it was leaving our solar system. So much life in that little Pale Blue Dot  25 billion kilometers from Earth: Voyager 1 sets a new record: https://www.alpha.shhurli.com/?p=36 Launched: Mon, 05 Sept 1977 12:56:00 UTC
25 billion kilometers from Earth: Voyager 1 sets a new record: https://www.alpha.shhurli.com/?p=36 Launched: Mon, 05 Sept 1977 12:56:00 UTC
200 000 år av framsteg på väg mot total undergång?
Ser ni? Vi och vårt liv är så obetydligt, så skört, så fullständigt förgängligt! Ett enda blått dammkorn i det oändliga Kosmos och ändå fyllt av liv, hopp, drömmar och framtid.
Varför kastar vi bort allt detta med krig, hat och förstörelse? Vi har så lite, men ändå förstör vi det lilla vi har kvar. Istället för att vårda vår planet och varandra, river vi sönder våra samhällen med våld och splittring.
En global uppvärmning smyger sig allt närmare och har redan börjat förändra vår värld. Växtligheten vissnar, våra skogar brinner, haven stiger och kokar, luften blir allt giftigare, och våra dricksvattenreserver minskar. Orkaner, översvämningar, jordskred, jordbävningar alla dessa naturkatastrofer sker nu med skrämmande frekvens och kraft. Ser ni inte vad vi gör? Vi är mitt i vår egen självförstörelse!!
Nu när vi äntligen har nått en avancerad teknologisk och materiell nivå där vi kunde ha säkrat vår framtid, håller vi istället på att gräva vår egen grav. Vi har till och med skapat artificiell intelligens ett verktyg som skulle kunna hjälpa oss att bygga en bättre värld men vad använder vi det till? Övervakning, manipulation och vapenutveckling.
Skärp er! Tänk! Agera! Stoppa dessa meningslösa krig som hotar att spridas och förgöra hela vår civilisation allt vi har kämpat för under över 200 000 år! Vi måste välja klokskap framför dårskap. Fred framför konflikt. Framtid framför undergång.
Vi har bara en chans. Bara en värld.
Goran Candan |
NASA Woke Up Voyager 1 From 13 Billion Miles Away, And
The Spacecraft Actually Signalled Back

NASA sent a signal 13 billion miles into space - and got a response
NASA'S Voyager 1 has astounded its operators after answering a call to fire thrusters that have laid dormant for 37 years, the space agency has revealed.
, Mon, Dec 4, 2017

The Milky Way galaxy contains an astonishing 100 to 400 billion stars, many with planets.
This means there could be up to 3 trillion planets, and who knows how many might be Earth-like or support life!
#MilkyWay #Galaxy #Planets #SpaceExploration #CosmicNeighborhood


The Entire History of the Universe - Big Bang Theory
13.8 billion years ago, the universe began with the Big Bang an explosive moment when space, time, and matter came into existence.
In less than a second, it expanded faster than the speed of light in an event called cosmic inflation.
As the universe cooled, matter formed from energy, creating a dense, hot plasma of particles. About 380,000 years later, atoms began to form, allowing light to travel freely for the first timethis ancient glow, known as the cosmic microwave background, still fills the universe today.
Gravity then sculpted the cosmos, pulling gas into massive stars and galaxies.
These early stars illuminated the universe, breaking apart surrounding hydrogen in a process called reionization. Over billions of years, galaxies evolved into the vast structures we see today. Scientists once believed cosmic expansion would slow down, but in 1998, they discovered that dark energy is accelerating it.
If this continues, the universe may expand endlessly, growing colder and emptier until all the stars go out and the cosmos will be nothing but an infinite abyss of darkness.
learn more https://science.nasa.gov/universe/overview/
#universe #bigbangtheory #creation #DarkMatter #nasa #spaceexploration #SpaceMysteries

Ever wondered how long each planet takes to orbit the Sun?
 Mercury 88 days
Mercury 88 days
 Venus 225 days
Venus 225 days
 Earth 365 days
Earth 365 days
 Mars 687 days
Mars 687 days
 Jupiter 12 years
Jupiter 12 years
 Saturn 30 years
Saturn 30 years
 Uranus 84 years
Uranus 84 years
 Neptune 165 years
Neptune 165 years
Even the Sun rotates once every 2538 days,
depending on the region!
Our solar system really is dynamic!

Estimated Travel Times to Each Planet in our Solar System from Earth
--- Imagine how insignificantly small we are or how unimaginably vast our galaxy and the universe are!

SOLAR SYSTEM !! There are eight ( planets in the solar system 2. Jupiter is the biggest planet of the solar system 3. Mercury is the smallest planet of the solar system 4. Jupiter is the heaviest planet of the solar system 5. Mercury is the lightest planet of the solar system 6. Neptune is the coldest planet of the solar system 7. Venus is the hottest planet of the solar system 8. Neptune is the farthest planet from the sun 9. Mercury is the closest planet from the sun 10. Venus is the brightest planet 11. Jupiter is the darkest planet 13. Earth is the blue planet (In some books Neptune is also) 14. Mars is the Red planet 15. Earth is the most colorful planet 16. Venus is the planet with the longest day time (225 earth days) 17. Jupiter is the planet with shortest day time (10 hours) 18. Mercury is the fastest revolving planet 19. Neptune is the slowest revolving planet 20. Jupiter is the fastest rotating planet (on its axis) 21. Venus is the slowest rotating planet (on axis) 22. Mercury and Venus are planets with no Moons or Satellites 23. Venus is called the Morning Star 24. Earth is the only planet with Life 25. Jupiter is the planet with maximum number of Moons or Satellites (79)
planets in the solar system 2. Jupiter is the biggest planet of the solar system 3. Mercury is the smallest planet of the solar system 4. Jupiter is the heaviest planet of the solar system 5. Mercury is the lightest planet of the solar system 6. Neptune is the coldest planet of the solar system 7. Venus is the hottest planet of the solar system 8. Neptune is the farthest planet from the sun 9. Mercury is the closest planet from the sun 10. Venus is the brightest planet 11. Jupiter is the darkest planet 13. Earth is the blue planet (In some books Neptune is also) 14. Mars is the Red planet 15. Earth is the most colorful planet 16. Venus is the planet with the longest day time (225 earth days) 17. Jupiter is the planet with shortest day time (10 hours) 18. Mercury is the fastest revolving planet 19. Neptune is the slowest revolving planet 20. Jupiter is the fastest rotating planet (on its axis) 21. Venus is the slowest rotating planet (on axis) 22. Mercury and Venus are planets with no Moons or Satellites 23. Venus is called the Morning Star 24. Earth is the only planet with Life 25. Jupiter is the planet with maximum number of Moons or Satellites (79)

|
Mikrodan Makroya: Evren Bir Atom Olabilir mi? İç İçe Geçmiş Dünyalar?!
Güneş Sistemi ile atomun benzerliğinden yola çıkarak, evrenin nasıl bir yer olduğunun bilimsel ve felsefi açıdan sorgulanması yeni bir fenomen değildir. Hiç düşündünüz mü, içinde yaşadığımız Güneş Sistemi de büyük bir atom olabilir mi? Bu soru hem bilimsel hem de felsefi açıdan derin bir tartışma alanı sunuyor.
İlk bakışta, Güneş Sistemi ve atom modelleri arasındaki görsel benzerlik çarpıcıdır. Her iki yapıda da merkezde yoğun bir çekirdek bulunur: atomda bu çekirdek protonlar ve nötronlardan, Güneş Sisteminde ise Güneşten oluşur. Elektronlar, tıpkı gezegenlerin Güneşin etrafında döndüğü gibi çekirdeğin etrafında döner. Ancak bu görsel benzerlik, yapısal veya fiziksel bir özdeşlik anlamına gelmez.
Bilimsel olarak atomlar kuantum mekaniğiyle, Güneş Sistemi ise klasik mekanikle açıklanır. Atom altı parçacıkların davranışları, belirsizlik ilkesi ve dalga fonksiyonları gibi olgularla tanımlanırken, gezegenlerin hareketleri Newtonun ve Einsteinın yasalarıyla belirlenir. Elektronların yörüngeleri sabit daireler değil, olasılık bulutlarıdır. Gezegenler ise oldukça öngörülebilir, düzenli yörüngelerde hareket eder. Bu farklar, evrenin farklı ölçeklerde farklı kurallar altında işlediğini gösterir.
Felsefi açıdan bakıldığında, Biz bir atomun içinde yaşıyor olabilir miyiz? sorusu gerçekliğin doğası ve insan algısının sınırlarıyla ilgilidir. Eğer evren sonsuzsa ya da çok katmanlı bir yapıya sahipse, bizim evrenimiz daha büyük bir varlığın yapı taşı olabilir mi? Bu, antik çağlardan beri var olan mikrokozmos-makrokozmos benzetmesini hatırlatır: İnsan küçük bir evrendir, evren büyük bir insandır. Belki de bizim evrenimiz, başka bir varlık için bir atomdan farksızdır.
Simülasyon teorisi gibi modern felsefi yaklaşımlar da bu fikri destekler nitelikte olabilir. Eğer yaşadığımız gerçeklik bir simülasyon ise, bizim gerçeklik düzeyimiz başka bir düzeyin mikroskobik parçası olabilir. Bu durumda, bizim Güneş Sistemimiz başka bir düzeydeki bir maddenin bileşeni olabilir. Ancak bu hipotezler, henüz bilimsel olarak doğrulanmış değildir ve daha çok varsayımsaldır.
Ayrıca geometri gibi matematiksel kavramlar da bu benzetmeyi destekleyebilir. Fraktal yapılar (Kendinebenzerlik), aynı desenin farklı ölçeklerde tekrar ettiği yapılardır. Evrenin de fraktal bir yapıya sahip olduğu bazı teorilerde öne sürülmektedir. Eğer bu doğruysa, atomun yapısıyla galaksilerin ya da Güneş Sisteminin yapısı arasında bir tür kendini tekrar eden desen olabilir.
Yaşadığımız Güneş Sisteminin bir atom gibi olup olmadığı sorusu, daha çok metaforik ve felsefi bir anlam taşır. Bilimsel olarak iki yapı çok farklı fiziksel prensiplere dayanır. Ancak insan zihni benzerlikleri ve desenleri görmeye eğilimlidir. Bu tür sorular, evrenin doğası hakkında düşünmemizi sağlar ve bilimle felsefe arasındaki ince çizgide yürümemize olanak tanır. Atom kadar küçük ve evren kadar büyük şeyler arasındaki bu bağlar, belki de insanlığın bilgi arayışının en felsefik-şiirsel yönüdür.
Goran Candan
|

Vücudunda yaklaşık 7 oktilyon atom var

Çin'e bu konuda başarılar diliyoruz. Hem insanlık için iyi bir adım olacak hem de kendi büyük nüfusunun sorununu kökten çözmek için çok ideal bir girişim olacak. Umarım Çin bu faaliyetinde başarılı olur ve dünyanın gelişen insan nüfusu için dünya kadar güzel veya dünyadan daha güzel ve daha iyi yaşam koşullarının hakim olduğu yeni bir dünya keşfeder ki insanlık burada nüfus artışından dolayı birbirini katletmekten ve birbirini yemekten kurtulmuş olur.
Bu proje, aynı zamanda bilimin sınırlarını genişletecek çok önemli bir adım olacaktır. Ayın uzak tarafına yerleştirilecek bir teleskop, evrenin derinliklerinden gelen sinyalleri yeryüzündeki radyo parazitlerinden etkilenmeden yakalayabilecek. Böylece, evrenin başlangıcı, kara delikler, karanlık madde ve hatta dünya dışı yaşam gibi büyük sorulara dair yeni ipuçları elde edilebilir. Bilim insanları için benzersiz bir gözlem noktası sağlayacak olan bu proje, uzay araştırmalarında yeni bir çağın kapısını aralayabilir.
Ayrıca, bu tür büyük projeler, sadece bilimsel keşiflerle sınırlı kalmayıp ülkeler arasındaki uzay rekabetini de farklı bir boyuta taşıyacaktır. Çin, bu hamlesiyle uzaydaki varlığını güçlendirirken, diğer ülkeleri de benzer büyük projelere yönlendirebilir. Belki de bu adım, insanlığın sadece Dünyaya bağımlı kalmadığı, yeni gezegenler keşfedip kolonileşmeye hazırlandığı bir dönemin başlangıcı olacaktır.
31.03.2025
G.C.
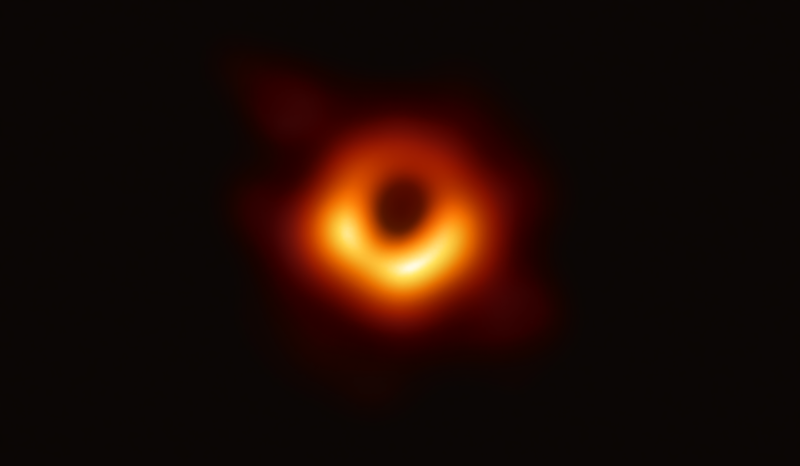

Wêneyeke rasteqîn a Kuna Reş a Herî Tund (Super Massive Black Hole), 2019
(Credits: Event Horizon Telescope collaboration et al.)

Komplike ve anlaşılmaz bir fenomen gibi bize gözükse de, Evrenin işleyen bir mekanizma ve dinamiği vardır.
Bu mekanik ve dinamik bileşkeninde sürekli hareket ve sürekli değişim yaşayan Evrende yeni yıldız ve gezegenler doğup geliştiği gibi,
bunlar aynı etkenlerden dolayı da 'ölüyorlar'.. Acaba insan ırkı kendini Evrende ebedişetirebilecek bir atılım gerçekleştirebilecek midir,
yoksa içinde hayvan gibi debelendiği sosyal ve siyasal sorunların menfi etkisinin ebedi kurbanı olarak kendi kendini yok edecek bir eşekliğe mi imza atacaktır?
En büyük soru hala budur: olmak veya olmamak:
To be or not to be.. G.C.
What Are Black Holes?
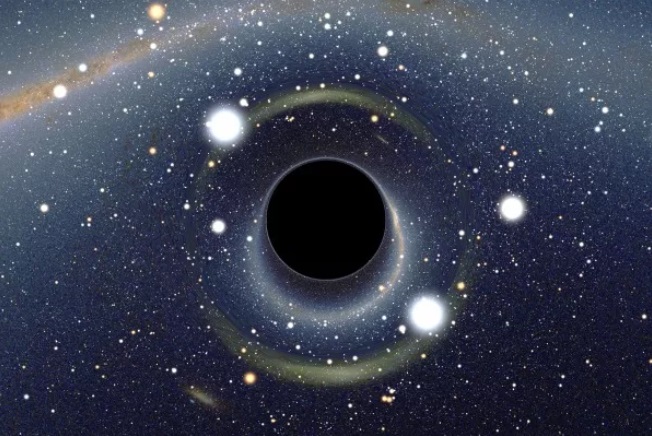

Simulated view of a black hole in front of the Large Magellanic Cloud.
(Image: © Alain R. | Wikimedia Commons)
Black holes are some of the strangest and most fascinating objects in outer space. They're extremely dense, with such strong gravitational attraction that even light cannot escape their grasp if it comes near enough.
Albert Einstein first predicted the existence of black holes in 1916, with his general theory of relativity. The term "black hole" was coined many years later in 1967 by American astronomer John Wheeler. After decades of black holes being known only as theoretical objects, the first physical black hole ever discovered was spotted in 1971.
Then, in 2019 the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) collaboration released the first image ever recorded of a black hole. The EHT saw the black hole in the center of galaxy M87 while the telescope was examining the event horizon, or the area past which nothing can escape from a black hole. The image maps the sudden loss of photons (particles of light). It also opens up a whole new area of research in black holes, now that astronomers know what a black hole looks like.
So far, astronomers have identified three types of black holes: stellar black holes, supermassive black holes and intermediate black holes.
Stellar black holes small but deadly
When a star burns through the last of its fuel, the object may collapse, or fall into itself. For smaller stars (those up to about three times the sun's mass), the new core will become a neutron star or a white dwarf. But when a larger star collapses, it continues to compress and creates a stellar black hole.
Black holes formed by the collapse of individual stars are relatively small, but incredibly dense. One of these objects packs more than three times the mass of the sun into the diameter of a city. This leads to a crazy amount of gravitational force pulling on objects around the object. Stellar black holes then consume the dust and gas from their surrounding galaxies, which keeps them growing in size.
According the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, "the Milky Way contains a few hundred million" stellar black holes.
Supermassive black holes the birth of giants
Small black holes populate the universe, but their cousins, supermassive black holes, dominate. These enormous black holes are millions or even billions of times as massive as the sun, but are about the same size in diameter. Such black holes are thought to lie at the center of pretty much every galaxy, including the Milky Way.
Scientists aren't certain how such large black holes spawn. Once these giants have formed, they gather mass from the dust and gas around them, material that is plentiful in the center of galaxies, allowing them to grow to even more enormous sizes.
Supermassive black holes may be the result of hundreds or thousands of tiny black holes that merge together. Large gas clouds could also be responsible, collapsing together and rapidly accreting mass. A third option is the collapse of a stellar cluster, a group of stars all falling together. Fourth, supermassive black holes could arise from large clusters of dark matter. This is a substance that we can observe through its gravitational effect on other objects; however, we don't know what dark matter is composed of because it does not emit light and cannot be directly observed.
Scientists once thought that black holes came in only small and large sizes, but recent research has revealed the possibility that midsize, or intermediate, black holes (IMBHs) could exist. Such bodies could form when stars in a cluster collide in a chain reaction. Several of these IMBHs forming in the same region could then eventually fall together in the center of a galaxy and create a supermassive black hole.
In 2014, astronomers found what appeared to be an intermediate-mass black hole in the arm of a spiral galaxy.
"Astronomers have been looking very hard for these medium-sized black holes," study co-author Tim Roberts, of the University of Durham in the United Kingdom, said in a statement. "There have been hints that they exist, but IMBHs have been acting like a long-lost relative that isn't interested in being found."
Newer research, from 2018, suggested that these IMBHs may exist in the heart of dwarf galaxies (or very small galaxies). Observations of 10 such galaxies (five of which were previously unknown to science before this latest survey) revealed X-ray activity common in black holes suggesting the presence of black holes of from 36,000 to 316,000 solar masses. The information came from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, which examines about 1 million galaxies and can detect the kind of light often observed coming from black holes that are picking up nearby debris.
What do black holes look like?
Black holes have three "layers": the outer and inner event horizon, and the singularity.
The event horizon of a black hole is the boundary around the mouth of the black hole, past which light cannot escape. Once a particle crosses the event horizon, it cannot leave. Gravity is constant across the event horizon.
The inner region of a black hole, where the object's mass lies, is known as its singularity, the single point in space-time where the mass of the black hole is concentrated.
Scientists can't see black holes the way they can see stars and other objects in space. Instead, astronomers must rely on detecting the radiation black holes emit as dust and gas are drawn into the dense creatures. But supermassive black holes, lying in the center of a galaxy, may become shrouded by the thick dust and gas around them, which can block the telltale emissions.
Sometimes, as matter is drawn toward a black hole, it ricochets off the event horizon and is hurled outward, rather than being tugged into the maw. Bright jets of material traveling at near-relativistic speeds are created. Although the black hole remains unseen, these powerful jets can be viewed from great distances.
The Event Horizon Telescope's image of a black hole in M87 (released in 2019) was an extraordinary effort, requiring two years of research even after the images were taken. That's because the collaboration of telescopes, which stretches across many observatories worldwide, produces an astounding amount of data that is too large to transfer by internet.
With time, researchers expect to image other black holes and build up a repository of what the objects look like. The next target is likely Sagittarius A*, which is the black hole in the center of our own Milky Way galaxy. Sagittarius A* is intriguing because it is quieter than expected, which may be due to magnetic fields smothering its activity, a 2019 study reported. Another study that year showed that a cool gas halo surrounds Sagittarius A*, which gives unprecedented insight into what the environment around a black hole looks like.
Shining light on binary black holes
In 2015, astronomers using the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) detected gravitational waves from merging stellar black holes.
"We have further confirmation of the existence of stellar-mass black holes that are larger than 20 solar masses these are objects we didn't know existed before LIGO detected them," David Shoemaker, the spokesperson for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration (LSC), said in a statement. LIGO's observations also provide insights about the direction a black hole spins. As two black holes spiral around one another, they can spin in the same direction or in the opposite direction.
There are two theories on how binary black holes form. The first suggests that the two black holes in a binary form at about the same time, from two stars that were born together and died explosively at about the same time. The companion stars would have had the same spin orientation as one another, so the two black holes left behind would as well.
Under the second model, black holes in a stellar cluster sink to the center of the cluster and pair up. These companions would have random spin orientations compared to one another. LIGO's observations of companion black holes with different spin orientations provide stronger evidence for this formation theory.
"We're starting to gather real statistics on binary black hole systems," said LIGO scientist Keita Kawabe of Caltech, who is based at the LIGO Hanford Observatory. "That's interesting because some models of black hole binary formation are somewhat favored over the others even now, and in the future, we can further narrow this down."
Weird facts about black holes
- If you fell into a black hole, theory has long suggested that gravity would stretch you out like spaghetti, though your death would come before you reached the singularity. But a 2012 study published in the journal Nature suggested that quantum effects would cause the event horizon to act much like a wall of fire, which would instantly burn you to death.
- Black holes don't suck. Suction is caused by pulling something into a vacuum, which the massive black hole definitely is not. Instead, objects fall into them just as they fall toward anything that exerts gravity, like the Earth.
- The first object considered to be a black hole is Cygnus X-1. Cygnus X-1 was the subject of a 1974 friendly wager between Stephen Hawking and fellow physicist Kip Thorne, with Hawking betting that the source was not a black hole. In 1990, Hawking conceded defeat.
- Miniature black holes may have formed immediately after the Big Bang. Rapidly expanding space may have squeezed some regions into tiny, dense black holes less massive than the sun.
- If a star passes too close to a black hole, the star can be torn apart.
- Astronomers estimate that the Milky Way has anywhere from 10 million to 1 billion stellar black holes, with masses roughly three times that of the sun.
- Black holes remain terrific fodder for science fiction books and movies. Check out the movie "Interstellar," which relied heavily on Thorne to incorporate science. Thorne's work with the movie's special effects team led to scientists' improved understanding of how distant stars might appear when seen near a fast-spinning black hole.
Additional resources:
This article was updated on July 11, 2019 by Space.com Contributor Elizabeth Howell.
by Lee Sandberg, Institute for Advanced Study
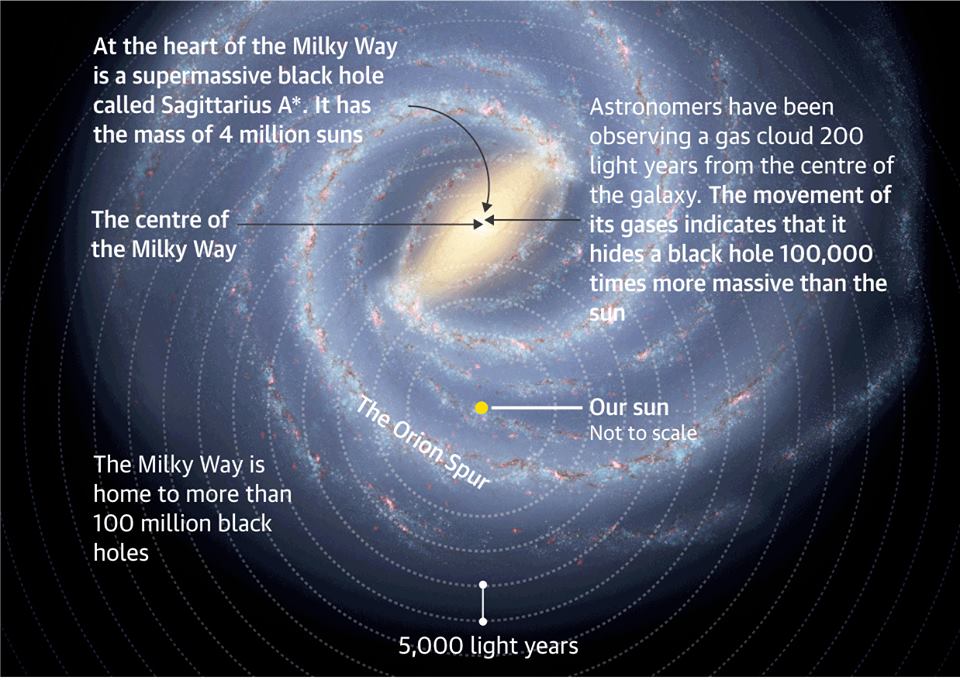
Our adress approaching: Black hole WARNING: Huge void 100,000 bigger than sun discovered in centre of Milky Way
05.09.2017

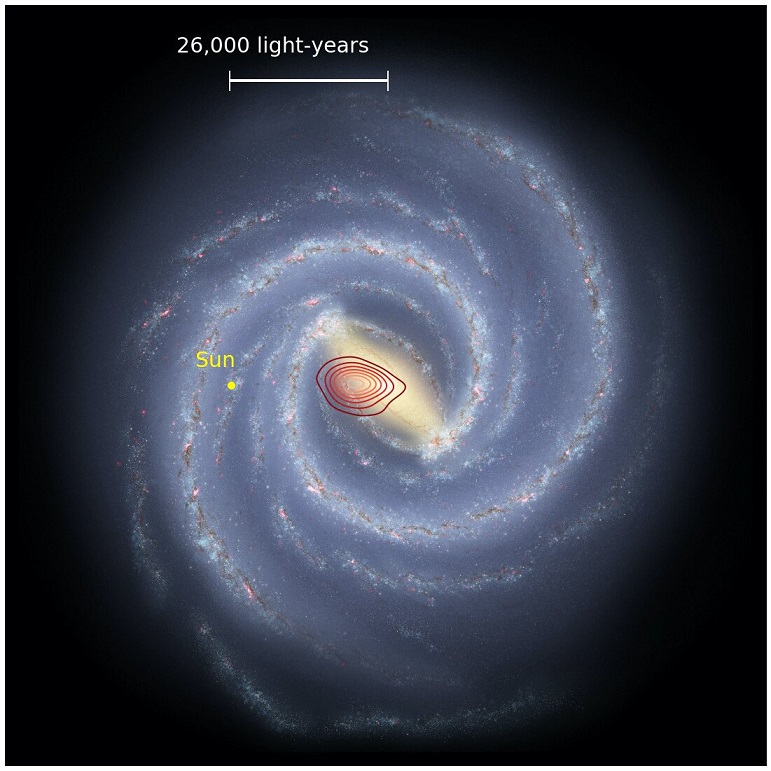
Our adress in the Universe
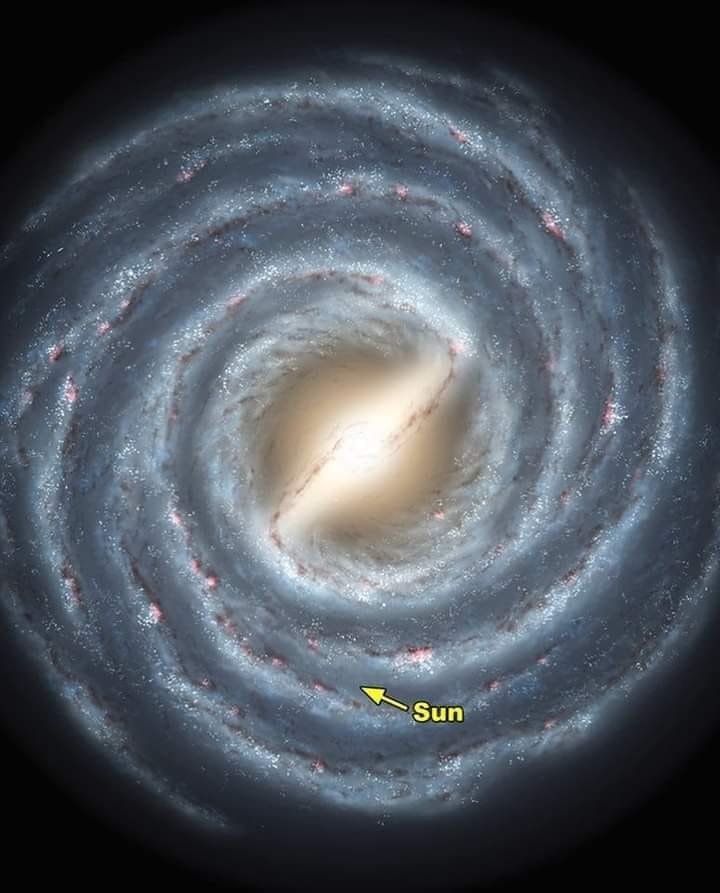

Earth is 2,000 light-years closer to a supermassive black hole at the center of our galaxy than first thought (2020)
- Japan's space agency has created a new map of the Milky Way
- The team has been collecting data for the past 15 years, revealing new insights
- Earth is only 25,800 light years away from a supermassive black hole
- A previous analysis from 1985 suggested it is 27,700 light years away
- The team also found Earth is moving 141 miles per second faster in orbit
Earth is closer to a supermassive black hole in the center of the Milky Way Galaxy that previously believed, new data reveals.
The National Astronomical Observatory of (NAOJ) found our planet is 2,000 light years closer to Sagittarius A.
The initial analysis projected Earth was initially 27,700 light years away, but it is only 25,800 light years away.
Along with being closer to the black hole, the new data shows Earth is orbiting the Galactic Center of the Milky Way 141 miles per second faster.
Although the findings may spark fear around the world, the results are due to new observation data that created a better model of our galaxy.

Milky Way galaxy map unveiled as astronomers reveal Earth is heading toward a black hole
By Charlotte Edwards , The Sun
December 4, 2020 | 4:33pm
_______________________________
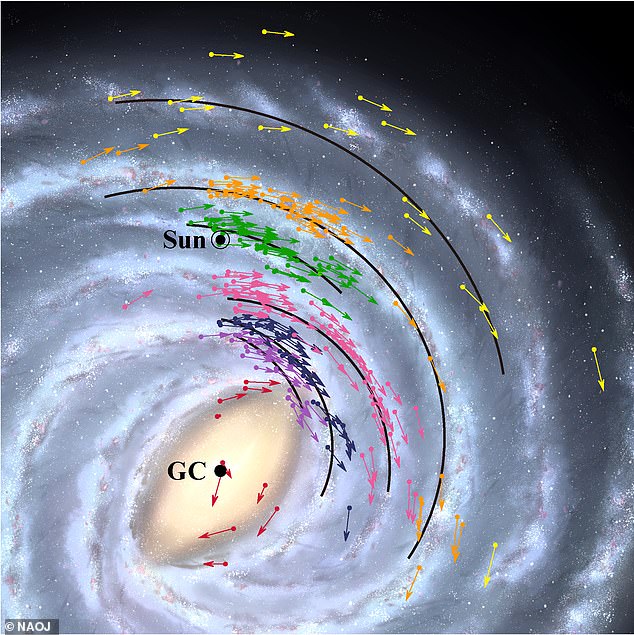
The stars are constantly moving across the sky. Known as proper motion, this motion is imperceptible to the unaided eye but is being measured with increasing precision by Gaia.
The most precise 3-D map of our Milky Way galaxy has been revealed by astronomers.
The 3-D Milky Way map was created using data from the European Space Agencys Gaia space probe thats been scanning the stars since 2013.
The hope is that the map will shed new light on the workings of the galaxy we call home.
It allows astronomers to measure acceleration and hopefully find out how much the universe has expanded since the dawn of time.
An impressive 1.8 billion stars feature on the map.
The ESA unveiled the map and uploaded a mesmerizing YouTube video of how stars move in the Milky Way.
The ESA said: The new Gaia data have allowed astronomers to trace the various populations of older and younger stars out towards the very edge of our galaxy the galactic anticenter.
Computer models predicted that the disc of the Milky Way will grow larger with time as new stars are born.
The new data allow us to see the relics of the 10 billion-year-old ancient disc and so determine its smaller extent compared to the Milky Ways current disc size.
The new 3D map was revealed just as another set of researchers claimed that Earth is closer to the black hole at the centre of our galaxy than previously thought.
The Milky Way has a huge black hole at the centre called Sagittarius A*.
Astronomers from the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan used their own data collected over 15 years to create another Milky Way map.
They estimated Earths position relative to the black hole at the centre of the Milky Way.
Back in 1985, Earth was thought to be 27,700 light years away from Sagittarius A*.
The new map puts it at 25,800 light-years away.
Scientists think Earth would be pulled apart inside a black hole but theres no need to panic just yet.
25,800 light-years away is a huge distance so Earth wont be anywhere near Sagittarius A* for a long time.
One light year works out at about six trillion miles.
Read More: NYP - Link
|
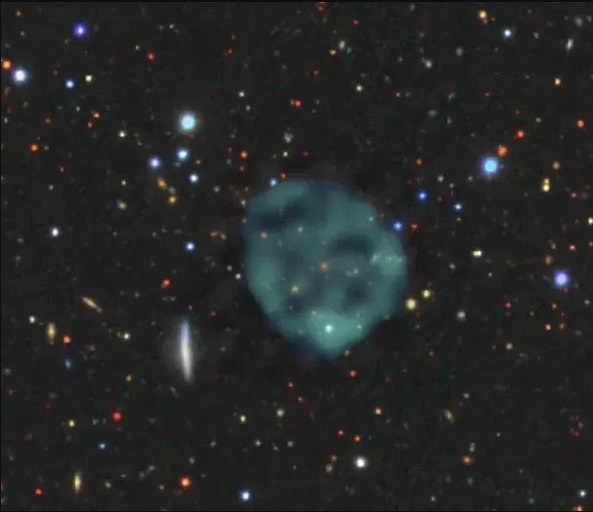

The ghostly circles are baffling scientists
Mysterious ghostly circles found looming in space and baffled scientists think they could be WORMHOLES
STRANGE ghostly circles spotted in space are baffling astronomers as they try to work out what they could be.
Scientist Anna Kapinska initially labelled one as "WTF?" after spotting the cosmic ring while browsing through radio astronomical data.
According to a report in The Conversation, Kapinska's colleague found another of the spooky shapes a few days later.
The researchers had been studying new photos from the the Evolutionary Map of the Universe (EMU) project.
They were taken by the new Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder (ASKAP) telescope.
The telescope is very powerful and sensitive to faint objects like the never-before-seen circles.
More mysterious blobs have been spotted since the initial two and they're now referred to as ORCs or "odd radio circles"
A software error of the telescope was ruled out after other radio telescopes confirmed the circles existed.
Supernova remnants have also been ruled out as a possible explanation.
A research paper called Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia runs through all the possibilities and concludes that the circles aren't anything we currently know about.

An artist's impression of a wormhole
They might be shockwaves from a huge explosion in a distant galaxy.
Two Russian scientists have even suggested that they could be the "throats" of wormholes.
In theory, wormholes could act like a magical gateway easily connecting two points in space and time with each other.
In science fiction, theyre often depicted as gateways that can let people step into another time or galaxy.
It's a bit of a confusing concept but a wormhole is essentially a theoretical method of folding space and time so two places in space can be connected together.
Fans of the movie Interstellar will be familiar with this concept.
It shows how astronauts on a spacecraft could travel through a wormhole with only a small amount of time passing for them but, for people back on Earth, hundreds or even thousands of years could have passed.
Its like drawing a line between two dots on a piece of paper, folding the paper over so the dots are touching and then forcing your pen through the page.
The hole created represents the wormhole.
Einstein theorised that space time can be tangled up so tightly that two points can share the same physical location.
Then all you need is a short wormhole between the two for instantaneous travel.
For now, the ghostly circles will need a lot more research before anyone can be more certain about what they are.
Read More: Link

Astronomers Discovered Cosmic Superhighways for Fast Travel Through the Solar System

Invisible structures generated by gravitational interactions in the Solar System have created a network of space superhighways, astronomers have discovered. These channels allow fast travel of objects in space and can be used for the purpose of human space exploration and research of comets and asteroids.
Applying analyzes to both observations and simulation data, a team of researchers led by Nataa Todorovic of the Belgrade Astronomical Observatory in Serbia noticed that these superhighways consisted of a series of connected arches in these invisible structures called cosmic collectors and each planet generates its own collectors, creating together what researchers call a true celestial autobahn.
This network can transport objects from Jupiter to Neptune in a matter of decades, rather than much longer periods of the order of hundreds of thousands to millions of years, which are usually calculated for the solar system.
Finding hidden structures in space is not always easy, but looking at the way things are moving can provide useful clues especially comets and asteroids.
Scientists say they have analyzed data from millions of orbits in the solar system to find their interaction. The benefits of such an analysis will be not only for the possible acceleration of space travel. Studying these processes can also help move and even control comets and asteroids that could be dangerous to Earth.


Stargates ?!

Time Traveler
Finally, some good news

|
Supermassive Black Holes Might Really Be 'Traversable' Wormholes, Astrophysicists Suggest
The wormholes we are considering are traversable wormholes, so theoretically spacecraft can travel through them, said the lead author of a new study.
Our universe is astonishingly colossal in scale, which can be a bummer if you are interested in traveling beyond our tiny corner of it. Wormholes, which are speculative bridges between distant locations in space, offer a potential cosmic shortcut to destinations that would be unreachable by other means.
Though wormholes are predicted by Einsteins theory of general relativity, their existence has yet to be empirically proven. Now, a team led by Mikhail Piotrovich, an astrophysicist at the Central Astronomical Observatory at Pulkovo in Saint Petersburg, Russia, has proposed a new way to search for the hypothetical tunnels: by investigating whether some supermassive black holes are actually entrances to wormholes.
Wormholes at the center of extremely bright galaxies might radiate with a distinctive spectrum that could be observationally detected, according to the teams forthcoming study in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Capturing this signature would not only provide evidence for the existence of wormholes, it would open up an entirely new avenue of potential spaceflightand even time travel.
A very interesting and unusual consequence of the existence of wormholes of this type is the fact that such wormholes are natural time machines, Piotrovich said in an email.
The wormholes we are considering are traversable wormholes, so theoretically spacecraft can travel through them, he added. But of course, it should be understood that we know very little about the internal structure of wormholes and moreover, we do not even know for sure whether they exist at all.
Some galaxies contain luminous cores called active galactic nuclei (AGN) that blast out massive twin jets, made of energized matter, that travel close to the speed of light. Scientists think AGN are fueled by tidal interactions between supermassive black holes and accretion disks that form from the gas, dust, and stars falling into them.
Piotrovich and his colleagues suggest that AGN are wormhole mouths rather than supermassive black holes. If this were true, it would mean that these galactic cores might be linked to each other across space and time, which could cause matter to fall in through both mouths of a linked AGN pair.
If two gulps of matter from either end of the mouths were to collide inside the wormhole throat, it would release a truly mind-boggling amount of energy and radiation. The wormhole would belch plasma out of both mouths that could reach temperatures of about 10 trillion°C. It would also emit high-energy gamma rays that could be distinguished from the light of the accretion disk.
Accretion disks of AGN dont emit gamma radiation, because their temperature is too low for that, said Piotrovich. Secondly, jets have a very specific radiation pattern, i.e. most of the gamma radiation is directed along the direction of the jet.
The notion that AGN might be wormholes dates back to 2005, but the new study is the first to propose this novel way of possibly detecting the fabled tunnels. Observatories such as NASAs Fermi gamma-ray space telescope might be able to pick up gamma rays from crashes inside wormholes, if they exist.
The nearest AGN are millions of light years from the Milky Way, so its not as if we could hop in a spaceship and visit one if we suspected it was a secret wormhole. Moreover, a wormhole that was initially put on the map due to violent plasma outbursts might not be a place any human would particularly want to enter, even in the most robust spaceship.
That said, finding evidence for wormholeseven from afarwould be an amazing breakthrough in our understanding of the universe, and would validate the futuristic dreams of science fiction enthusiasts around the world. |

An Astonishing New Theory Claims Past, Present And Future Exist Simultaneously
DEM (Time)

Ev GERDÛNa ji hev belave, ber bi PAŞVEKÊŞANÊ dîsan dikare were hev! Hingê HEMÎ TIŞT diçe destpêka xwe, divegere serî ..
--- Kê gotiye ku vegerana ber bi mêjû, vegerana ber bi paş ne mumkun e?
Bijkoja demê bizivirîne ber bi paş, hingê hertişt dîsan divegere serî. Dem kilîta guherînê ye, çawa ber bi pêş ve diçe, her wisa jî dikare ber bi paş ve here ..
Gava dem diguhere erd û ezmanê Gerdûn'ê jî bi xwe re digujerîne, çi gava diçe pêş, çi jî gava bizivire, vegere paş ..
Geşta li demê desthilateke a wisa mezin dike li ser maddeyê. Madde, bêdem BÊLIV e, hîç û pûç e. ''Can''ê maddeyê dem e.
|

Avarege temperatures in our solar system

A Galactic Year = 230 Million Earth Years
Den mänskliga historien började för bara 0,001 galaktiska år sedan ett ögonblick i den kosmiska tidsskalan. I det stora hela borde detta ödmjuka oss: vi är nästan ingenting, flyktiga gnistor i ett uråldrigt och likgiltigt universum.

Revolving planets
Aslında beni dünyadaki olaylar ilgilendirmiyor.
Beni en çok ilgilendiren, dünyanın dışındaki olaylardır. Bunun insanlığın kaderini ne kadar yakından etkilediğini bir düşünün. Evrenin sürekli hareket halinde olduğunu, her şeyin bir döngü içinde değiştiğini hayal edin. Peki, neden her şey hareket halindedir? Hareket yalnızca bir konum değişikliği değil, aynı zamanda bir dönüşümdür. Her hareketin bir sonu olduğu gibi, bu süreç içinde farklı evrelerden geçtiğini de unutmamak gerekir.
Dünyanın hareketliliği, yaşam koşullarımızın olmazsa olmazıdır. Dünya, kendi ekseni etrafında dönerken gece ve gündüzü oluşturur, Güneş etrafındaki hareketi ise mevsimleri meydana getirir. Eğer bu hareketlilik bir gün durursa, yaşamın sürdürülebilirliği imkansız hale gelir. Örneğin, Dünya'nın kendi ekseni etrafındaki dönüşü durursa, bir tarafı sürekli gündüz, diğer tarafı ise sürekli gece olurdu. Bu da aşırı sıcaklık farklarına, iklim krizlerine ve biyolojik dengenin bozulmasına yol açardı.
Ayrıca, evrendeki hareket yalnızca Dünya ile sınırlı değildir. Güneş Sistemi de Samanyolu Galaksisi içinde sürekli bir devinim halindedir. Gök cisimlerinin bu hareketi, gezegenlerin yörüngelerini korumasına yardımcı olur. Eğer bu düzen bozulursa, Dünyanın Güneşe olan mesafesi değişebilir, bu da gezegenimizin yaşanabilir olma özelliğini kaybetmesine neden olabilir. Kısacası, hareket sadece fiziksel bir olgu değil, varoluşumuzun temel şartıdır. G.C.

Kan Galaxerna synas såhär från jorden?
Denna bild (K.P.) togs 24 mars kl runt 22:00 i Stockholm
Scientists discover how to use time crystals to power superconductors

Physicists propose using time crystals to bring about a quantum computing revolution.
13 February, 2020
- A team of scientists proposes using time crystals to power topological superconductors.
- The approach could lead to error-free quantum computers.
- Time crystals appear to break laws of physics.
The concept of time crystals comes from the realm of counterintuitive mind-melding physics ideas that may actually turn out to have real-world applications. Now comes news that a paper proposes merging time crystals with topological superconductors for applications in error-free quantum computing, extremely precise timekeeping and more.
Time crystals were first proposed as hypothetical structures by the Nobel-Prize winning theoretical physicist Frank Wilczek and MIT physicists in 2012. The remarkable feature of time crystals is that they would would move without using energy. As such they would appear to break the fundamental physics law of time-translation symmetry. They would move while staying in their ground states, when they are at their lowest energy, appearing to be in a kind of perpetual motion. Wilczek offered mathematical proof that showed how atoms of crystallizing matter could regularly form repeating lattices in time, while not consuming or producing any energy.
Time crystals have since been experimentally created in various labs.
Now researchers at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and the Weizmann Institute in Israel found that theoretically you can create a system that combines time crystals with so-called topological superconductors.
The field of topology looks at the properties of objects that are unchangeable (or "invariant') despite deformations like stretching, twisting, or bending. In a topological insulator, the properties linked to the electron wave function would be considered topologically invariant.
As the scientists themselves explain, "Time crystals form when arbitrary physical states of a periodically driven system spontaneously break discrete time-translation symmetry." What the researchers noticed is that when they introduced "one-dimensional time-crystalline topological superconductors" they found a fascinating interaction where "time-translation symmetry breaking and topological physics intertwineyielding anomalous Floquet Majorana modes that are not possible in free-fermion systems."
Majorana fermions are particles that have their own anti-particles.
How to tie a quantum knot
"Physicists Gil Refael and Jason Alicea explain the unique properties of electrons constrained to a 2 Dimensional world, and how they can be used to make noise-proof Quantum Computers."
The research was led by Jason Alicea and Aaron Chew from CalTech, as well as David Mross from the Weizmann Institute in Israel.
While studying Majorana fermions, the team observed that it is possible to enhance topological superconductors by coupling them to magnetic degrees of freedom that could be controlled. "Then we realized that by turning those magnetic degrees of freedom into a time crystal, topological superconductivity responds in remarkable ways," shared Alicea.
One way the phenomen noticed by the scientists could be potentially exploited is to create more stable qubits - the bit of quantum information in quantum computing. The race to create qubits is at the threshold of bringing on a true quantum technology revolution, as writes Popular Mechanics.
"It's tempting to imagine generating some useful quantum operations by controlling the magnetic degrees of freedom that intertwine with the topological physics. Or perhaps certain noise channels can be suppressed by exploiting time crystals," said Alicea.
Check out their new paper in Physical Review Letters.
KÛANTÛM

Ev babet pêşî li çîrokên gelêrî li ber guha diket:
Ji hev pir dûr ketibûn. Li navbera wan heft çiya û heft behr hebû. Ji nişkê ve pencereyek li ber çavê wî vebû û hezkiriya wî têde xuya bû. Bi rojan li vê pencereyê hev didîtin û pêk ve diaxivîn û merem û hesreta dilê xwe ji hev re digotin.
Paşê, li destpêka salên 1900î bi çêkirina telefon û televîzyonê ev xewna li hiş û dilan bû rastî. Bi rastî jî pencereyek (tv) vebûbû û mirov têde diaxivîn.
Li demeke piştî hingê jî, êdî her heman tiştên ku li çîrokan dihatin gotin, bûbûn rastî; mirov li nav van tvan di heman demê de yekser di gel hev deng dikirin û diaxivîn.
Êdî guhestina deng û rengan (wêneyan/dirûban) li heman demê li du waran gengaz (mumkun) bû.
Baş e, gelo nuha hingava sêyemîn çi ye?
Hingava sêyemîn jî ev e ku li nav van tvan li heman demê GUHESTINA MADDEYÊ ji warek bo wareke din e. Jê re dibêjin Teleporting û bo cîbicîkirina vê azîneyê û bi karhanîna wê jî pir hindik maye.
Piştî wê jî, rêbaza Kûantûmê tê: Maddeyek, tiştek li heman demî li DU WARAN peyda dibe.
Nuha hişê mirovî vê digre. Êdî em wek berê ne bêhiş in ..
|
Is Our Universe One of Many? Here's How We Can Find Out

A multiverse consists of many separate and distinct universes, as depicted in this artist's concept. (Credit: Jaswe/Shutterstock)
The idea that we could live in a multiverse of infinite parallel universes is a real scientific theory. Here's what we know about it.
The existence of parallel universes may seem like something cooked up by science fiction writers, with little relevance to modern theoretical physics. But the idea that we live in a multiverse made up of an infinite number of parallel universes has long been considered a scientific possibility although it is still a matter of vigorous debate among physicists.
The race is now on to find a way to test the theory, including searching the sky for signs of collisions with other universes. It is important to keep in mind that the multiverse view is not actually a theory, it is rather a consequence of our current understanding of theoretical physics. This distinction is crucial. We have not waved our hands and said: Let there be a multiverse. Instead the idea that the universe is perhaps one of infinitely many is derived from current theories like quantum mechanics and string theory.
Quantum Implications
You may have heard the thought experiment of Schrödingers cat, a spooky animal who lives in a closed box. The act of opening the box allows us to follow one of the possible future histories of our cat, including one in which it is both dead and alive. The reason this seems so impossible is simply because our human intuition is not familiar with it. But it is entirely possible according to the strange rules of quantum mechanics. The reason that this can happen is that the space of possibilities in quantum mechanics is huge.
Mathematically, a quantum mechanical state is a sum (or superposition) of all possible states. In the case of the Schrödingers cat, the cat is the superposition of dead and alive states. But how do we interpret this to make any practical sense at all? One popular way is to think of all these possibilities as bookkeeping devices so that the only objectively true cat state is the one we observe. However, one can just as well choose to accept that all these possibilities are true, and that they exist in different universes of a multiverse.
The String Landscape
String theory is one of our most, if not the most, promising avenue to be able to unify quantum mechanics and gravity. This is notoriously hard because gravitational force is so difficult to describe on small scales like those of atoms and subatomic particles which is the science of quantum mechanics. But string theory, which states that all fundamental particles are made up of one-dimensional strings, can describe all known forces of nature at once: gravity, electromagnetism and the nuclear forces. However, for string theory to work mathematically, it requires at least ten physical dimensions.
Since we can only observe four dimensions: height, width, depth (all spatial) and time (temporal), the extra dimensions of string theory must therefore be hidden somehow if it is to be correct. To be able to use the theory to explain the physical phenomena we see, these extra dimensions have to be compactified by being curled up in such a way that they are too small to be seen. Perhaps for each point in our large four dimensions, there exists six extra indistinguishable directions?
A problem, or some would say, a feature, of string theory is that there are many ways of doing this compactification 10^500 possibilities is one number usually touted about. Each of these compactifications will result in a universe with different physical laws such as different masses of electrons and different constants of gravity.
However there are also vigorous objections to the methodology of compactification, so the issue is not quite settled. But given this, the obvious question is: which of these landscape of possibilities do we live in? String theory itself does not provide a mechanism to predict that, which makes it useless as we cant test it. But fortunately, an idea from our study of early universe cosmology has turned this bug into a feature.
The cosmic microwave background. Scoured for gravitational waves and signs of collisions with other universes. (Credit: NASA/WMAP Science Team)
The Early Universe
During the very early universe, the universe underwent a period of accelerated expansion called inflation. Inflation was invoked originally to explain why the current observational universe is almost uniform in temperature. However, the theory also predicted a spectrum of temperature fluctuations around this equilibrium which was later confirmed by several spacecraft such as Cosmic Background Explorer, Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe and the PLANCK spacecraft.
While the exact details of the theory are still being hotly debated, inflation is widely accepted by physicists. However, a consequence of this theory is that there must be other parts of the universe that are still accelerating. However, due to the quantum fluctuations of space-time, some parts of the universe never actually reach the end state of inflation.
This means that the universe is, at least according to our current understanding, eternally inflating. Some parts can therefore end up becoming other universes, which could become other universes, etc. This mechanism generates a infinite number of universes. By combining this scenario with string theory, there is a possibility that each of these universes possesses a different compactification of the extra dimensions and hence has different physical laws.
Testing the Theory
The universes predicted by string theory and inflation live in the same physical space (unlike the many universes of quantum mechanics which live in a mathematical space), meaning they can overlap or collide. Indeed, they inevitably must collide, leaving possible signatures in the cosmic sky which we can try to search for. The exact details of the signatures depends intimately on the models ranging from cold or hot spots in the cosmic microwave background to anomalous voids in the distribution of galaxies.
Nevertheless, since collisions with other universes must occur in a particular direction, a general expectation is that any signatures will break the uniformity of our observable universe. These signatures are actively being pursued by scientists. Some are looking for it directly through imprints in the cosmic microwave background, the afterglow of the Big Bang. However, no such signatures are yet to be seen.
Others are looking for indirect support such as gravitational waves, which are ripples in space-time as massive objects pass through. Such waves could directly prove the existence of inflation, which ultimately strengthens the support for the multiverse theory. Whether we will ever be able to prove their existence is hard to predict. But given the massive implications of such a finding it should definitely be worth the search.
This article was originally published on The Conversation.

Is the universe controlled by gigantic structures?

Image source: Mike Rosecope/procy/Shutterstock/Big Think
The idea that celestial objects exist within utterly immense cosmic structures is becoming inescapable.
18 November, 2019
- New findings in astronomy are making some astronomers doubt our basic model of the universe.
- Alignments of celestial objects suggest that they may be embedded in large-scale structures.
- Galaxies too far apart to be influencing each other are moving through space together.
Solidity is a function of magnification. We know that anything we experience as solid is actually a structure of atoms packed closely enough that to our eyes they appear to be a single solid thing. If we were small enough, we'd see the spaces between them; if we were even smaller, those spaces might seem vast. Likewise, in 1989 Margaret Geller and John Huchra, analyzing redraft survey data, discovered the immense "Great Wall," a "sheet" formed from galaxies many light years apart. That first large-scale structure is 500 million light-years long, 200 million light years wide, and with a thickness of 15 million light years.
Other gigantic large-scale structures been discovered since sheets, filaments, and knots, with bubble-like voids intersperse among them. They appear to be connected by clouds and filaments of hydrogen gas and dark matter. Though the bodies that comprise the structures are not gravitationally bound to each other the distances between them are too great evidence is piling up that they are linked by something.
Recent observations indicate that galaxies far, far apart are somehow synchronously moving. Something appears to be binding large-scale structures, many light years apart, together after all. Is the currently accepted view of the universe as various clumps of material simply expanding outward from the Big Bang and gravitationally pulling on each other wrong?
Large-scale structures
The existence and mechanics of large-scale structures are a tantalizing puzzle with obviously major implications for our understanding of the universe. As Noam Libeskind, of the Leibniz-Institut for Astrophysics (AIP) in Germany tells VICE, "That's actually the reason why everybody is always studying these large-scale structures. It's a way of probing and constraining the laws of gravity and the nature of matter, dark matter, dark energy, and the universe."
The identification and study of large-scale structures is a product of analyzing and modeling simulations of redshift survey for specific regions of the sky that visually reveal these immense structures.

The large-scale structures revealed in one segment of sky
Image source: National Center for Supercomputer Applications by Andrey Kravtsov (The University of Chicago) and Anatoly Klypin (New Mexico State University).
Visualizations by Andrey Kravtsov.
Billions of light years apart
Several pieces of research are causing interest in these large-scale structures to heat up. The most mind-blowingly distant synchronized motion was reported in 2014, when the rotation axes of 19 super-massive black holes at the centers of quasars out of 100 quasars studied were found to be in alignment, billions of light years apart. According to the study's lead author, astronomer Damien Hutsemékers of the University of Liège in Belgium, "Galaxy spin axes are known to align with large-scale structures such as cosmic filaments but this occurs on smaller scales. However, there is currently no explanation why the axes of quasars are aligned with the axis of the large group in which they are embedded."
The first word of the research paper's title, "Spooky Alignment of Quasars Across Billions of Light-years," invokes cosmic-scale quantum entanglement as a possible explanation.
Galaxies of a feather
Astronomer Joon Hyeop Lee of the Korea Astronomy and Space Institute is the lead author of "Mysterious Coherence in Several-megaparsec Scales between Galaxy Rotation and Neighbor Motion," published in October of this year in Astrophysical Journal. Comparing data from two catalogs of redshift survey data the Calar Alto Legacy Integral Field Area (CALIFA) and NASA-Sloan Atlas (NSA) catalogs the researchers' analysis of 445 galaxies revealed, surprisingly, that galaxies six meparsecs, or 20 million light years, apart were moving in the same way. Those observed, for example, a galaxy moving toward the Earth was mirrored by other distant galaxies moving in the same direction.
"This discovery is quite new and unexpected," according to Lee, "I have never seen any previous report of observations or any prediction from numerical simulations, exactly related to this phenomenon."
Since the galaxies are too distant for their gravitational fields to be influencing each other, Lee poses another explanation: That the linked galaxies are both embedded within the same, large-scale structure.

Image source: sripfoto/Shutterstock/Big Think
Flatness
Another puzzle suggesting the influence of large-scale structures has become clear over recent years. It's been observed that galaxies surrounding our own Milky Way are weirdly arranged in a single, flat plane. Big-Bang thinking would suggest that they should be circling us at all different sorts of angles. Obviously, for adherents of that way of viewing the galaxy known as the ?CDM model this at the very least a troubling anomaly.
The hope that it was an anomaly weakened with the discovery of the same thing occurring around the Andromeda galaxy, and then again around Centaurus A in 2015. By the time "A whirling plane of satellite galaxies around Centaurus A challenges cold dark matter cosmology" was published in 2018, the phenomenon was starting to seem quite common, and possibly universal. The idea that the satellite galaxies might part of a large-scale structure had become even worthier of serious consideration.
Just the beginning
As more astronomers embrace the notion of large-scale structures and related research accelerates, we can only hope that these perplexingly oddball movements and associations are eventually made clear. Certainly, imagining a vast arrangement of utterly gigantic structures in which galaxies are embedded paints a very different picture of the universe, and one that makes one wonder if these structures are themselves embedded in something even larger. In this mid-boggling case, we are indeed small enough to see only the space between objects in this case galaxies. We've been no more aware of them than whatever it is that may be living between our own atoms.
İSLAMO-FAŞİST TURK-ARAB & FARS REAKSİYONERİZMİ ve İNSANLIĞIN AYDINLIKLI GELECEĞİ

DUNYA DEREWÎN E.

"We are the universe and the universe is in us"
"Everything you see is an illusion. We ourselves are a projection from a reality whose source we do not know. But we are beginning to sense that it is possible through quantum physics and dualism. Everything is in pairs. twice. Everything happens in a double sense. Time and space here in the earthly illusory life is only constant and fixed here but not at the other end. Here you can't have control over time and space, but there it's the opposite. Time and space can be controlled."

New hypothesis argues the universe simulates itself into existence
A physics paper proposes neither you nor the world around you are real.

Tetrahedrons representing the quasicrystalline spin network (QSN), the fundamental substructure of spacetime, according to emergence theory.
Credit: Quantum Gravity Institute
- A new hypothesis says the universe self-simulates itself in a "strange loop".
- A paper from the Quantum Gravity Research institute proposes there is an underlying panconsciousness.
- The work looks to unify insight from quantum mechanics with a non-materialistic perspective.
How real are you? What if everything you are, everything you know, all the people in your life as well as all the events were not physically there but just a very elaborate simulation? Philosopher Nick Bostrom famously considered this in his seminal paper "Are you living in a computer simulation?," where he proposed that all of our existence may be just a product of very sophisticated computer simulations ran by advanced beings whose real nature we may never be able to know. Now a new theory has come along that takes it a step further what if there are no advanced beings either and everything in "reality" is a self-simulation that generates itself from pure thought?
The physical universe is a "strange loop" says the new paper titled "The Self-Simulation Hypothesis Interpretation of Quantum Mechanics" from the team at the Quantum Gravity Research, a Los Angeles-based theoretical physics institute founded by the scientist and entrepreneur Klee Irwin. They take Bostrom's simulation hypothesis, which maintains that all of reality is an extremely detailed computer program, and ask, rather than relying on advanced lifeforms to create the amazing technology necessary to compose everything within our world, isn't it more efficient to propose that the universe itself is a "mental self-simulation"? They tie this idea to quantum mechanics, seeing the universe as one of many possible quantum gravity models.
One important aspect that differentiates this view relates to the fact that Bostrom's original hypothesis is materialistic, seeing the universe as inherently physical. To Bostrom, we could simply be part of an ancestor simulation, engineered by posthumans. Even the process of evolution itself could just be a mechanism by which the future beings are testing countless processes, purposefully moving humans through levels of biological and technological growth. In this way they also generate the supposed information or history of our world. Ultimately, we wouldn't know the difference.
But where does the physical reality that would generate the simulations comes from, wonder the researchers? Their hypothesis takes a non-materialistic approach, saying that everything is information expressed as thought. As such, the universe "self-actualizes" itself into existence, relying on underlying algorithms and a rule they call "the principle of efficient language."
Vıdeo:
What Is Reality? [Official Film]

The Big Bang Theory
DEM JIYAN GERDÛN
Dem bi tevgerê re heye. Heger liv û tevger nebe, dem jî nîn e. Gava em demê têbigehin, hingê em hemû nihênî û serveşartiyên Gerdûn û jiyanê jî têdigehin. Gerdûn heye loma tevger heye. Tevger heye, loma Gerdûn heye. Yek bê yekî nabe. Goran Candan
Did A Black Hole Give Birth To Our Universe?
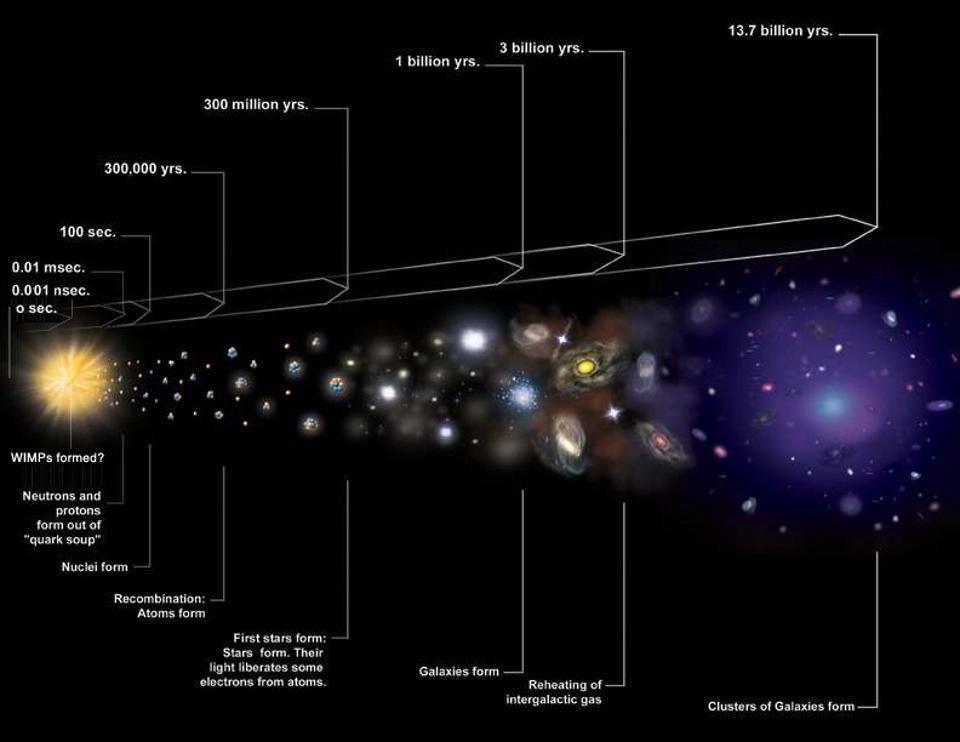
When a black hole forms, the mass and energy collapses down to a singularity. Similarly, continuing ... [+]
NASA / CXC / M. WEISS
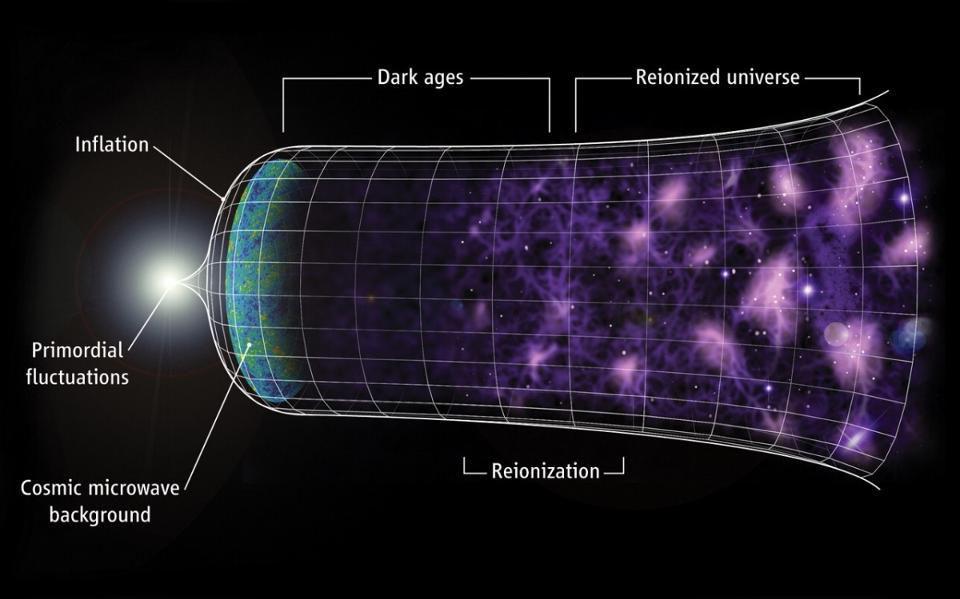
During the earliest stages of the Universe, an inflationary period set up and gave rise to the hot ... [+]
C. FAUCHER-GIGUÈRE, A. LIDZ, AND L. HERNQUIST, SCIENCE 319, 5859 (47)
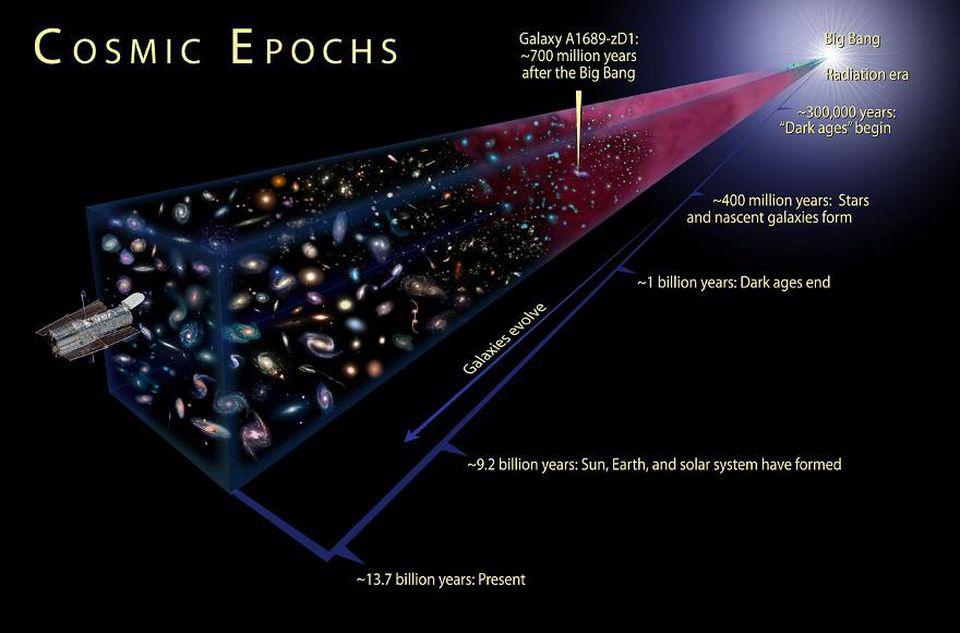
Nearby, the stars and galaxies we see look very much like our own. But as we look farther away, we ... [+]
NASA, ESA, AND A. FEILD (STSCI)
NEZANIYA ME asteng e li ber têgehîştina me ya nihêniyên jiyana li Gerdûnê.
GELO em ê kengê girêka vê nihêniyê verisînin nihêniyên jiyana Gerdûnê nas bikin?
When a black hole is formed, one speculative but spectacular idea is that it gives birth to a new, ... [+]
NICOLLE RAGER FULLER
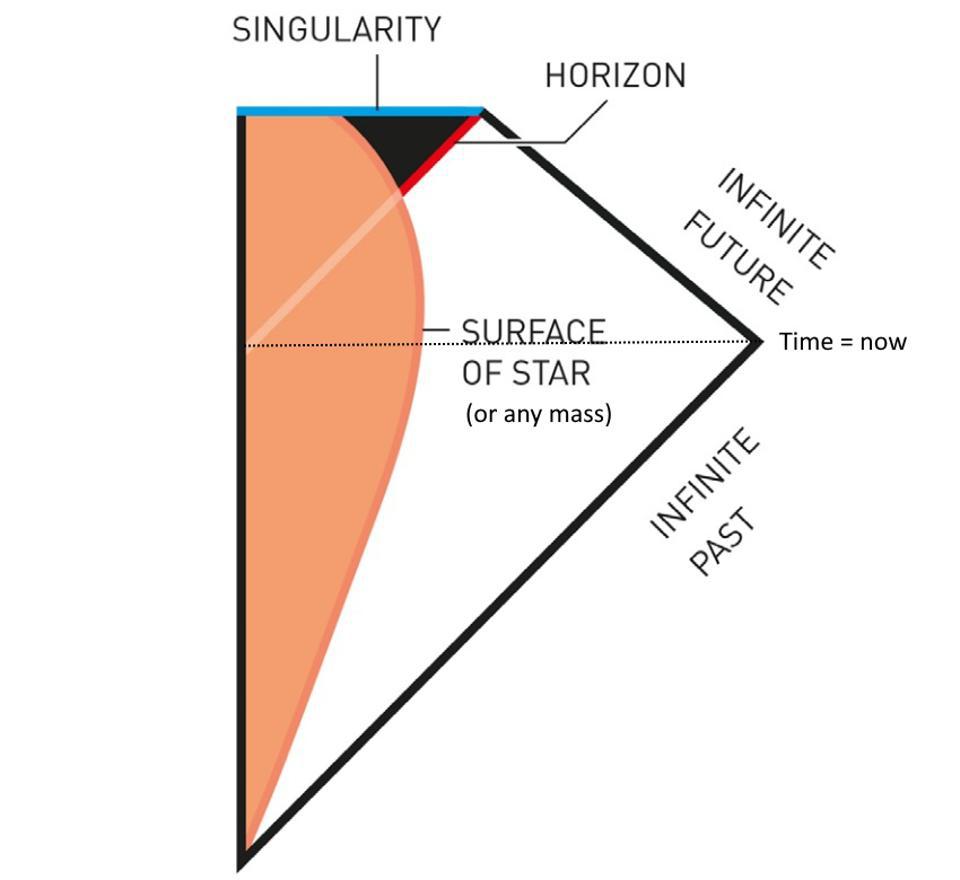
When matter collapses, it can inevitably form a black hole. Penrose was the first to work out the ... [+]
JOHAN JARNESTAD/THE ROYAL SWEDISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
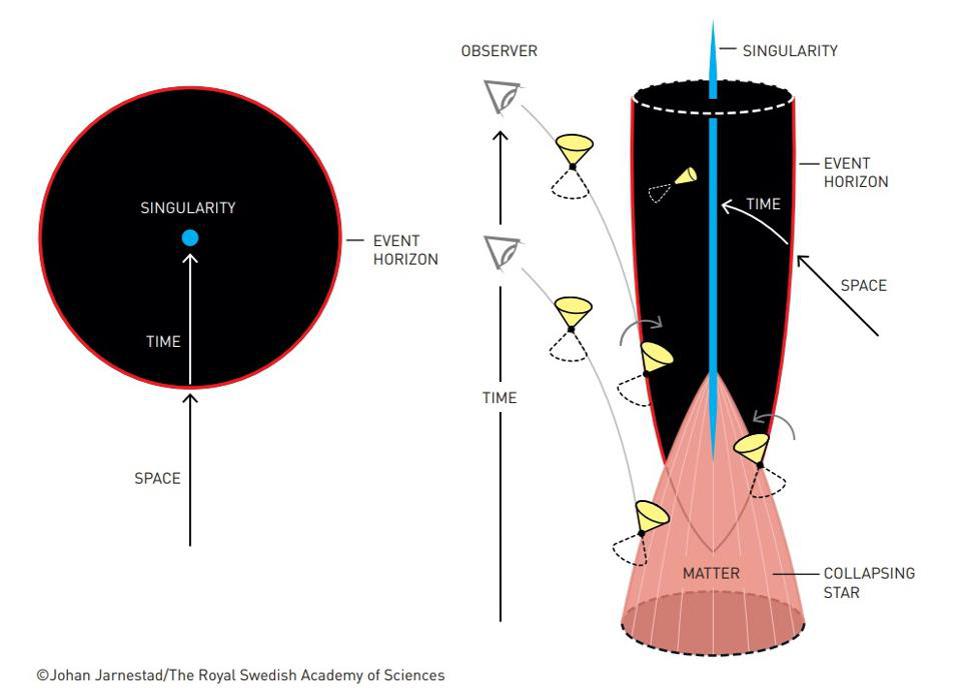
When matter collapses, it can inevitably form a black hole. Penrose was the first to work out the ... [+]
JOHAN JARNESTAD/THE ROYAL SWEDISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Pictures: Ethan Siegel
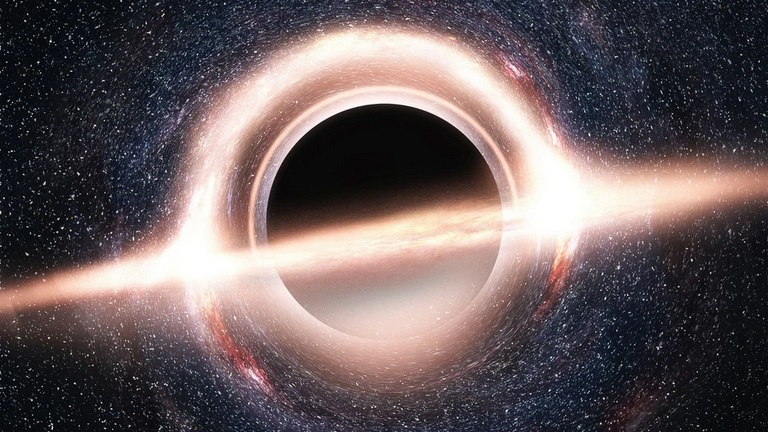

Image keanu 2 via Gety
Astronomers agree: Universe is nearly 14 billion years old

Credit: CC0 Public Domain
by Linda B. Glaser, Cornell University
From an observatory high above Chile's Atacama Desert, astronomers have taken a new look at the oldest light in the universe.
Their observations, plus a bit of cosmic geometry, suggest that the universe is 13.77 billion years oldgive or take 40 million years. A Cornell University researcher co-authored one of two papers about the findings, which add a fresh twist to an ongoing debate in the astrophysics community.
The new estimate, using data gathered at the National Science Foundation's Atacama Cosmology Telescope (ACT), matches the one provided by the standard model of the universe, as well as measurements of the same light made by the European Space Agency's Planck satellite, which measured remnants of the Big Bang from 2009 to '13.
The research was published in the Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics.
The lead author of "The Atacama Cosmology Telescope: A Measurement of the Cosmic Microwave Background Power Spectra at 98 and 150 GHz" is Steve Choi, NSF Astronomy and Astrophysics Postdoctoral Fellow at the Cornell Center for Astrophysics and Planetary Science, in the College of Arts and Sciences.
In 2019, a research team measuring the movements of galaxies calculated that the universe is hundreds of millions of years younger than the Planck team predicted. That discrepancy suggested a new model for the universe might be needed and sparked concerns that one of the sets of measurements might be incorrect.
"Now we've come up with an answer where Planck and ACT agree," said Simone Aiola, a researcher at the Flatiron Institute's Center for Computational Astrophysics and first author of one of two papers. "It speaks to the fact that these difficult measurements are reliable."
Mysterious radio signals from deep space detected
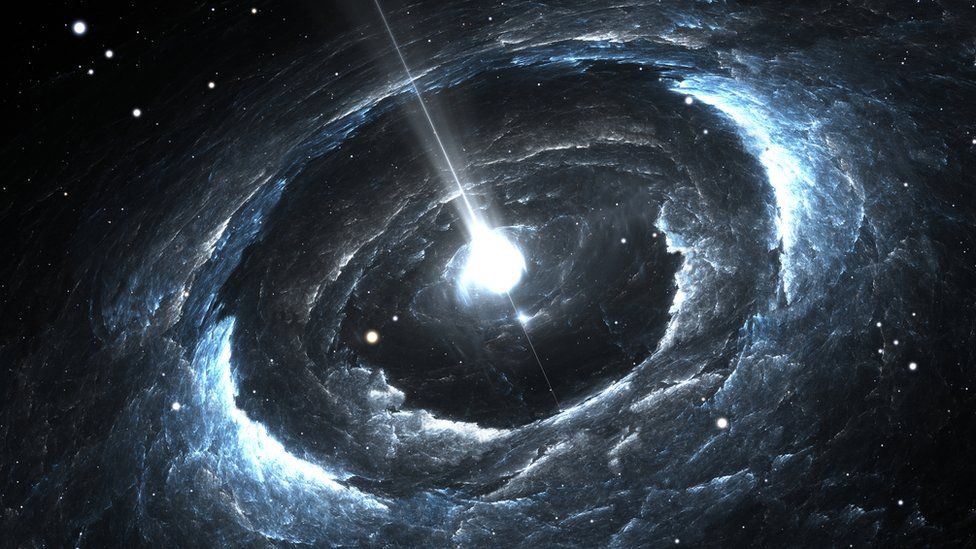

Artwork: A highly magnetised rotating neutron star. Astronomers say one of these could be a source of the signals
By Helen Briggs
BBC News
9 January 2019
Astronomers have revealed details of mysterious signals emanating from a distant galaxy, picked up by a telescope in Canada.
The precise nature and origin of the blasts of radio waves is unknown.
Among the 13 fast radio bursts, known as FRBs, was a very unusual repeating signal, coming from the same source about 1.5 billion light years away.
Such an event has only been reported once before, by a different telescope.
"Knowing that there is another suggests that there could be more out there," said Ingrid Stairs, an astrophysicist from the University of British Columbia (UBC).
"And with more repeaters and more sources available for study, we may be able to understand these cosmic puzzles - where they're from and what causes them."
The CHIME observatory, located in British Columbia's Okanagan Valley, consists of four 100-metre-long, semi-cylindrical antennas, which scan the entire northern sky each day.
The telescope only got up and running last year, detecting 13 of the radio bursts almost immediately, including the repeater.
Read More Here
How Can a Star Be Older Than the Universe?

This Digitized Sky Survey image shows the oldest star with a well-determined age in our galaxy. Called the Methuselah star, HD 140283 is 190.1 light-years away.
Astronomers refined the star's age to about 14.3 billion years (which is older than the universe), plus or minus 800 million years. Image released March 7,
For more than 100 years, astronomers have been observing a curious star located some 190 light years away from Earth in the constellation Libra. It rapidly journeys across the sky at 800,000 mph (1.3 million kilometers per hour). But more interesting than that, HD 140283 or Methuselah as it's commonly known is also one of the universe's oldest known stars.
In 2000, scientists sought to date the star using observations via the European Space Agency's (ESA) Hipparcos satellite, which estimated an age of 16 billion years old. Such a figure was rather mind-blowing and also pretty baffling. As astronomer Howard Bond of Pennsylvania State University pointed out, the age of the universe determined from observations of the cosmic microwave background is 13.8 billion years old. "It was a serious discrepancy," he said.
Related: The Methuselah Star: Oldest Known Star Revealed (Gallery)
Taken at face value, the star's predicted age raised a major problem. How could a star be older than the universe? Or, conversely, how could the universe be younger? It was certainly clear that Methuselah named in reference to a biblical patriarch who is said to have died aged 969, making him the longest lived of all the figures in the Bible was old, since the metal-poor subgiant is predominantly made of hydrogen and helium and contains very little iron. It's composition meant the star must have come into being before iron became commonplace.
But more than two billion years older than its environment? Surely that is just not possible.
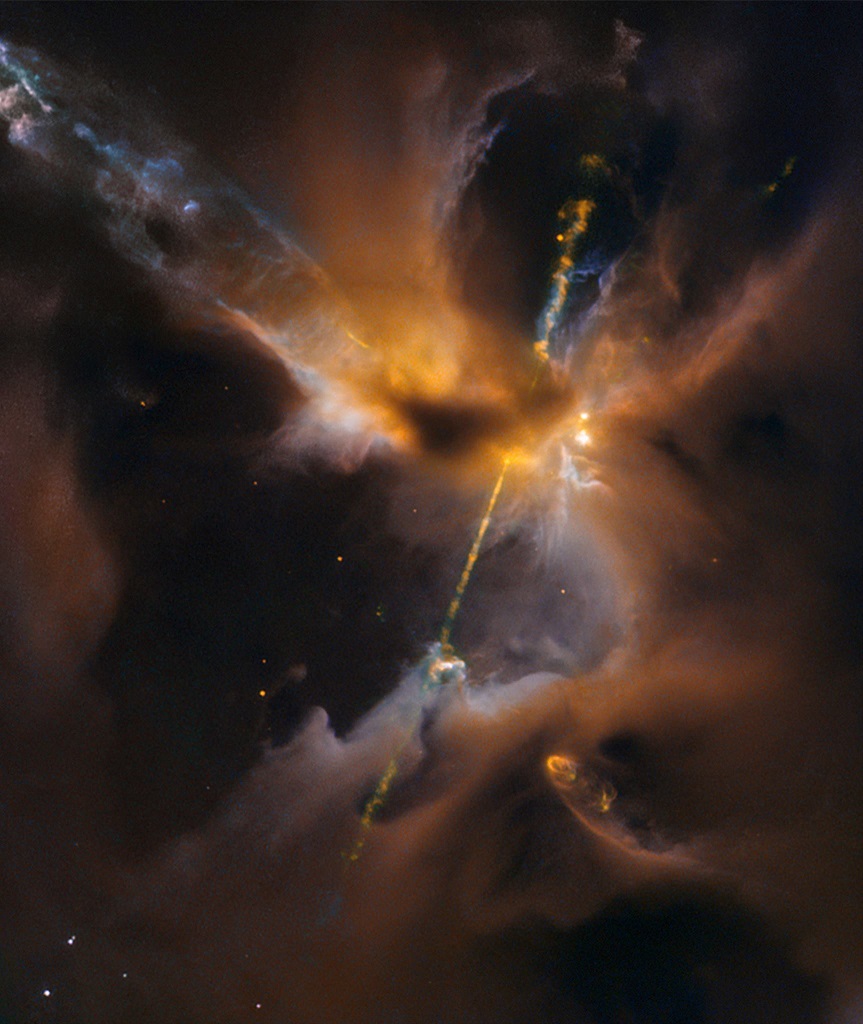


Our Hubble Space telescope found what looks like a cosmic, double-bladed lightsaber just in time for the release of #StarWars.
This celestial lightsaber does not lie in a galaxy far, far away, but rather inside our home galaxy, the Milky Way.
Learn more: http://go.nasa.gov/1PbjYCD
The cosmos is admirable, wonderful and also very secretive to us.
These stars in the night sky's black infinities, seems to be as mysterious as distant to us.
However, like imagining how they could be, we have the tools today showing us how they roughly look like. As I believed when I was a child
we people will one day go to them and touch them too and see how exactly they are. I am absolutely convinced of it. G.C.
MILKY WAY

Another project using an early release of the data includes a map showing the movement of the stars in our immediate stellar neighbourhood - that is within about 300 light years of the Earth. They are shown as streaks of white across the galaxy plane
These scientists have a new theory about the universe.
Here's what you need to know
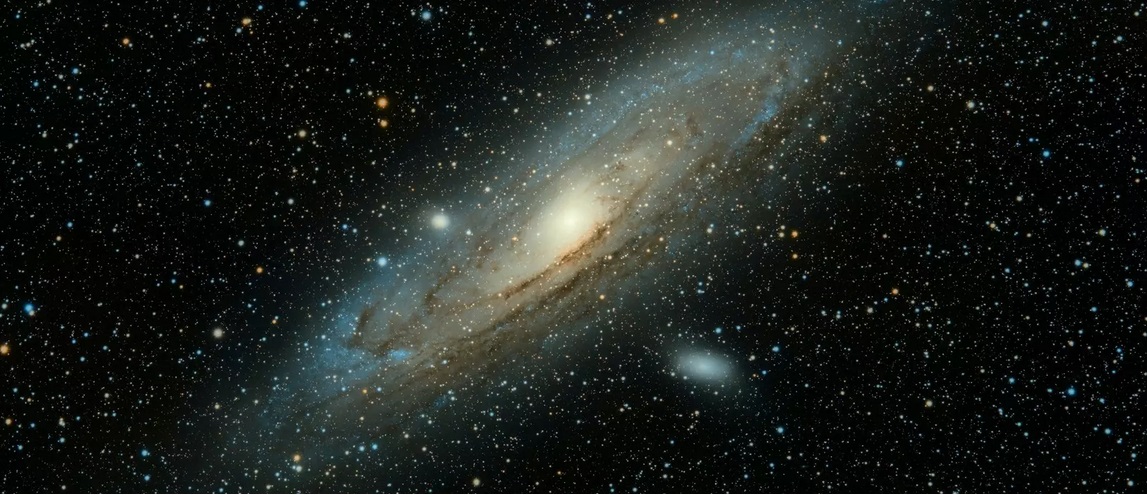

One less mystery in the universe? Image: Unsplash/Guillermo Ferla
- Matter makes up everything, but what makes up matter?
- Two physicists have a new theory
- Central to the new theory is the idea that fragments of energy, not waves or particles, may be the fundamental building blocks of the universe.
Matter is what makes up the universe, but what makes up matter? This question has long been tricky for those who think about it especially for the physicists. Reflecting recent trends in physics, my colleague Jeffrey Eischen and I have described an updated way to think about matter. We propose that matter is not made of particles or waves, as was long thought, but more fundamentally that matter is made of fragments of energy.
The ancient Greeks conceived of five building blocks of matter from bottom to top: earth, water, air, fire and aether. Aether was the matter that filled the heavens and explained the rotation of the stars, as observed from the Earth vantage point. These were the first most basic elements from which one could build up a world. Their conceptions of the physical elements did not change dramatically for nearly 2,000 years.
Then, about 300 years ago, Sir Isaac Newton introduced the idea that all matter exists at points called particles. One hundred fifty years after that, James Clerk Maxwell introduced the electromagnetic wave the underlying and often invisible form of magnetism, electricity and light. The particle served as the building block for mechanics and the wave for electromagnetism and the public settled on the particle and the wave as the two building blocks of matter. Together, the particles and waves became the building blocks of all kinds of matter.
This was a vast improvement over the ancient Greeks five elements, but was still flawed. In a famous series of experiments, known as the double-slit experiments, light sometimes acts like a particle and at other times acts like a wave. And while the theories and math of waves and particles allow scientists to make incredibly accurate predictions about the universe, the rules break down at the largest and tiniest scales.
Einstein proposed a remedy in his theory of general relativity. Using the mathematical tools available to him at the time, Einstein was able to better explain certain physical phenomena and also resolve a longstanding paradox relating to inertia and gravity. But instead of improving on particles or waves, he eliminated them as he proposed the warping of space and time.
Using newer mathematical tools, my colleague and I have demonstrated a new theory that may accurately describe the universe. Instead of basing the theory on the warping of space and time, we considered that there could be a building block that is more fundamental than the particle and the wave. Scientists understand that particles and waves are existential opposites: A particle is a source of matter that exists at a single point, and waves exist everywhere except at the points that create them. My colleague and I thought it made logical sense for there to be an underlying connection between them.
Flow and fragments of energy
Our theory begins with a new fundamental idea that energy always flows through regions of space and time.
Think of energy as made up of lines that fill up a region of space and time, flowing into and out of that region, never beginning, never ending and never crossing one another.
Working from the idea of a universe of flowing energy lines, we looked for a single building block for the flowing energy. If we could find and define such a thing, we hoped we could use it to accurately make predictions about the universe at the largest and tiniest scales.
There were many building blocks to choose from mathematically, but we sought one that had the features of both the particle and wave concentrated like the particle but also spread out over space and time like the wave. The answer was a building block that looks like a concentration of energy kind of like a star having energy that is highest at the center and that gets smaller farther away from the center.
Much to our surprise, we discovered that there were only a limited number of ways to describe a concentration of energy that flows. Of those, we found just one that works in accordance with our mathematical definition of flow. We named it a fragment of energy. For the math and physics aficionados, it is defined as A = -?/r where ? is intensity and r is the distance function.
Using the fragment of energy as a building block of matter, we then constructed the math necessary to solve physics problems. The final step was to test it out.
Back to Einstein, adding universality
These problems were at the two extremes of the size spectrum. Neither wave nor particle theories of matter could solve them, but general relativity did. The theory of general relativity warped space and time in such way as to cause the trajectory of Mercury to shift and light to bend in precisely the amounts seen in astronomical observations.
If our new theory was to have a chance at replacing the particle and the wave with the presumably more fundamental fragment, we would have to be able to solve these problems with our theory, too.
For the precession-of-Mercury problem, we modeled the Sun as an enormous stationary fragment of energy and Mercury as a smaller but still enormous slow-moving fragment of energy. For the bending-of-light problem, the Sun was modeled the same way, but the photon was modeled as a minuscule fragment of energy moving at the speed of light. In both problems, we calculated the trajectories of the moving fragments and got the same answers as those predicted by the theory of general relativity. We were stunned.
Our initial work demonstrated how a new building block is capable of accurately modeling bodies from the enormous to the minuscule. Where particles and waves break down, the fragment of energy building block held strong. The fragment could be a single potentially universal building block from which to model reality mathematically and update the way people think about the building blocks of the universe.
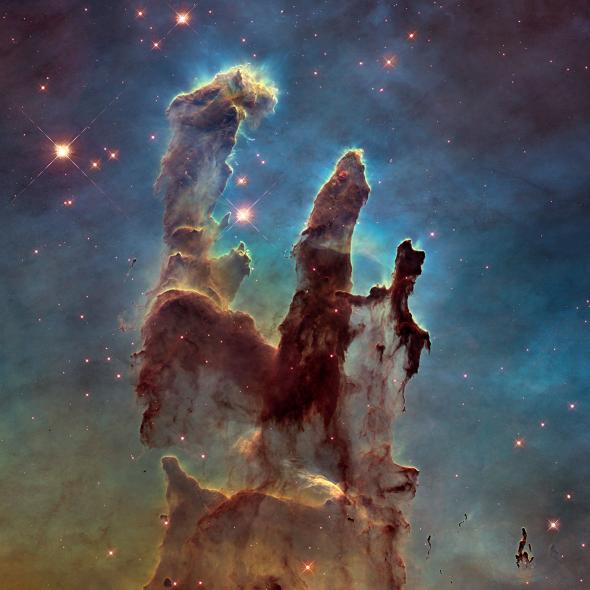

Dûrbînê (teleskop) Gerdûnî Spîtzer
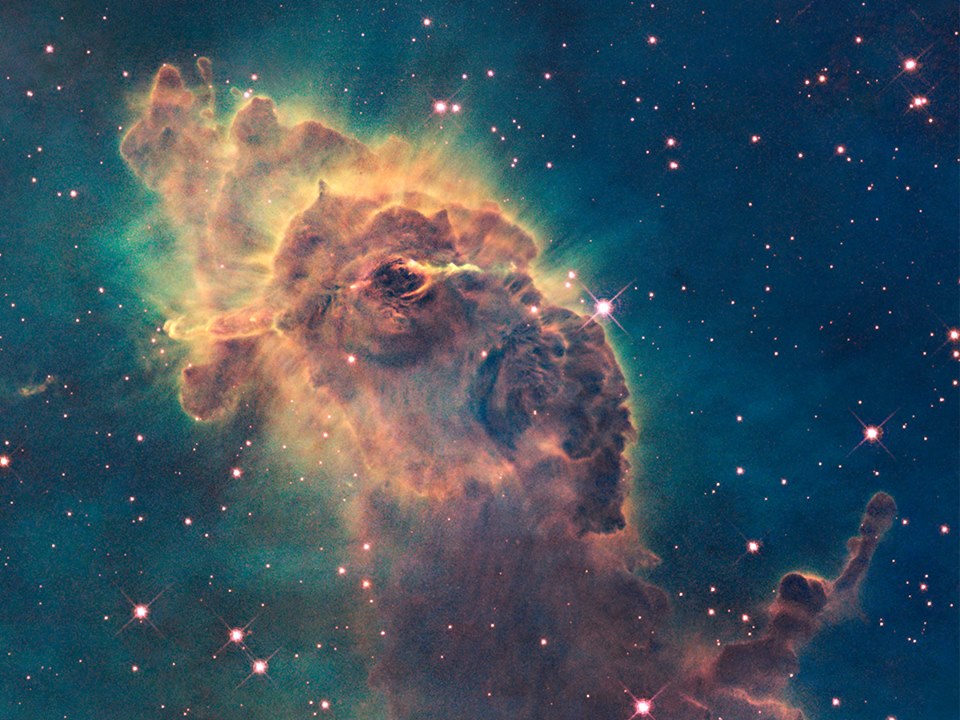

Carina Nebulosa by Hubble

HEPSİ/HERŞEY/HER MEKAN 'ŞİMDİKİ ZAMAN'DIR
Zaman mefhumu'nun anlaşılabilmesi ve doğru tanımlanabilmesi için bilim adamları hala gece ve gündüz harıl-harıl düşünmekte ve çalışmaktadırlar. Acaba zamanı tüm yönleriyle nasıl açıklayabiliriz diye çok uğraşmaktadırlar.
Oysa, ne ararsan önce kendinde ara özdeyişinde olduğu gibi, zaman nedir sorusunun anlaşılmasının anahtarı bizdedir. Onu evrenin derinliklerinde, dışarda aramaya gerek yoktur.
Madem evren hayal edilemeyecek kadar çok büyüktür, madem biz bu koskoca evrende farkedilemeyecek, görülemeyecek, dikkate alınamayacak kadar küçüğüz, o zaman, 'zaman mefhumu' da bize endeksli ve bize özgü olan bir şeydir ve hepsi şimdiki zamandır. Başka bir deyişle zaman şimdidir. Yani zaman ne eskiden vardı ve nede gelecekte olacaktır.
Daha da açıklarsak, zaman bizim gözlem ve aklımızın bir algı birimidir. Bize göre zaman vardır, çünkü biz evreni hareket halinde görüyoruz ve hareket olmasa zaman da olmaz diye düşünüyoruz. Oysa evren, hareket fenomeni boyutlu bir şey olmayabilir.
Ne kadar da büyük yanılmış oluruz o zaman, değil mi?

2020

Hebû nebû - her tişt li ser van her du peyvan ava bûye û ev her du peyv destpêka hemû çîroka me ye; hebû, nebû..
Hebû = 1
Nebû = 0
ŞARISTANIYA ME
Şaristaniya me, ji bo têgehîştina Gerdûnê û nihêniyên jiyanê, pirsên xwe yên herî grîng kiriye û bersiva gelek ji van pirsan jî karibûye bibîne.
Va ye êdî riya şaristaniya me li Gerdûnê hêdî hêdî vedibe. Mirov qesta çûna bo Merîxê dikin.
Heger hin neteweyên paşketî û ne-şaristan pirsgirêkên mezin li ber şaristaniya me dernexin, li nav demeke nêzîk wê HEMÛ nexweşî bi dermanan werin çareserkirin, ta ku çare ji mirinê re jî wê were dîtin.
Pirsa mezinbûna şêniyê dunyayê jî pirseke pir grîng e, lê heger ne van dewlet û neteweyên hov bin, şaristaniya me wê çareyek ji bo vê pirsgirêkê jî bibîne.
Serkeftin bo Şaristaniya Me
Rojên dilxweş, ronahî û azad li pêş me ..
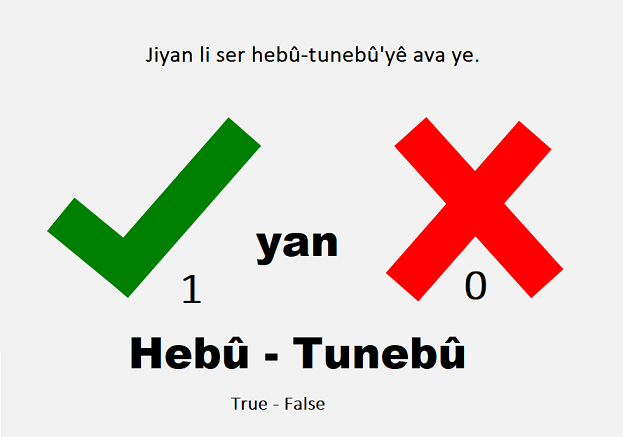
DEM Û WAR & WAR Û DEM

- Çawa û çima li zimanê kurdî XWE-DÊ / XWE-DA / XWU-DA ?
ZEMAN ta ku madde û cism hebe naqede. Zeman bi warê re ye û li dor û li gor warê ye.
Zemanê warê me, zemanê gerdûna me, ''bi peqîna mazin, bi Big Bang'ê re DEST PÊ KIRIYE''. Gava warê (gerdûna) me bi dawî were, zeman jî namîne. Ma ne welê? Ca bifikirin ji xwe re bê madde û cism, zeman wê li ku derê hebe û ji bo çi hebe?
Zeman bi xwezayê (siruştê/fîzikê) ve guncaye. Zeman gava madde û cism li holê hebe, ew bi xwe dizê. Loma li zimanê kurdî hatiye gotin: (bi) xwe za = XWEZA. Bi peyveke din; zeman xwedayê xwedayan (astronaut'an) e. Li gor hin hizirdozan (teorîsyenan); yên ku em bi riya kopîkirinê (cloning) ji laşê xwe, wek laşê xwe afirandine; ew astonot in ku ji stêrên dûr hatine.
Pirs ev e:
Gelo yê ku madde û cism afirandiye, zeman jî pê re afirandiye?
Encam: Dibe ku mirovên herî pêşî, ku li ser cografya Kurdistana mêjûyî jiyane, HER TIŞTÎ bi van bîr û hizrên fîlozofîkî hiziribîn û baweriya min ew e, ku ji xwe hizirîne jî. Loma ev peyva ciwan û watedar, peyva XWUDA (xwe da) ji me re afirandine.
Vegotina Xwedê ji vê peyvê pir hêsan têt têgehîn: anku xwe bi xwe hatiye afirandin.
Çima me vê nedizanî? Ji ber ku pêwîstiya me ya hizir û fikirkirinê wek mirovên pêşî (îptîdaî) nemaye/nîn e.
Mirovên berê, wan pir pêwîstî bi têgehînê hebû. Têgehîna der û dora xwe, têgehîna war û demê... Wan tegehîna her tiştî diviya. Her tişt ji bo wan pirseke pir mazin bû.
Mirovên berî me, li ser her warî hizirîne, ku bikaribin xeterên li serûberê jiyanê têbigehin û bi ewletî û bi hêsanî jiyana xwe berdewam bikin, bijîn.
Mirovên berî me, li ser her warî hizirîne û em î roj van hizrên wan bi kar dihênin û dijîn. Ew li ser her tiştî hizirîne ji bo me.
Pirseke din jî ev e: Em, mirovên serdemên hevdem û nuh, tiralên hizirkirinê ne.
Goran Candan
______________
DEM (Zem): Time [taym]
Peyva kurdî ZEMAN: Dem+an, Zem+an |
STÊR = ASTARE A-STAR-E = STAR (yıldız)

Kirdkî= Astare
Kurmancî= Stêr
Soranî= Estêre
Îngîlîzce= Star
Almanca Ster(n)
Îsveççe: Ster(na)
Kelimenin kökü: Stêr= yıldız
Stêrik veya kısaltılmış şekli: Stêrk = küçük yıldız
Astro (latin)= yıldız
|

Gerdûn, stêr û kewkeb
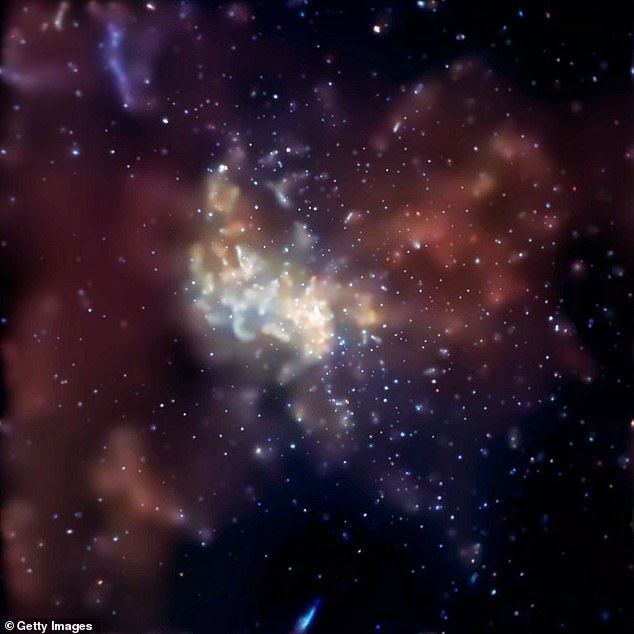





____________________________________________
The Year in Physics
Featuring paradoxical black holes, room-temperature superconductors and a new escape from the prison of time.



METALLISKT VATTEN !!
Är det möjligt att producera så ledande vatten som koppartråd?
I extraordinärt experiment förvandlade forskare vatten till en guldmetall.
Välkommen till framtidens tröskel!
DILOPA AVÊ ZIVIRANDIN Û KIRIN HESIN (metal)
-- Kero êdî ji xwe re hinek bi aqil bin.
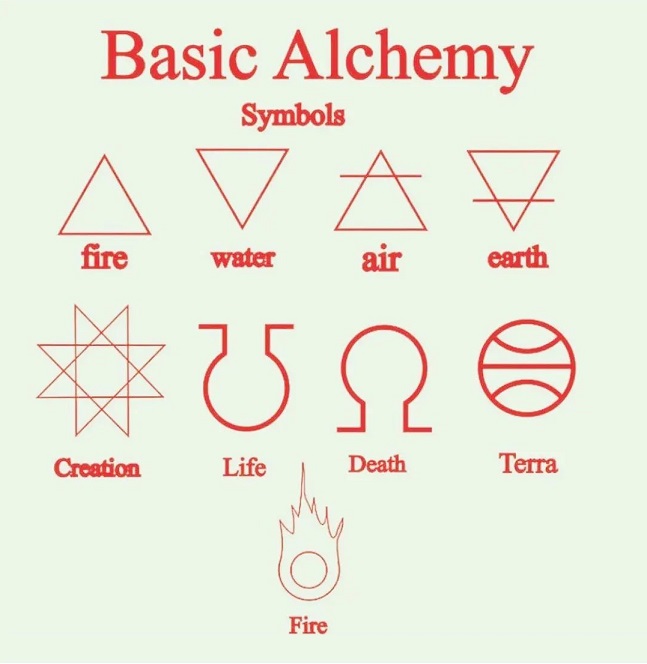
Basic Alchemy Tablet




Merîx, Mars
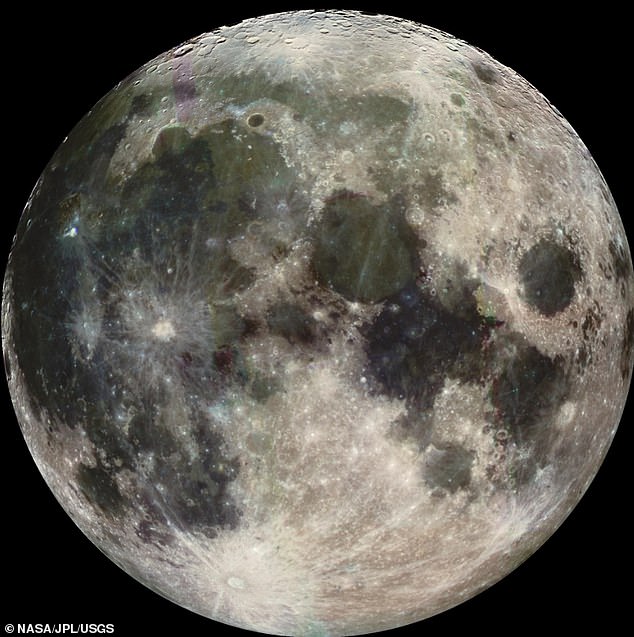

Heyv

Supercomputer simulation shows how the Moon may have formed
Clearest picture of mercury 2020

PSR J1810-148b A diamond planet
Dunya 1670 km zû li dora xwe dizivire

Evîn û hezkirin û dilşewatî gerdûnî ye.
Gerdûn biçûk e - Evîn MAZIN e.
Universe is little - Love is BIG

Evîn û hezkirin û dilşewatî gerdûnî ye.
Gerdûn biçûk e - Evîn MAZIN e.
Universe is little - Love is BIG
Universum är litet - Kärleken är STOR
In addition to the four basic elements of earth, air, fire and water there is another element: love .. and that is the basis of all these four.
Förutom de fyra grundelementen jord, luft, eld och vatten finns en till element: kärlek.. och det är grunden till alla dessa fyra.
Melayê Cizîrî 1407-1481
http://www.saradistribution.com/melaye-ciziri.htm

Mirov, hemî cûre zindiyên din, tevî yê xwe ditirsînin, lê heywan, ji xeynî xetereya birçîbûnê ku gihîştibe sînorê mirinê, hema hema di her rewşê de jî, qet têkilê zindiyek din nabin.
Ji aliyê din ve mirov, îşkencekirina hemî cûre zindiyan kirine karekî tam keyfî û adet û çandeke ku nayê guherandin.
Heger bala we kişandibe, li civaka tirk û ereb û farsan, ne tenê jiyana rojane û civakî ya ajalan, jiyana wan a psîkolojîkî jî bi temamî hatiye rûxandin.
Berî heywanên van civakên ne-humanîst, mirov berê xwe didin hev, û hev jî parçe parçe dikin.
Ji bilî têkoşîna rojane ya heywanan ya bo peydakirina av û xurakê, ku li van civakên navbirî karekî pir zehmetî û astengiyên bêserûber in, hevparçekirina mirovan li ber çavê wan, wan hê bêhtir narehet û hovtir dike. Weke ku hûn di wêneyê jorîn de jî dibînin, gur û berx dikarin bi hev re bijîn, lê mixabin ku mirov qet nikarin pêkve bijîn.
(İnsan kendi türü dahil, diğer bütün canlı türlerini neredeyse her halükarda terörize ederken, hayvanlar ise, ölüm sınırına varmış bir açlık tehlikesi dışında, başka bir canlıya asla dokunmazlar.
İnsanlar ise bütün canlı türlerine eziyet etmeyi tam keyfi bir muamele, vazgeçilmez bir alışkanlık ve kültür haline getirmiştir.
Eğer dikkat etmişseniz türk, arap ve fars toplumlarında'daki hayvanların sadece günlük ve sosyal yaşamları değil, aynı zamanda psikolojik yaşamları da tamamen tahrip edilmiştir.
Bu adı geçen toplumlarda hayvanlara varmadan, insanlar biribirini darp edip, yiyip parçalayıp bitiriyor zaten.
Bu toplumlardaki hayvanların çekilmez zorluklar ve aşılmaz engellerle dolu günlük yaşam mücadeleleri yanında, bir de bu hayvanların gözü önünde insanların biribirini boğazlanması onları daha da tedirginleştirip vahşileştiriyor. Yukarıdaki resimde gördüğünüz gibi, kurtla kuzu bir arada yaşabiliyor ama insanlar ne yazık ki asla..) |

İÇİMİZDEKİ VOLKANI DURDURAN TEK GÜÇ: SEVGİ
-- Savaşmak Yerine Sevmek: İnsanlığın İnce Çizgisi
İlkel özelliğimizin en derin yerinden fışkıran şiddet ve hırçınlık duygularını, en çok öfkelendiğimiz anlarda hissederiz. Bu öfke, içimizde kontrol edilmesi neredeyse imkansız bir ivmeyle büyür. O an hiçbir değer, hiçbir ölçü gözümüzde kalmaz; benliğimizi büyük bir ilkellik sarar ve bizi adeta vahşi bir hayvana dönüştürür. Kırarız, dökeriz, koparırız, keseriz. Fakat bu ilkel duyguyu her ne kadar %0,1 gibi çok küçük bir oranda da olsa dizginlemek mümkündür. Peki nedir bu içimizdeki büyük ilkel volkanın patlamasınbu kadar küçük bir marginel imkanla durduran şey? Tek kelimeyle: Sevgi.
Nörobilim (asabiyet bilimi) alanında yapılan araştırmalar, beynimizin "savaş ya da kaç" (fight or flight) tepkisini yöneten bir mekanizmanın; Amigdala'nın, yoğun öfke anlarında devreye girdiğini ortaya koyar. Ancak ilginçtir ki, bu tepkiyi bastırabilecek bir başka bölge vardır: Prefrontal Korteks. Bu bölge, sevgi, empati ve mantıklı düşünme ile ilişkilidir. Psikiyatrist Dr. Dan Siegel'e göre, "Sevgi ve şefkat duyguları, beyinde sakinleştirici bir etki yaratır ve saldırganlığı azaltır." Yani biyolojik olarak da sevginin öfke karşısında gerçek bir PANZEHİR olduğu artık kanıtlanmış bir gerçek.
Tarih boyunca büyük dönüşümler sadece öfkeyle değil, sevgi temelli direnişle de gerçekleşmiştir. Gandhi'nin şiddetsizlik üzerine kurduğu mücadele, bunun en somut örneklerinden biridir. O, halkını ingiliz sömürgeciliğine karşı başkaldırmaya çağırırken bile, Nefretle değil, sevgiyle karşı koyun diyordu. Aynı şekilde Martin Luther Kingin mücadelesi de, öfkeye sevgiyle karşılık verme ilkesine dayanıyordu. Bu örnekler, insanın içindeki volkanı kontrol altına alabildiğinde neler başarabileceğini gösteriyor.
Günlük yaşamımızda da bu gerçeklik kendini gösterir. Bir ebeveyn, öfkeyle ağlayan çocuğunu sevgiyle kucakladığında, ortamda anında bir dönüşüm olur. Ya da bir tartışmada, taraflardan biri bağırmak yerine yumuşak bir ses tonuyla yaklaşırsa, tansiyon hızla düşer. Sevgi burada bir zayıflık değil, aksine, en güçlü tepki biçimi haline gelir. Çünkü sevgi, insanın en derininde saklı duran ilkel dürtüleri bile yumuşatacak kadar etkilidir.
Elbette kimse kusursuz değildir. Hepimiz zaman zaman öfkenin kontrolsüz girdabına kapılabiliriz. Ancak mesele, bu duyguları yok saymak değil; onları tanıyıp, dönüştürebilmekte yatıyor. İçimizdeki volkanla barışmak, onu sevgiyle dizginleyebilmek, hem bireysel huzurun hem toplumsal barışın anahtarıdır. Bizi insan yapan şey, öfkemizi sevgiyle dengeleyebilme kapasitemizdir. Çünkü en güçlü olan, yıkabilen değil; sevebilen ve bağışlayabilendir.
.. ve sevgi EVRENSELDİR.
Goran Candan
|







|

Rotation Speed of Galaxies
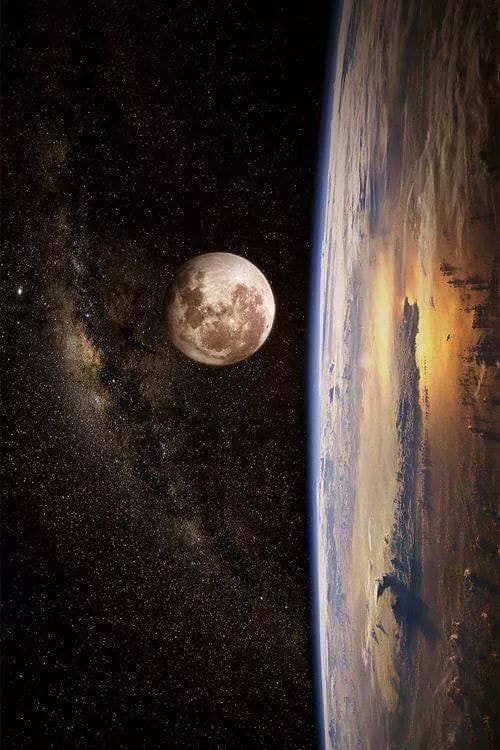

Moon-Earth from Space
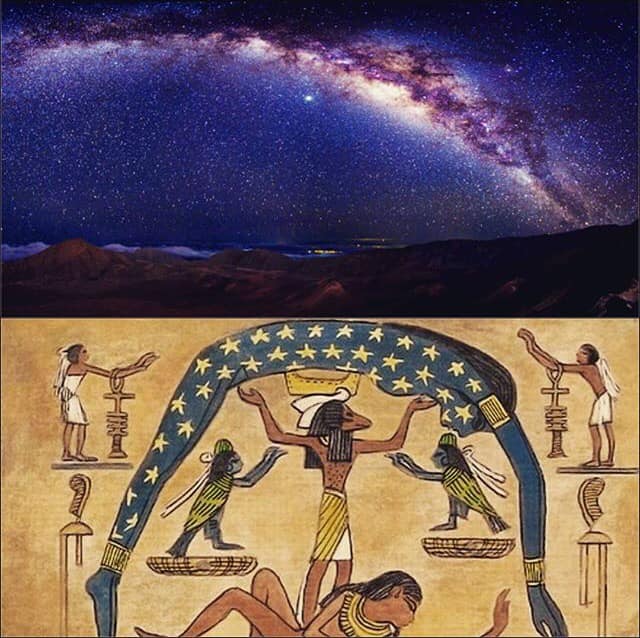

Milky way at the Egyptian opinion and feeling

Milky way seen from Namibian Desert

Milky way seen from Namibian Desert


Em rêwiyê li gerdûnê ne




ERDEMLİ İNSAN OL
Herşeyin mümkün olabildiği sınırı ve muhtevası belirsiz Evren'in içinde miskali zerre kadar anlamsız ve önemsiz olan bu yerimizde kaderimizin ne olacağının, başımıza ne geleceğinin belirsizliği içindeki zavallı insanlar! Birbirinize ve üzerinde yaşam imkanı bulduğunuz dünya evinize karşı sorumlu ve saygılı davranın! Bir hiçsiniz şimdi ama bribirinize ve tabiat anaya karşı biraz sorumlu ve saygılı davranırsanız, belki sizden iyi bir şey çıkar ve belki bu iyi tarafınız sayesinde neslinizi devam ettirebilecek bir kapı ve yol görünebilir size bu sürekli yokoluşların yaşandığı muammalı Evren'in içinde ..
Bu sözleri sadece insan olan kültürlü toplumlar anlar.. Ortadoğu gibi bugün tamamen gericileşmiş toplumların bu sözlerin anlamını kavraması asla mümkün değildir.
İnsan ol
İnsanca yaşa
İnsanlık erdemlilik ve aklı selimlik demektir
(GC)
HAYAT BİZDEKİ FORMATIYLA BİR HİÇTİR - İNSAN BUGÜNKÜ HALİYLE ACİZ VE ZAVALLIDIR
Bizim erişilmez ve yeri doldurulamaz olarak yüksek bir paha biçtiğimiz hayatın genel olarak ve bizim hayat biçimimizin de özel olarak Evren'de 5 kuruşluk bile bir değeri yoktur. Bu ispat edildi. Evrenin haritasını çizen insan, Evren'e yerleştirilebilecek dev teleskoplarla bile bakıldığında dünyanın yeri görülmeyecek kadar ufak ve cismi de YOK denecek kadar küçüktür.
EVREN'DE YAŞAM ÇOK SIRADAN BİR FENOMEN'DİR, bu nedenle Evrendeki yaşam bizim böyle gördüğümüz şekliyle aslında neredeyse hiçbir değeri yoktur.
Yaşam, Evrenin her yerinde var ve çok yönlü ve çok çeşitlidir. Evrenin tüm bölümleri yaşamla doludur. Biz ha varız, ha yokuz hiç kimsenin umurunda bile değil.
Evren'e Açılım çağında dünyada insanlar/ülkeler akıllı (teknik-donanımlı) insanlar/ülkeler ve akılsız (teknik-donanımsız) insanlar/ülkeler diye ikiye ayrılır. Teknik donanımlı/akıllı insanlar, yaptıkları uzay deney ve pratikleriyle, bizim yaşam türümüzün Evren'de idame edilebilmesi ve sürdürülebilmesi için uzaya ve Evren'e açılmak suretiyle içinde bulunduğumuz bu küçüklükten sıyrılmaya çalışyor şuan.
Bu başarılır mı başarılmaz mı ayrı bir konudur. Çünkü bu uçsuz bucaksız Evren'de mikroskopik bir canlı kadar ancak varız.
İNSAN ZAVALLIDIR
İnsan ''Evren'de en üstün varlıktır'' sözü Evren'in büyüklüğü karşısında anlamsız ve saçma geliyor. Bu koca Evren'de bunu ispat etmek mümkün gibi görünmüyor. Don Kişot'un yel değirmenlerini alt edebileceği inancı gibi ham bir hayalden ibarettir bu çocuksu düşünce.
Bu yüzden eğer insanlar Evren'de hatırı sayılan bir şey olmak istiyorlarsa o zaman dünya gezegeninde yaşayan bütün insanlar birbirini iyi tanımalı ve birbirlerine çok değer vermeli ve birbirine kötülük yapmamalıdır. Tabiata ve çevreye zarar vermeden insanlara en iyi ve en rahat hayat şartlarını yaratmalıdır. Çünkü bir insana yapılan kötülük bütün TABİAT'a yapılmış olan bir kötülük bütün insanlığa yapılmış bir kötülük sayılır. Tam tersi tabiata yapılan bir kötülük bütün insanlığa yapılmış sayılır.
İnsanlar şimdiye kadar sahip oldukları geri ve saçma inançlarını bir kenara bırakarak bu bilinç ve inançla insana, insanlığa inanarak YENİ BİR YAŞAM VE DÜNYA FELSEFESİ oluşturup İNSANSI bir medeniyet kurabilirlerse, o zaman mutlaka Evren'de hatırı sayılır bir yere gelebilirler.
Yoksa bugünkü bu halleriyle ancak kendi kendilerini imha etme yönüne doğru gitmekten başka hiçbir yöne gidemezler.
|

Quo vadis human?

01281986
x
A New Theory On Time Indicates Present And Future Exist Simultaneously

The box Universe theory describes now as an arbitrary place in time and states that the past, the future and the present all exist simultaneously.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology professor of philosophy Dr. Bradford Skow suggests that if we look down on the universe as if we were looking at a piece of paper, we would see time spanning all directions, exactly the same way that we see space at some point.
So what does this really mean? Well, this suggests that time as we know it is incorrect, in other words, it is not linear as we have always thought. In fact, everything around us is always present.

Dr. Skow is not the first scientist to question the way we all perceive time.
In 1915, Einstein introduced a theory of unified space and time. In his general theory of relativity, he proposes that space-time takes shape in a multiple or continuous way. And that if viewed, youll see both as a four-dimensional vector space. And this vector is known as the block theory.
The distinction between past, present and future is only a stubbornly persistent illusion.
The author argues that he wouldnt want to believe in that unless I saw good arguments for it.
I was interested in seeing what kind of view of the universe you would have if you took these metaphors about the passage of time very, very seriously, Skow says.
Dr. Skow further details:
The block universe theory says youre spread out in time, something like the way youre spread out in space. Were not located at a single time.
Dr. Skow agrees that while things change and we see time as if it were passing, Dr. Skow believes that we are in a scattered conditions and that different parts of time may be dotted around the infinite universe.
Time Travel
Once you try to wrap your head around this theory, youll begin to realize that it could also change the way we think of time travel.
If this theory is real, then we cant simply travel time and change it. If everything is happening simultaneously your past, present, future laid out in space then it would be impossible to create grandfather paradoxes.
Instead, you will only travel through time and experience it as it is and as it always would be.
Dr. Kristie Miller, who is the joint director for the Centre for Time at the University of Sydney, explained the theory in a piece published by ABC Science. Miller described how all moments that exist are relative to each other within three spatial dimensions and a single time dimension.
The block universe theory is also known in some scientific circles as Eternalism, in which the past, present, and future all co-exist now. This is opposed to Presentism, which states that the past doesnt exist anymore and is constantly disappearing thanks to that pesky notion of present time.

Watch here:
An illustration of the hypothetical box universe, Source: ABC Science
|


Time travelling

Sergei Krikalev, The Only Time Traveled Person. The Soviet Union forgot him in space.

SpaceX'in sahibi Elon Musk:
'6 yıl içinde Mars'a insan gönderebiliriz,şanslı olabilirsek, bu 4 yıl içinde'de olabilir'.

Good Luck to humanity for discovering and colobnizing the Outer Space !!
God damn Putin and other similar dictators (in Turkey and Iran) who are destroying the nature of our planet by war and
slows down the necessary international scientific development and cooperation

IT (Interstallar Travel) HAS ALLREADY BEGUN
MARS SURFACE TOUCH DOWN Feb18, 2021

The Perseverance rover's first high-def Mastcam panorama of Jezero Crater is a doozy. NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS/ASU
Click To See The Film From Mars
By landing an unmanned vehicle on Mars, Humanity has taken the FIRST step of its attempt to discover and conquer the Universe, and this step has carried progressive humanity to a brand new stage, THE STAGE OF INTERSTALLER TRAVEL. We wish a tremendous progress and success to the progressive humanity!

Since landing on Feb. 18, 2021 the NASA Perseverance rover has had a chance to look around and scope out the surrounding landscape,
which shows off some pretty typical Mars sights of dust, dirt and rocks. NASA/JPL-Caltech
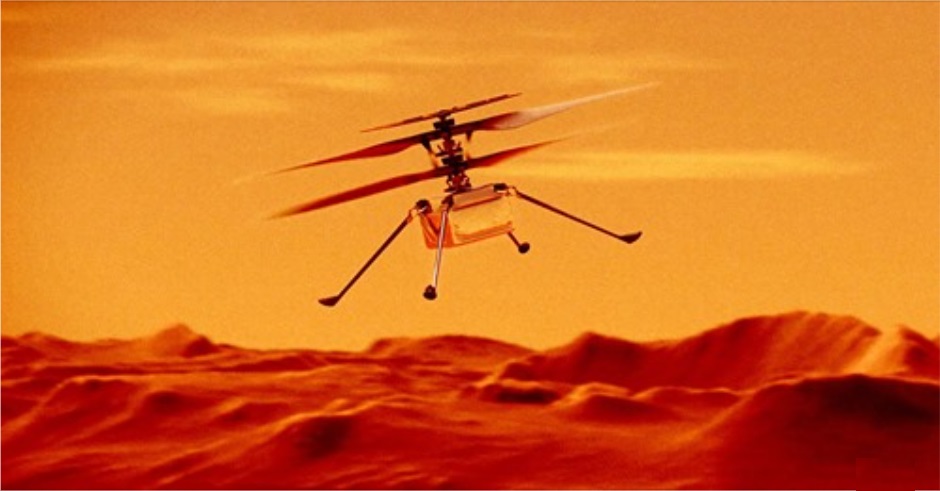

The Nasa Helicopter
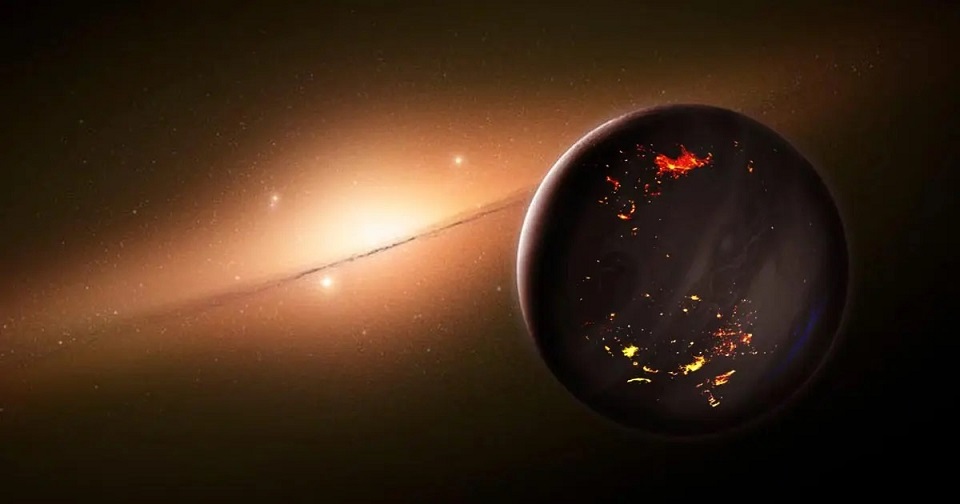


Scientist Proposes Using Entire Planet as Spaceship to Different Star System
Escape... from a dying star.
Futurism
Even at the speed of light, it would take over four years to get to the nearest star system.
Needless to say, escaping a solar system is much easier said than done. But according to a new paper published in the International Journal of Astrobiology and spotted by Universe Today, an advanced civilization could do exactly that by using an entire planet as a giant spacecraft.
In other words, according to Houston Community College professor Irina Romanovskaya, a rogue planet could act as a lifeboat, letting a civilization leave its old host star behind.
"I propose that extraterrestrial civilizations may use free-floating planets as interstellar transportation to reach, explore, and colonize planetary systems," Romanovskaya wrote.
Nature may have already inadvertently done just that by shooting rogue planets with habitable subsurface oceans through the cosmos. Astronomers have long suspected the existence of a region enveloping the solar system called the Oort Cloud, a region enveloping our system that's suspected to be home to tiny, icy planets.
If we commandeered such a world, Romanovskaya proposes, it could provide everything needed to survive the long journey.
"Free-floating planets can provide constant surface gravity, large amounts of space and resources," she argued. "Free-floating planets with surface and subsurface oceans can provide water as a consumable resource and for protection from space radiation."
If such a planet were inhospitable or too dark, the astronomy professor suggests advanced civilizations may have already developed technologies such as fusion reactors to make them habitable.
Romanovskaya proposes that "cosmic hitchhikers" could one day use objects like Sedna, a dwarf planet with an eccentric orbit in our deep solar system, as means of escape.
One potential problem with hitching a ride on a rogue planet, however, is that its core could run out of heat and "eventually fail to sustain oceans of liquid water (if such oceans exist)," Romanovskaya wrote.
They'd also be really far away from any other resources important for a civilization's survival.
"Therefore, instead of making free-floating planets their permanent homes, extraterrestrial civilizations would use the free-floating planets as interstellar transportation to reach and colonize other planetary systems," Romanovskaya concludes.
The theory also raises the intriguing possibility that SETI researchers could try to spot any aliens employing a planet as a transportation device.
"I propose possible technosignatures and artifacts that may be produced by extraterrestrial civilizations using free-floating planets for interstellar migration and interstellar colonization, as well as strategies for the search for their technosignatures and artifacts," Romanovskaya wrote.
Which means it may be possible for us to catch a glimpse of a civilization during its great escape and perhaps learn a thing or two, in case the Sun threatens the Earth by turning into a deadly red giant in the distant future.
READ MORE: Interstellar Travel Could Be Possible Even Without Spaceships, Scientist Says [Universe Today]

Mr Spak

Yûrî Gagarîn -
Yekem Kesê Ji Atmosfera Dunyayê Derketiye 1961

Valentina Tereşkova -
Yekem Jina Çûye Fezayê
Valentina Tereşkova,1937, yekem kozmonot û jina sivîl e ku çûye Ffezayê.
Tereşkova di rojeke wekî îro de ango 16-ê Hezîrana 1963ê, bi firokeya fezayî ku navê wê 'Vostok 6 e, çû Fezayê.
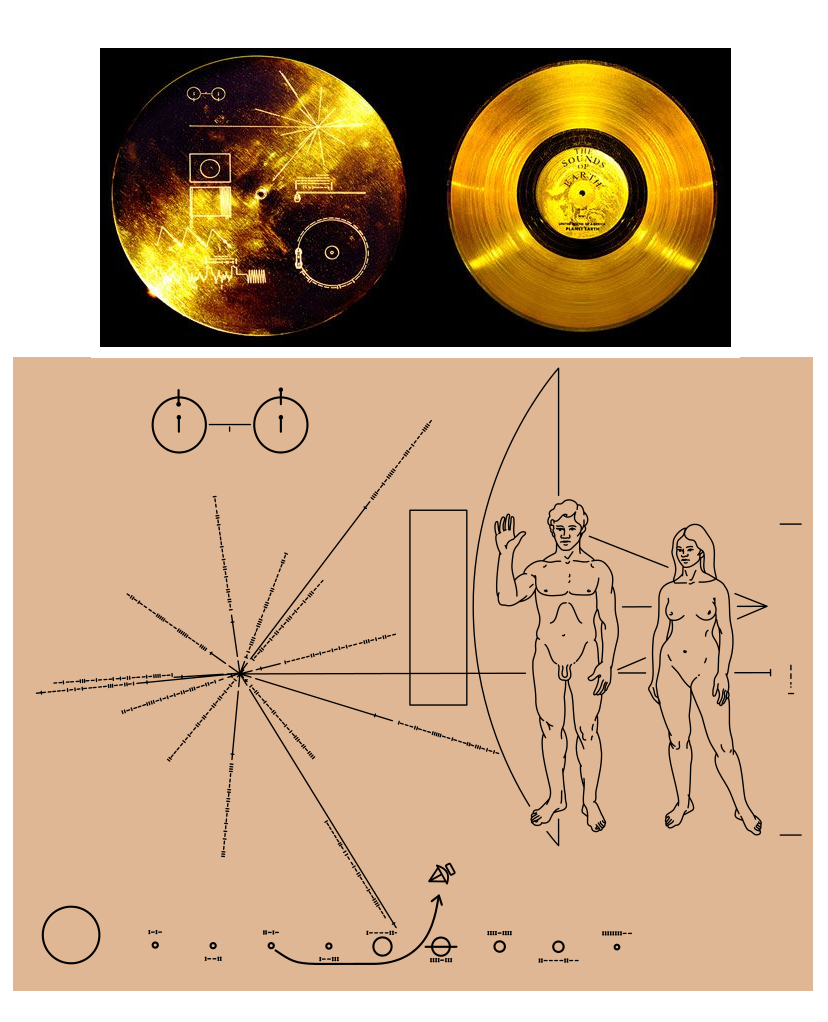
In September 1977, NASA launched Voyager 1 from Cape Canaveral, Florida. The craft carried a golden record that contained a message to aliens from the people of Earth.
If love is universal, then so is egocentrism
The universe is infinitely large and there are certainly much more intelligent cultures than ours there. The reason why we are not found is simply due to the infinitely large room of the universe. Our galaxy is insignificantly small, very old and also the supermassive black hole in the middle of it is devouring the entire galaxy. When our galaxy was young someone definitely visited it but at that time, our planet earth was not a quiet haunt as it was in its volcanic phase.
According to a Japanese calculation made in 1985, there are only about some ten light-years left until our galaxy's black hole has time to devour the earth. More precisely; our sun is only 25,800 light-years from the supermassive black hole. Who would want to visit a doomed insignificant little galaxy? Also, if some pirates of the universe find us, then they will, in the full sense of the word, enslave and colonize our entire planet. It would be best NOT to SEND our address into space without knowing in WHOS hands it ends up. It's probably very stupid to do that. Mankind may deeply regret this enormous mistake. The best thing would be for humanity to build bases on both the moon and Mars and then build large spaceships capable of traveling interstellarly and colonizing large parts of space in the universe for the survival of mankind. To be able to realize this, a revolutionary ultra-technical know-how in nuclear energy is needed. It will provide humanity with both effective weapons and powerful interstellar spacecraft 2020.

Voyager Timeline (Voyager 1 & 2)
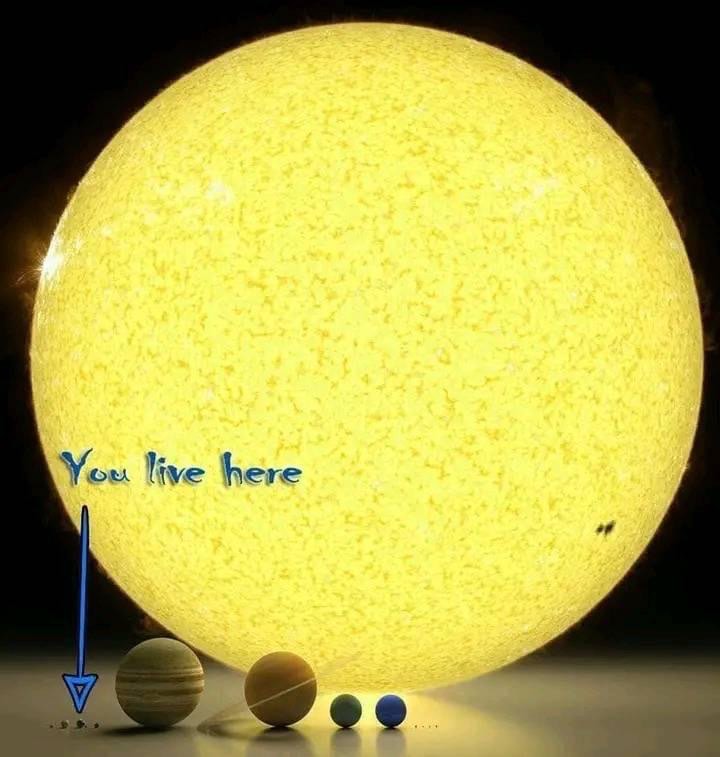
Den obetydliga människans betyselselösa, dumma gärningar fortsätter tyvärr.

You are here

Ultra-Fast Space Travel Possible After Scientists Discover Hidden Super-Highways

(Representational Image: NASA
Sarthak Dogra Dec 18, 2020
Published in the journal Science Advances, the study by researchers from UC San Diego mentions a connected series of arches inside space manifolds that extend from the asteroid belt to Uranus and beyond The scientists believe that such a route can be used to send spacecrafts to large astronomical distances in a very short time, just as they act on asteroids and comets. Deeming it a "celestial autobahn," or celestial highway, it is believed to cut short the time to travel such a distance to a mere decade, as opposed to the hundreds of thousands or millions of years
Researchers have discovered a space manifold that can act as a superhighway network to travel through the Solar System much faster than previously thought.

Image of the heart of nearby active galaxy IC 5063 reveals a mixture of bright rays and dark shadows. (Image: NASA/ Hubble Space Telescope)
The scientists believe that such a route can be used to send spacecrafts to large astronomical distances in a very short time, just as they act on asteroids and comets.
Published in the journal Science Advances, the study by researchers from UC San Diego mentions a connected series of arches inside space manifolds that extend from the asteroid belt to Uranus and beyond.
Deeming it a "celestial autobahn," or celestial highway, it is believed to cut short the time to travel such a distance to a mere decade, as opposed to the hundreds of thousands or millions of years. The authors claim that the route can enable a travel across 100 astronomical units (about 150 million kilometres) in less than a century.
In their research, the authors highlight that the most prominent arch structures are linked to Jupiter and its strong gravitational forces. The paper mentions that such manifolds in space control the Jupiter-family comets or comets that have an orbital period of 20 years as well as Centaurs (small-size solar system bodies) on unprecedented time scales.
Some of these bodies will end up colliding with Jupiter or being ejected from the Solar System, a release by UC San Diego News Centre mentions. Scientists resolved the structures through the numerical data about millions of orbits in our Solar System. They then computed how these orbits fit within the already-known space manifolds.
It is yet unknown as to how these space manifolds will react near Earth. They are sure to control the asteroid and meteorite reaching Earth, or even the man-made objects in the Earth-Moon system. But the way in which they will react is yet unclear. A deeper study into the same can also provide a possible way of using these space manifolds to send space probes into the deep ends of our solar system.
There are 5 eras in the universe's lifecycle. Right now, we're in the Second era

Image source: Pablo Carlos Budassi
Image based on logarithmic maps of the Universe put together by Princeton University researchers,
and images produced by NASA based on observations made by their telescopes and roving spacecraft
Astronomers find these five chapters to be a handy way of conceiving the universe's incredibly long lifespan.
27 March, 2020
- We're in the middle, or thereabouts, of the universe's Stelliferous era.
- If you think there's a lot going on out there now, the first era's drama makes things these days look pretty calm.
- Scientists attempt to understand the past and present by bringing together the last couple of centuries' major schools of thought.
If you're fortunate enough to get yourself beneath a clear sky in a dark place on a moonless night, a gorgeous space-scape of stars waits. If you have binoculars and point them upward, you're treated to a mind-bogglingly dense backdrop of countless specks of light absolutely everywhere, stacked atop each other, burrowing outward and backward through space and time. Such is the universe of the cosmological era in which we live. It's called the Stelliferous era, and there are four others.
The 5 eras of the universe
There are many ways to consider and discuss the past, present, and future of the universe, but one in particular has caught the fancy of many astronomers. First published in 1999 in their book The Five Ages of the Universe: Inside the Physics of Eternity, Fred Adams and Gregory Laughlin divided the universe's life story into five eras:
- Primordial era
- Stellferous era
- Degenerate era
- Black Hole Era
- Dark era
The book was last updated according to current scientific understandings in 2013.
It's worth noting that not everyone is a subscriber to the book's structure. Popular astrophysics writer Ethan C. Siegel, for example, published an article on Medium last June called "We Have Already Entered The Sixth And Final Era Of Our Universe." Nonetheless, many astronomers find the quintet a useful way of discuss such an extraordinarily vast amount of time.
The Primordial era

Image source: Sagittarius Production/Shutterstock
For the first little, and we mean very little, bit of time, spacetime and the laws of physics are thought not yet to have existed. That weird, unknowable interval is the Planck Epoch that lasted for 10-44 seconds, or 10 million of a trillion of a trillion of a trillionth of a second. Much of what we currently believe about the Planck Epoch eras is theoretical, based largely on a hybrid of general-relativity and quantum theories called quantum gravity. And it's all subject to revision.
That having been said, within a second after the Big Bang finished Big Banging, inflation began, a sudden ballooning of the universe into 100 trillion trillion times its original size.
Within minutes, the plasma began cooling, and subatomic particles began to form and stick together. In the 20 minutes after the Big Bang, atoms started forming in the super-hot, fusion-fired universe. Cooling proceeded apace, leaving us with a universe containing mostly 75% hydrogen and 25% helium, similar to that we see in the Sun today. Electrons gobbled up photons, leaving the universe opaque.
About 380,000 years after the Big Bang, the universe had cooled enough that the first stable atoms capable of surviving began forming. With electrons thus occupied in atoms, photons were released as the background glow that astronomers detect today as cosmic background radiation.
Inflation is believed to have happened due to the remarkable overall consistency astronomers measure in cosmic background radiation. Astronomer Phil Plait suggests that inflation was like pulling on a bedsheet, suddenly pulling the universe's energy smooth. The smaller irregularities that survived eventually enlarged, pooling in denser areas of energy that served as seeds for star formationtheir gravity pulled in dark matter and matter that eventually coalesced into the first stars.
The Stelliferous era

Image source: Casey Horner/unsplash
The era we know, the age of stars, in which most matter existing in the universe takes the form of stars and galaxies during this active period.
A star is formed when a gas pocket becomes denser and denser until it, and matter nearby, collapse in on itself, producing enough heat to trigger nuclear fusion in its core, the source of most of the universe's energy now. The first stars were immense, eventually exploding as supernovas, forming many more, smaller stars. These coalesced, thanks to gravity, into galaxies.
One axiom of the Stelliferous era is that the bigger the star, the more quickly it burns through its energy, and then dies, typically in just a couple of million years. Smaller stars that consume energy more slowly stay active longer. In any event, stars and galaxies are coming and going all the time in this era, burning out and colliding.
Scientists predict that our Milky Way galaxy, for example, will crash into and combine with the neighboring Andromeda galaxy in about 4 billion years to form a new one astronomers are calling the Milkomeda galaxy.
Our solar system may actually survive that merger, amazingly, but don't get too complacent. About a billion years later, the Sun will start running out of hydrogen and begin enlarging into its red giant phase, eventually subsuming Earth and its companions, before shrining down to a white dwarf star.
The Degenerate era

Image source: Diego Barucco/Shutterstock/Big Think
Next up is the Degenerate era, which will begin about 1 quintillion years after the Big Bang, and last until 1 duodecillion after it. This is the period during which the remains of stars we see today will dominate the universe. Were we to look up we'll assuredly be outta here long before then we'd see a much darker sky with just a handful of dim pinpoints of light remaining: white dwarfs, brown dwarfs, and neutron stars. These"degenerate stars" are much cooler and less light-emitting than what we see up there now. Occasionally, star corpses will pair off into orbital death spirals that result in a brief flash of energy as they collide, and their combined mass may become low-wattage stars that will last for a little while in cosmic-timescale terms. But mostly the skies will be be bereft of light in the visible spectrum.
During this era, small brown dwarfs will wind up holding most of the available hydrogen, and black holes will grow and grow and grow, fed on stellar remains. With so little hydrogen around for the formation of new stars, the universe will grow duller and duller, colder and colder.
And then the protons, having been around since the beginning of the universe will start dying off, dissolving matter, leaving behind a universe of subatomic particles, unclaimed radiation
and black holes.
The Black Hole era

Image source: Vadim Sadovski/Shutterstock/Big Think
For a considerable length of time, black holes will dominate the universe, pulling in what mass and energy still remain.
Eventually, though, black holes evaporate, albeit super-slowly, leaking small bits of their contents as they do. Plait estimates that a small black hole 50 times the mass of the sun would take about 1068 years to dissipate. A massive one? A 1 followed by 92 zeros.
When a black hole finally drips to its last drop, a small pop of light occurs letting out some of the only remaining energy in the universe. At that point, at 1092, the universe will be pretty much history, containing only low-energy, very weak subatomic particles and photons.
The Dark Era

We can sum this up pretty easily. Lights out. Forever.
Tonight, if it's clear, maybe you want to step outside, take a nice deep breath, and look up, grateful that we are where we are, and when we are, in spite of all the day's hardships. We've got a serious amount of temporal elbow room here, far more than we need, so not to worry, and those stars aren't going anywhere for a long, long time.
The Universe Is Very Slowly Dying As Scientists Helplessly Look On

We have hardly become acquainted with it, and we have witnessed its demise
Read More
Scientists Propose Permanent Human Habitat Built Orbiting Ceres

It's like something straight out of "The Expanse."
A group of Finnish researchers are proposing a permanent human habitat in the orbit of Ceres, a massive asteroid and dwarf planet in the asteroid belt, between Mars and Jupiter.
According to the team, this megasatellite settlement could be built by collecting materials from Ceres itself.
If that sounds familiar to fans of the popular sci-fi book and TV series The Expanse, thats because in that fictional universe, Ceres Station plays a pivotal role as one of humanitys first human off-world colonies. In the series, however, the space rock itself was spun up to create a crewed habitat on its surface with artificial gravity.
In a paper uploaded to the prewrite repository arXiv this week, the team argues that Ceres would be prime real estate because it has nitrogen, which could enable the creation of an Earth-like atmosphere.
In fact, they argue that the environment could even be better than Earth, since theres no adverse weather or natural disasters, and plenty of living space to grow into.
They propose a number of smaller spinning satellites, attached to each other via magnetic tethers to create a massive disk-shaped megasatellite. Artificial gravity approximately equal to that of Earth could be achieved by spinning the massive structure around Ceres.
Such a habitat would have to make a full rotation around the dwarf planet in just 66 seconds to maintain the artificial gravity.
Connecting each habitat would be maglev train-like vehicles, a weightless experience to passengers.
When first encountered, weightlessness causes nausea and vomiting for some people, the paper reads. However, in a settlement where people experience occasional weightlessness from childhood, it is plausible to think that they can tolerate it well during short trips.
The settlement could also act as a stepping stone to other reaches of the solar system.
The motivation is to have a settlement with artificial gravity that allows growth beyond Earths living area, while also providing easy intra-settlement travel for the inhabitants and reasonably low population density of 500/km2, the abstract reads. Thats about the population density of New Jersey.
Thanks to its low gravity and fast rotation, the researchers argue that a space elevator is feasible, allowing easy transportation of materials from Ceres to other settlements without the need for much fuel.
So what about space radiation and the threat of meteorite impacts? The team has considered those threats as well. They propose a set of massive cylindrical mirrors that could do double duty by collecting sunlight and passing it onto the habitat, while also blocking submeter scale meteoroids.
China made an artificial star that's 6 times as hot as the sun, and it could be the future of energy

- Nuclear fusion could be the future of energy, replacing fossil fuels with our own artificial stars.
- China built a fusion reactor that reaches temperatures of 100 million degrees Celsius that's six times as hot as the sun.
- The reactor is called Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) and sustained nuclear fusion for about 10 seconds before shutting down.
- While it was a milestone for EAST, we're still a long way from generating sustainable energy on Earth.
Imagine if we could replace fossil fuels with our very own stars. And no, we're not talking about solar power: We're talking nuclear fusion. And recent research is helping us get there. Meet the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak, or EAST.
EAST is a fusion reactor based in Hefei, China. And it can now reach temperatures more than six times as hot as the sun. Let's take a look at what's happening inside. Fusion occurs when two lightweight atoms combine into a single, larger one, releasing energy in the process. It sounds simple enough, but it's not easy to pull off. Because those two atoms share a positive charge. And just like two opposing magnets, those positive atoms repel each other.
Stars, like our sun, have a great way of overcoming this repulsion ... their massive size, which creates a tremendous amount of pressure in their cores ... So the atoms are forced closer together making them more likely to collide. There's just one problem: We don't have the technology to recreate that kind of pressure on Earth.
But luckily, there's another way. You can also generate fusion with extreme temperatures. And that's exactly what devices like EAST do. The higher the temperature, the faster the atoms move around and the more likely they are to collide.
But it quickly becomes a balancing act. If the temperature is too hot, the atoms move too fast and zip passed each other. If it's too cold, the atoms won't move fast enough. So, the ideal temperature to generate fusion is around 100 million degrees Celsius. That's more than 6 times as hot as our sun's core.
Only a few fusion experiments in the world have surpassed this milestone. And the latest one was EAST. It sustained nuclear fusion for about 10 seconds before shutting down. And while it was a breakthrough for EAST, it's a long way from generating sustainable energy for the people of Earth.
And that's actually on purpose. EAST is a tiny reactor. At only a few meters across, it's not meant to be a full-fledged power plant. It's an experiment. And right now, its job is to help us design more effective fusion technology that could, one day, power entire cities.
Like ITER, short for International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor, it's the world's biggest fusion project to date. Thirty-five countries have poured billions of dollars into its construction. And it is designed to be the first fusion reactor to ever produce more fusion power than the power used to heat it up.
You see, you need to pour a lot of energy into these machines to get them to work. This recent EAST test, for example, guzzled over 10 Megawatts of power. Enough to power 1,640 American homes for a year. And it didn't yield even half that amount. Since the entire point of a power plant is to, well, produce power, it's a pretty important issue to work out.
But it's worth the effort. Why? Well for one thing, fusion reactors would produce practically no radioactive waste compared to the kind of reaction we see in today's nuclear fission power plants. But even better. Fusion reactors can run on seawater a renewable, sustainable resource.
For perspective, the amount of water just on the top inch of Lake Erie is enough to produce more power than all the fossil fuels left on the planet. And unlike other energy sources, it doesn't need the sun to shine or the wind to blow.
In a time of dwindling resources and worsening climate change, we could sure use it.
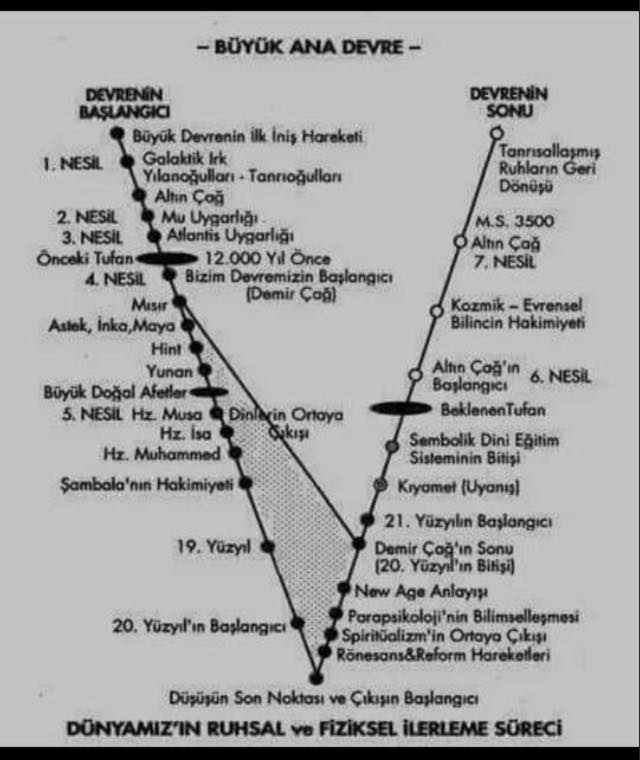
Bu şema Tanrı veya Tanrıların 7 boyutlu saltanat devridir.
Bizler şu anda 6. Boyutun 5. Nesil Devrini yaşıyoruz. 'Küresel Sermaye Güçleri'nin Devri' olan çağdayız.
Bizim çağımızda dinler artık sembolik olarak varlığını sürdürmektedir.
21. yüzyılın sonlarına doğru dini inançlar bitecek ve altın çağa girilecek. Daha sonra da Cozmik Çağ başlayacaktır.
Son olarak 6. Boyutun 7. Nesil döneminde Tanrısallaşmış Ruhlar geri dönecek.
3597 yılına kadar sürecek olan Tanrıların lazer ışınlarıyla yapacak olduğu savaşlardan sonra gökyüzü ile yeryüzünü bütünleştirecekler ve insanları ölümsüzlüğe eriştirecekler. Böyle bir olay milyonlarca yıl önce yaşanmış.
Hindistan'da bir yeraltı şehrinde bulunan bir tablette bunlar yazıyormuş.
Tanrısal 7. Boyutu milyonlarca yıl sonra başlayacağı için bizim neslimizden olan insanlar o çağları göremeyeceklerdir.
_________________________
Benim bu konudaki tahmin ve faraziyem şudur:
Yeryüzünün ultra-ileri medeniyetleri bu dünyayı terk ederek uzaydaki yeni bir dünyada insan ırkını ve neslini geliştirecekler.
İnsanık, yaşlanmış ve insanın gayri-tabii müdahalesi sonucu ekolojik dengesini tam kaybetmiş bu dünyada, bugün hepimize kan kusturan geri milletleri yeryüzünde bırakarakö GELİŞMİŞ MEDENİYET VE İNSANLIK böylece yeni ölümsüz medeniyetler ufuklarına doğru ebedi bir seyrüsefere başlayacaktır.G.C.
23.09.2020
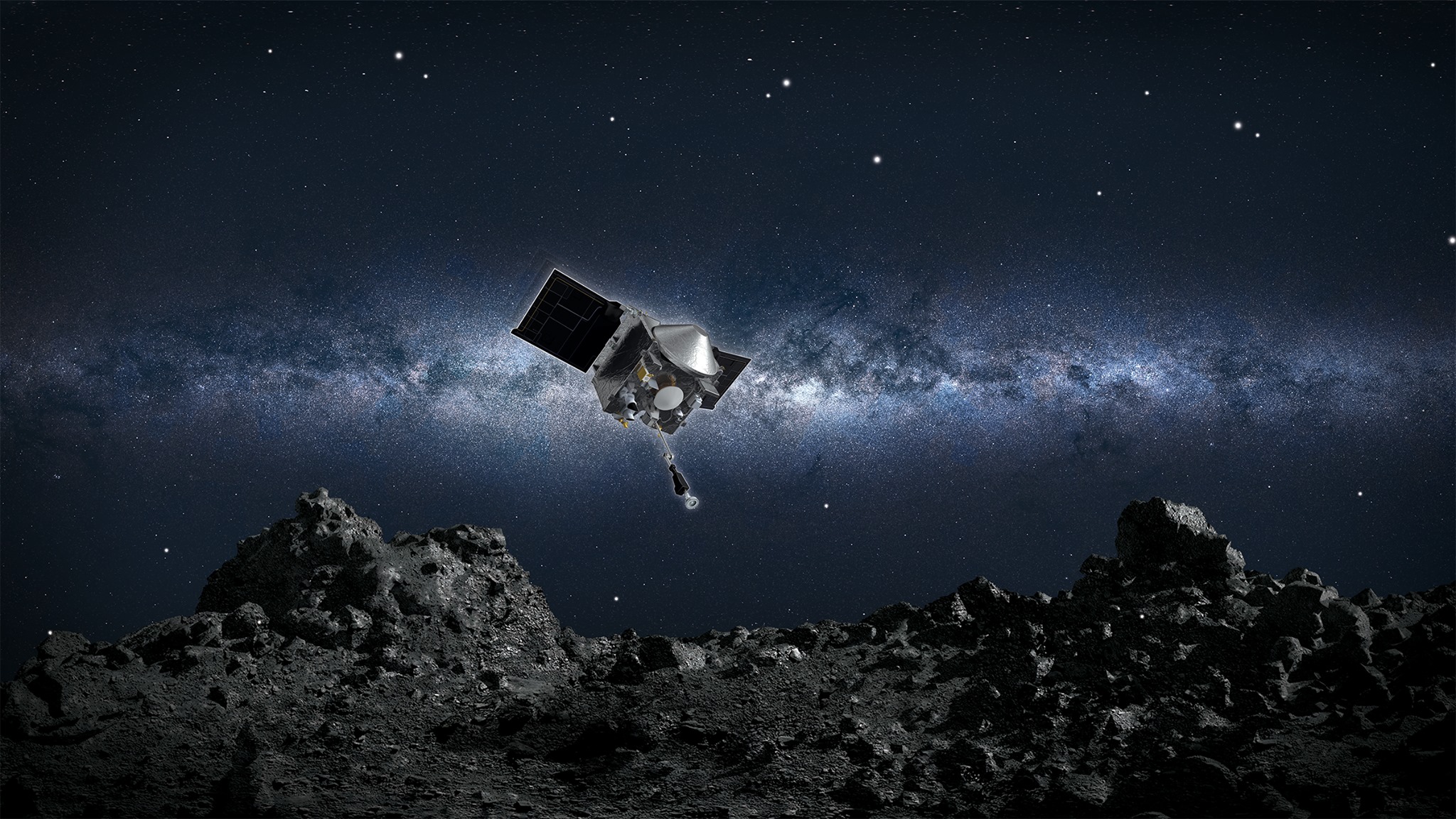

BELÊ, DUNYA 'WÎ ALÎ' HEYE,
- Lê ne ji bo her kesî ye!
Dunyayên wek dunyayê me, bê hejimar in. Gava şeveke sayî mirov berê xwe bide kûrahiyên ezmanên reş û tarî,
piraniya stêr û sitêrikên li pêş çavê me, dunyayekî (gerînekekî/'gezegen') bi serê xwe ne.
Dunya me êdî pir kal bûye û xwedî temeneke
wisa mazin ê çar milyar salan e. Zanyar dibêjin, berî ku temenê dunya me bibe deh milyar sal, wê xirabibe û hilbiweşe.
Bi gotineke din; li dor çar milyar salan temenê vî dunyayî maye.
Ji nuha ve, çend nîşanên pîrbûna dunya me, xwe nîşan didin.
Wek erdhêjên berdewamî, wek qelş û qulbûna erdê, wek daketina çiyayan, wek guhertinên îklîmî yên dêmanî û hwd.
Ji ber vê yekê, fîrmaya amerîkî ya fezayê NASA, li pey peydakirina dunyayekî nû ye û li nav stêrên gerdûnê ji mirovahiyê re dunyayekî, ango maleke nuh digere.
Ji bo vê yekê xebateke zanistî ji vê heftê sal berê dest pê kiribû. Pêngava pêşîn a vê xebatê; çûn û bicihbûna li ser stêreke li Galaksa me (anku komestêrên cîranê me) bû. Piştî wê pêngavê jî, derketin û barkirina galakseke din a temenbiçûk(*).
Çûna vê dunya nuh, bêguman wê ji kes û grûbên bijarte pêk bihê. Jiyana li vir li vî dunya kevin û jiyana li dunya nuh, çend hezar sal, yan çend sed hezar sal bi awayeke paralel wê bi hev re bimeşin. Lê gava dunya ji ber kalbûna xwe, yan jî ji ber lêdana meteorekê (kevirên ezmanî), ber bi xirabûnê ve here, hingê li gor derfetê mirovên vir wê werine guhestin ser dunya nuh. Lê dîsan jî wê kesên bijarte herin, ne her kes..!
Kî û ji ber çi wê werin hilbijartin, di destê Amerîka'yê de ye.
Wek keştiya Peyamber Nûh, dikarin gelek cûreyên rawir û heywanan jî bi xwe re bibin,
lê ne wek îslambazên tirk, ereb û farsan. Aha ev pir xweş e!
Ez ji bo zarokên me yên li vê pêşerojê, ji dil û can hêviya jiyaneke rind û ciwan a li ser stêreke pir geş û xweş dikim! Bila li wir
di nav aştî û aramiyeke serteser û bêdawî de bijîn! Me vê nedît, bila ew bibînin.
Bimre paşdemayîn û kerîtiya îslambaziyê!
Bijî kurd û bijî mirovatî, dostanî û keda zanyariyê!
Goran Candan
__________
*): Sala 1977'an ez û hevalê min ê xortaniyê Ferid Metin ê xwoşevîst ê Golgulî (Dêrika Çiyayê Mazî) , em li ser vê mijarê beşdarê bernameya Radyoya Moskoyê bûn û gotara ku me li ser vê mijarê nivîsî, bi mehan li ser vê radyoyê hat xwandin û weşandin.
Pirsa radyoyê pirseke felsefî bû û bi kurtî pirs û mijar ev bû: Gelo lêkolînên li ser kûrahiyên fezayê ji bo mirovahiyê wê çi sûd û kelk bidin?
Vêca ez û Ferîd me her yek gotareke dûr û dirêj li ser vê mijarê nivîsî û şand Moskoyê. Welatiyekî afrîkî li vê pêşbirkê yekemîn hat, gotara min duwemîn û ya Ferîd jî sêyemîn hat.
Rojekê ez ê naveroka vê gotara xwe yad bikim û dîsan binivîsim.

Carl Sagan/ Cosmos

O nokta..
"Uzayın derinliğinden bu resmi çekmeyi başardık. eğer bu resme dikkatlice bakarsanız, orada bir nokta göreceksiniz. o noktaya tekrar bakın. işte o nokta burasıdır. evimizdir. o nokta biziz. sevdiğiniz herkes, tüm tanıdıklarınız, adını duyduklarınız, gelmiş geçmiş tüm insanlar hayatlarını o noktanın üzerinde geçirdiler. türümüzün tarihindeki tüm sevinçlerimiz ve acılarımız, kendinden emin bin çeşit inancımız, ideolojimiz ve ekonomik öğretimiz; her avcı ve her yağmacı, her kahraman ve her korkak, uygarlığımızın mimarları ve tahripçileri, her kral ve her köylü, birbirine aşık olan her genç çift, her anne ve her baba, umutları olan her çocuk, her mucit ve her kâşif, ahlak değerlerini öğreten her öğretmen, yozlaşmış her politikacı, her bir "yıldız", her bir "yüce önder", her aziz ve her günâhkar işte orada yaşadı; bir güneş ışınında asılı duran o toz zerreciğinde.
dünya, dev bir evrensel arenada yer alan çok küçük bir sahnedir. bütün o komutan ve imparatorların akıttıkları kan göllerini düşünün... şan ve şöhret içerisinde, bu noktanın küçük bir parçasında kısa bir süre için efendi olabildiler. bu noktanın bir köşesinde yaşayanların, başka bir köşesinde yaşayan ve kendilerinden zar zor ayırt edilebilen diğerleri üzerinde uyguladıkları zulmü düşünün... anlaşmazlıkları ne kadar sık, birbirlerini öldürmeye ne kadar istekliler, nefretleri ne kadar yoğun!
bu soluk ışık noktası, bütün o kasılmalarımıza, kendi kendimize atfettiğimiz öneme ve evrende öncelikli bir konuma sahip olduğumuz yolundaki yanlış inancımıza meydan okuyor. gezegenimiz, çevremizi saran o büyük evrensel karanlığın içerisinde yalnız başına duran bir toz zerreciğidir. içinde yaşadığımız bilinmezlik ve bütün bu enginliğin içerisinde, başka bir yerden bir yardımın gelip bizi bizden kurtaracağına dair hiçbir ipucu yoktur.
dünya... şu ana kadar, yaşam barındırdığı bilinen tek gezegen. en azından yakın gelecekte, türümüzün göçebileceği başka hiçbir yer yok. evet, ziyaret ediyoruz. ama henüz yerleşemiyoruz. beğenseniz de beğenmeseniz de şu an için dünya yaşadığımız yer.
Gökbiliminin alçakgönüllü ve kişiliği geliştiren bir uğraşı olduğu söyleniyor. bana kalırsa, insan kibrinin akıl dışılığını, küçük dünyamızın uzaktan çekilmiş bu görüntüsünden daha iyi gösterebilecek bir şey yoktur. bu görüntü, bildiğimiz tek evimiz olan bu soluk mavi noktayı daha içten paylaşmamız ve koruyup şefkat göstermemiz gerektiği konusundaki sorumluluğumuzun altını çiziyor."
Carl Sagan, 1994 |
Carl Sagan'ın Dünya'nın 6 Milyar Km'den Çekilen Fotoğrafı Hakkında Yazdığı Tüyleri Diken Diken Eden Yazı
Önemimiz ve daha doğrusu 'önemsizliğimiz' hakkında anlamasını bilen bir insanı hayatı boyunca en derinden etkileyecek sözlerden birini Carl Sagan söylemiş.
KİM ÖNCEYDİ - KİMLER KOPYACI
İslam diğer bütün önceki dinlerin bir kopyasıdır:

Paganizme dair: Bir tanrı ya da çok tanrı ikisi de tanrı varlığıyla alakalıdır. Hepsi de yaşanmış.. Çok tanrılı dönemler, tek tanrılı dönemler.
Biri diğerinden öncelikli değil mi.. Hepsi de aynı.. İnsanlar ne biliyor belki uzayda her birimin bir yöneticisi vardır..
Ya da çok tanrıya inananlar haklıysa, ya rüzgar tanrısı varsa, ya da deniz tanrısı..
Aralarında birlik varsa.. Nasıl ıspatlnacak aksi..
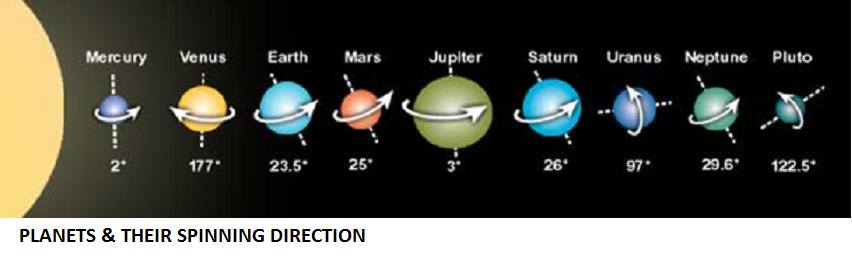
Planets spinning direction
REFLEXIONER:
- "Det finns mycket där ute och jorden är en del av det".
- "Vi är absolut ingenting".
- "Ingen kommer att hitta oss om vi inte söker aktivt de andra!"
- Tänk att kunna få resa mellan de olika universumen!!".
- "Hur stor är Gud? ?? "
- Multî-Universum; hîpotez e. Lê tiştek zanim ku erd/dunya li Unîversum'ê wek teneyê qûma li ber çem e".
- "İzledim. Yaa, gördün mü ne kadar anlamsızmışız Uzay'da. Burnumuzdan kıl aldırmamaya da devam ediyoruz".
- Coolt! ?? Vi är bra smaå i universum, svårt att fatta.
- "Man får svindel !"
- ''I can't believe it this is magical''.
- ''Muhteşem.. (Hiş na gire!)''
- ''Em li jiyanê ne misqalê zerrê jî ne''.
- ''I can't believe it this is magical''.
- "Denna videofilm ger känslan av att det finns så mycket att veta och vi människör är helt körda".

FROM EARTH TO MULTIVERSE - Youtube


Ancient civilization knew farmore about our Solar System
Dark Forest theory: A terrifying explanation of why we havent heard from aliens yet

If this theory is correct, the day after contact would look like this. (Pixababy)
The Fermi paradox asks us where all the aliens are if the cosmos should be filled with them. The Dark Forest theory says we should pray we never find them.
14 June, 2018
The Milky Way galaxy has 200 billion stars and perhaps 100 billion planets. If even a small fraction of those planets harbored life, and even if only a pathetic scattering of those planets had lifeforms which became intelligent, our galaxy would be teeming with alien civilizations, some of whom would be either looking for us or discoverable for at least a little while.
The number of alien civilizations the galaxy should have can be determined by an equation, the Drake equation, that turns the above factors into variables. When you plug them into the formula, you find that there should be at least 20 civilizations in our cosmic neighborhood. This makes the fact that we have yet to find any other life in the cosmos almost shocking when you think about it.
The seeming discord between how many advanced civilizations ought to be in space and the lack of evidence for any is known as the Fermi paradox. It has lead to dozens of hypotheses and potential solutions over the last few decades.
Many of the solutions aim at one of the variables in the Drake equation and try to make the supposed number of civilizations lower so it is more reasonable for us to not have met anybody yet.
Some propose that life starting at all is rare, others suggest that the development of intelligence is the bottleneck, others still posit that most civilizations would live for a short time before blowing themselves up or, conversely, never even manage to invent the radio.
One solution, however, is a bit darker than the others
The Dark Forest solution explains why we haven't heard from aliens by positing that they are purposefully keeping quiet.
The reasoning is laid out best in the science fiction novel The Dark Forest, by Liu Cixin. The plot of the book, the second in a series, concerns questions of how to best interact with potentially hostile alien life.
In the novel, the argument is laid out like this:
- All life desires to stay alive.
- There is no way to know if other lifeforms can or will destroy you if given a chance.
- Lacking assurances, the safest option for any species is to annihilate other life forms before they have a chance to do the same.
Since all other lifeforms in the novel are risk-averse and willing to do anything to save themselves, contact of any kind is dangerous, as it almost assuredly would lead to the contacted race wiping out whoever was foolish enough to give away their location. This leads to all civilizations attempting to hide in radio silence.
The reasoning behind the paranoia is explained in this paragraph from the novel:
The universe is a dark forest. Every civilization is an armed hunter stalking through the trees like a ghost, gently pushing aside branches that block the path and trying to tread without sound. Even breathing is done with care. The hunter has to be careful, because everywhere in the forest are stealthy hunters like him. If he finds another lifeanother hunter, angel, or a demon, a delicate infant to tottering old man, a fairy or demigodthere's only one thing he can do: open fire and eliminate them.
It's a bit like the prisoner's dilemma really, and the concept is based on applied game theory.
Is there a non-literary approach to this solution? Or is it just an idea that is good for a story?
It was also put forth by scientist David Brin as a potential solution to the lack of radio evidence for alien life. While the variant he describes relies on robotic probes carrying out the task of killing off civilizations other than the one that created it, the core concept remains the same. In this excerpt, he explains why this solution an attractive one for scientific purposes and terrifying for existential reasons:
It is consistent with all of the facts and philosophical principles described in the first part of this article. There is no need to struggle to suppress the elements of the Drake equation in order to explain the Great Silence, nor need we suggest that no ETIS anywhere would bear the cost of interstellar travel. It need only happen once for the results of this scenario to become the equilibrium condition in the Galaxy. We would not have detected extraterrestrial radio traffic- nor would any ETIS have ever settled on Earth- because all were killed shortly after discovering radio."
He then reminds us that broadcasts of I Love Lucy are racing across the cosmos, ready to reveal our location and sense of humor to anybody who can pick them up.
How plausible is this theory?
This theory has the advantage of only affecting one of the variables in the Drake equation and affecting the one that is the most open to speculation. It also doesn't require us to make broad assumptions about how all alien civilizations behave; a single advanced race that acts this way would be enough to cause the observed situation.
This would also explain why we haven't found any mundane alien radio signals despite a century of being able to pick them up. Just as we accidentally send our radio signals, meant for us, out into space, another civilization would be likely to as well. One possible reason for this is that other civilizations are so fearful of being detected that they purposely avoid sending out any radio evidence of their existence.
It does, however, assume that other species have a similar risk aversion level and reasoning process as we do or that there really is one civilization out there killing off anybody they think can harm them. This is a big assumption.
Why is this theory dark?
We've been screaming our existence to the cosmos for almost one hundred years now. Any aliens within a one hundred light year radius of us would be receiving a barrage of radio signals from our direction. If we had reason to avoid letting aliens know about us, as Stephen Hawking thought we did, we might have a problem.
Why haven't we heard from aliens yet? If this solution is correct, they are purposely hiding in the darkness of space for fear of death. Should we stop broadcasting our existence to the universe too then? Or would alien life be a little nicer than we've been in our history?
___________________________________________
If love is universal, then so is egocentrism
The universe is infinitely large and there are certainly much more intelligent cultures than ours there. The reason why we are not found is simply due to the infinitely large room of the universe. Our galaxy is insignificantly small, very old and also the supermassive black hole in the middle of it is devouring the entire galaxy. When our galaxy was young someone definitely visited it but at that time, our planet earth was not a quiet haunt as it was in its volcanic phase.
According to a Japanese calculation made in 1985, there are only about some ten light-years left until our galaxy's black hole has time to devour the earth. More precisely; our sun is only 25,800 light-years from the supermassive black hole. Who would want to visit a doomed insignificant little galaxy? Also, if some pirates of the universe find us, then they will, in the full sense of the word, enslave and colonize our entire planet. It would be best NOT to SEND our address into space without knowing in WHOS hands it ends up. It's probably very stupid to do that. Mankind may deeply regret this enormous mistake. The best thing would be for humanity to build bases on both the moon and Mars and then build large spaceships capable of traveling interstellarly and colonizing large parts of space in the universe for the survival of mankind. To be able to realize this, a revolutionary ultra-technical know-how in nuclear energy is needed. It will provide humanity with both effective weapons and powerful interstellar spacecraft

String theorist Michio Kaku has said that we should be cautious about contacting aliens because of the threat of extra-terrestrial life conquering us.
Kaku made the comments in light of the development of the James Webb telescope, a massive space telescope that will be the successor to Hubble.
Costing $8.8 billion, the 20-foot-long dish will be able to reach deep into the vastness of space. Monitoring invisible infrared wavelengths, the telescope will be able to gaze 13 billion years backwards in time - due to the speed of light travelling through space - and discover a huge number of galaxies previously invisible to scientists.
Nasa compares Hubbles capabilities as able to see toddler galaxies, while Webb can spot baby galaxies.
The construction of the Webb telescope will provide scientists with thousands of planets to look at, and thats why I think the chances are quite high that we may make contact with an alien civilisation, Kaku said in a recent interview with The Guardian.
There are some colleagues of mine that believe we should reach out to them. I think thats a terrible idea. We all know what happened to Montezuma when he met Cortés in Mexico so many hundreds of years ago. Now, personally, I think that aliens out there would be friendly but we cant gamble on it. So I think we will make contact but we should do it very carefully.
The allusion made here is to the 16th century Spanish conquistador Hernán Cortés, who killed the Aztec ruler Moctezuma Xocoyotzin. Moctezuma hosted Cortés and the Spaniards for months, but eventually tensions escalated between the two groups due to the increased presence of the Spanish army.
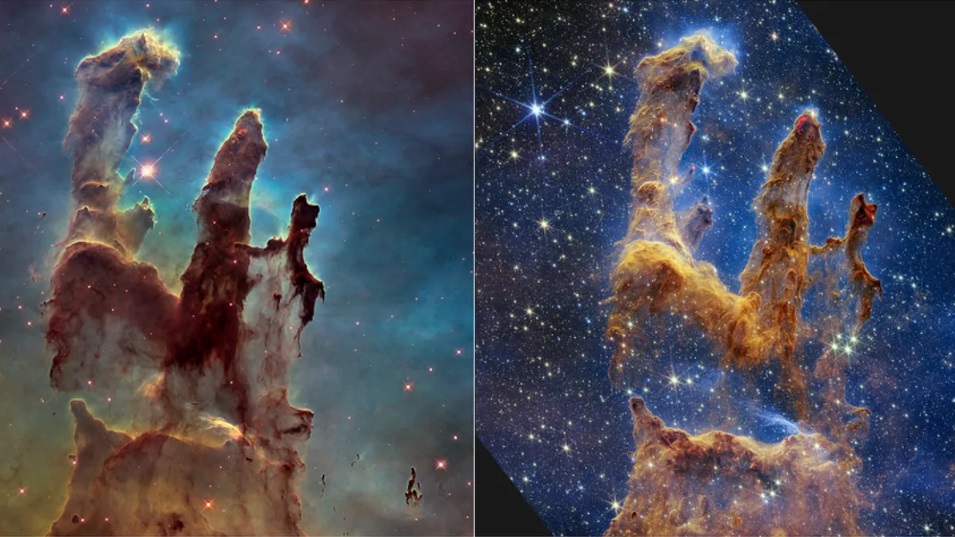

NASA's James Webb Telescope offers a lush and highly detailed view of the iconic Pillars of Creations. The place where new stars are forming in dense clouds of gas and dust. The pillars are revealed in 3D with a majestic rock looking formation, but in reality are more permeable. The column s of formed from interstellar gases and dust that are cool that appear at times to be semi-transparent in near-infrared light.
FUTURE OF THE UNIVERSUM
To be or not to be !!
The Beginning to the End of the Universe: A cold, lonely death
Everything — from creatures to stars to black holes — will eventually decay into nothingness.
By
Doug Adler | Published: Thursday, February 4, 2021

Our understanding of the cosmos is far from complete. There’s a chance our best educated guesses about
how the universe will end are missing something major — something that will allow life to survive and thrive forever.NASA

You'll Be Able To Carry Phone In Pocket In Future
News Paper Article from 1963.
--- And this became a reality 30 years later: in 1993
And what about this?
"In the future, you will travel using teleportation" the idea of teleportation as a method of travel in the future has appeared in science fiction literature since the mid-20th century.
One of the earliest popular references to teleportation as a means of movement can be found in science fiction stories from the 1930s and 1940s. The term "teleportation" was likely coined by the American paranormal researcher Charles Fort in his 1931 book Lo!, where he used it to describe mysterious displacements of objects without explanation.
In science fiction, teleportation as a method of human transportation became popular through examples such as:
-
Star Trek (1960s), where the phrase "Beam me up, Scotty!" refers to teleportation.
-
Short stories and novels by authors like Alfred Bester, particularly The Stars My Destination (1956), where teleportation is a central theme.
An exact phrase like this was first written in Swedish, it most likely began to appear in translated science fiction literature during the 1950s to 1970s, or in Swedish science fiction magazines like Häpna! (19541969).
THE END
NASA Calculated the Exact Date of the End of the World
People have always been obsessed with finding out what comes after death, and some have gone as far as calculating the end of the world as we know it. Previously, people thought the world would end on December 12, 2012, according to the Mayan Calendar. However, this time has long passed, and humanity is still here.
Several other predictions turned out as hoaxes, granted they were from unreliable sources. But, as the interest in this topic grows, large institutions are now trying their hand at predicting the end of the world.
Among these institutions is the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. It carried out over 400 computer simulations to determine the date of death of all life on Earth. And the results say that in 1,000,002,021 years, the Earth will be completely uninhabitable and swallowed by the Sun.
In these simulations, scientists tried to find out when solar radiation would destroy the atmosphere of the Earth. Of course, several factors shifted the date in their simulations, but given the consistencies shown by most of the results, they are certain that the Earth will cease to exist around this deadline.

NİCOLA TESLA
MILKY WAY
SPITZER SPACE TELESCOPE
JAMES WEBB TELESCOPE
CHARLES DARWIN
FRIDA KAHLO
CHE GUEVARA
VALENTINA TERESHKOVA
CHARLIE CHAPLIN
NELSON MANDELA
PÎSAGOR
GALERÎ

Foundation For Kurdish Library & Museum